Abstract
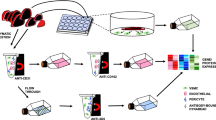
The endothelial cell (EC) membrane is an important interface, which plays a crucial role in signal transduction. Our aim was to selectively purify luminal EC membrane proteins from the coronary vasculature of the isolated perfused mouse heart and analyze its composition with mass spectrometry (MS). To specifically label coronary ECs in the intact heart, the colloidal silica method was applied, which is based on the binding of positively charged colloidal silica to the surface of EC membranes. Transmission electron microscopy revealed the specific labeling of ECs of macro and microvessels. Two different methods of tissue homogenization (Teflon pestle and ultra blade) together with density centrifugation were used for membrane protein enrichment. Enrichment and purity was controlled by Western blot analysis using the EC-specific protein caveolin 1 and various intracellular marker proteins. The ultra blade method resulted in a tenfold enrichment of caveolin 1, while there was negligible contamination as judged by Western blot. However, protein yield was low and required pooling of ten hearts for MS. When enriched endothelial membrane proteins were digested with trypsin and analyzed by LC-MS, a total of 56 proteins could be identified, of which only 12 were membrane proteins. We conclude that coronary endothelial membranes can be conveniently labeled with colloidal silica. However, due to the ionic nature of interaction of colloidal silica with the EC membrane the shear rate required for cardiac homogenization resulted in a substantial loss of specificity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anversa, P., Levicky, V., Beghi, C., McDonald, S. L., & Kikkawa, Y. (1983). Morphometry of exercise-induced right ventricular hypertrophy in the rat. Circulation Research, 52, 57–64.
Bassingthwaighte, J. B., Yipintsoi, T., & Harvey, R. B. (1974). Microvasculature of the dog left ventricular myocardium. Microvascular Research, 7, 229–249.
Chaney, L. K., & Jacobson, B. S. (1983). Coating cells with colloidal silica for high yield isolation of plasma membrane sheets and identification of transmembrane proteins. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 258, 10062–10072.
Danilov, S. M., Gavrilyuk, V. D., Franke, F. E., Pauls, K., Harshaw, D. W., McDonald, T. D., et al. (2001). Lung uptake of antibodies to endothelial antigens: Key determinants of vascular immunotargeting. American Journal of Physiology. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology, 280, L1335–L1347.
Durr, E., Yu, J., Krasinska, K. M., Carver, L. A., Yates, J. R., Testa, J. E., et al. (2004). Direct proteomic mapping of the lung microvascular endothelial cell surface in vivo and in cell culture. Nature Biotechnology, 22, 985–992.
Fischer, F., Wolters, D., Rogner, M., & Poetsch, A. (2006). Toward the complete membrane proteome: High coverage of integral membrane proteins through transmembrane peptide detection. Molecular and Cellular Proteomics, 5, 444–453.
Ghitescu, L., & Robert, M. (2002). Diversity in unity: The biochemical composition of the endothelial cell surface varies between the vascular beds. Microscopy Research and Technique, 57, 381–389.
Jacobson, B. S., Schnitzer, J. E., McCaffery, M., & Palade, G. E. (1992). Isolation and partial characterization of the luminal plasmalemma of microvascular endothelium from rat lungs. European Journal of Cell Biology, 58, 296–306.
Kroll, K., Deussen, A., & Sweet, I. R. (1992). Comprehensive model of transport and metabolism of adenosine and S-adenosylhomocysteine in the guinea pig heart. Circulation Research, 71, 590–604.
Mayr, M., Zhang, J., Greene, A. S., Gutterman, D., Perloff, J., & Ping, P. (2006). Proteomics-based development of biomarkers in cardiovascular disease: Mechanistic, clinical, and therapeutic insights. Molecular and Cellular Proteomics, 5, 1853–1864.
Oh, P., Li, Y., Yu, J., Durr, E., Krasinska, K. M., Carver, L. A., et al. (2004). Subtractive proteomic mapping of the endothelial surface in lung and solid tumours for tissue-specific therapy. Nature, 429, 629–635.
Schmidt, R., Ackermann, R., Kratky, Z., Wasserman, B., & Jacobson, B. (1983). Fast and efficient purification of yeast plasma membranes using cationic silica microbeads. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 732, 421–427.
Schnitzer, J. E. (1992). gp60 is an albumin-binding glycoprotein expressed by continuous endothelium involved in albumin transcytosis. American Journal of Physiology, 262, H246–H254.
Schnitzer, J. E., & Oh, P. (1994). Albondin-mediated capillary permeability to albumin. Differential role of receptors in endothelial transcytosis and endocytosis of native and modified albumins. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 269, 6072–6082.
Schnitzer, J. E., Oh, P., Jacobson, B. S., & Dvorak, A. M. (1995). Caveolae from luminal plasmalemma of rat lung endothelium: Microdomains enriched in caveolin, Ca(2+)-ATPase, and inositol trisphosphate receptor. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 92, 1759–1763.
Stolz, D. B., Ross, M. A., Salem, H. M., Mars, W. M., Michalopoulos, G. K., & Enomoto, K. (1999). Cationic colloidal silica membrane perturbation as a means of examining changes at the sinusoidal surface during liver regeneration. American Journal of Pathology, 155, 1487–1498.
Valadon, P., Garnett, J. D., Testa, J. E., Bauerle, M., Oh, P., & Schnitzer, J. E. (2006). Screening phage display libraries for organ-specific vascular immunotargeting in vivo. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103, 407–412.
Zhang, S. H., Reddick, R. L., Piedrahita, J. A., & Maeda, N. (1992). Spontaneous hypercholesterolemia and arterial lesions in mice lacking apolipoprotein E. Science, 258, 468–471.
Zhang, W., Zhou, Y. J., Guo, Z. G., Bi, F., Zhang, J., Kumar, P., et al. (2006). Preparation of tissue-specific monoclonal antibodies using purified endothelial membrane proteins from biotinylated pulmonary vasculature of rhesus monkey. Hybridoma, 25, 15–19.
Zhou, Y. J., Wang, S. Q., Zhang, J., Zhang, W., Bi, F., Guo, Z. G., et al. (2005). A novel method to isolate and map endothelial membrane proteins from pulmonary vasculature. American Journal of Physiology. Cell Physiology, 288, C950–C956.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arjunan, S., Reinartz, M., Emde, B. et al. Limitations of the Colloidal Silica Method in Mapping the Endothelial Plasma Membrane Proteome of the Mouse Heart. Cell Biochem Biophys 53, 135–143 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-009-9045-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-009-9045-8