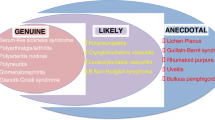
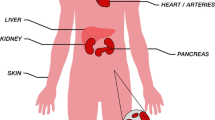
Abstract
Hepatitis C affects approximately 3% of the population worldwide and extrahepatic manifestations may occur in nearly 40% of all patients. Recent efforts have focused on incidence, prevalence, clinical significance, mechanism of disease, and the role of antiviral therapy in treatment. Cryoglobulinemia, cryoglobulinemic vasculitis, membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis, and lymphoproliferative disorders have a well-established link to hepatitis C, and many other endocrine, autoimmune, and dermatologic associations may exist. This article reviews the recent literature detailing the extrahepatic manifestations of chronic hepatitis C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Kamar N, Rostaing L, Alric L: Treatment of hepatitis C-virus-related glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int 2006, 69:436–439. An excellent review of the recent advances in treatment of glomerulonephritis associated with HCV.
Agnello V, De Rosa FG: Extrahepatic disease manifestations of HCV infection: some current issues. J Hepatol 2004, 40:341–352. This excellent discussion analyzes several of the controversial issues regarding extrahepatic manifestations of HCV infection, including prevalence, pathogenesis, and clinical significance of cryoglobulinemia, glomerulonephritis, and B-cell lymphoma.
Matsumori A: Role of hepatitis C virus in cardiomyopathies. Ernst Schering Res Found Workshop 2006, 55:99–120.
Tembl J, Ferrer J, Sevilla M, et al.: Neurologic complications associated with hepatitis C virus infection. Neurology 1999, 53:861–864.
Colombo E, Cermesoni L, Morganti D: Celiac sprue: another autoimmune syndrome associated with hepatitis C? Dig Liver Dis 2002, 35:64–65.
Cacoub P, Renou C, Rosenthal E, et al.: Extrahepatic manifestations associated with hepatitis C virus infection. Medicine 2000, 79:47–56.
Pascual M, Perrin L, Giostra E, et al.: Hepatitis C virus in patients with cryoglobulinemia type II. J Infect Dis 1990, 162:569–570.
Ferri C, Sebastiani M, Giuggioli D, et al.: Mixed cryoglobulinemia: demographic, clinical, and serologic features and survival in 231 patients. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2004, 33:355–374. This excellent study documents the clinical course of 231 patients with mixed cryoglobulinemia. Cumulative 10th-year survival was significantly reduced in these patients, with lower survival in males and patients with renal involvement.
Sansonno D, Dammacco F: Hepatitis C virus, cryoglobulinaemia, and vasculitis: immune complex relations. Lancet Infect Dis 2005, 5:227–236.
Brouet JC, Clouvel JP, Danon F, et al.: Biologic and clinical significance of cryoglobulins. Am J Med 1974, 57:775–788.
Ferri C, Mascia MT: Cryoglobulinemic vasculitis. Curr Opin Rheum 2006, 18:54–63.
Castillo I, Pardo M, Bartolome J, et al.: Occult hepatitis C virus infection in patients in whom the etiology of persistently abnormal results of liver-function tests is unknown. J Infect Dis 2004, 189:7–14. This report demonstrates that an aggressive search may be needed to provide an accurate diagnosis, especially if the level of suspicion is high.
Schmidt WN, Stapleton JT, LaBrecque DR, et al.: Hepatitis C infection and cryoglobulinemia: analysis of whole blood and plasma HCV RNA concentration and correlation with liver histology. Hepatology 2000, 31:737–744.
Casato M, Lilli D, Donato G: Occult hepatitis C virus infection in type II mixed cryoglobulinemia. J Viral Hepat 2003, 10:455–459.
Kayali Z, Buckwold VE, Zimmermann B, Schmidt WN: Hepatitis C, cryoglobulinemia, and cirrhosis: a meta-analysis. Hepatology 2002, 36:978–985.
Persico M, De Marino FA, di Giacomo Russo G, et al.: Prevalence and incidence of cryoglobulins and in hepatitis C virus-related chronic hepatitis patients: a prospective study. Am J Gastroenterol 2003, 98:884–888.
El-Serag HB, Hampel H, Yeh C, et al.: Extrahepatic manifestations of hepatitis C among United States male veterans. Hepatology 2002, 36:1439–1445.
Dammacco F, Sansonno D, Piccoli C, et al.: The lymphoid system in hepatitis C virus infection: autoimmunity, mixed cryoglobulinemia and overt B-cell malignancy. Semin Liver Dis 2000, 20:143–157.
Friedman G, Mehta S, Sherker AH: Fatal exacerbation of hepatitis C-related cryoglobulinemia with interferon-alpha therapy [case report]. Dig Dis Sci 1999, 44:1364–1365.
Misiani R, Bellavita P, Fenili D, et al.: Interferon alfa-2a therapy in cryoglobulinemia associated with hepatitis C virus. N Engl J Med 1994, 330:751–756.
Wilson RA: The benefit of long-term interferon alfa therapy for symptomatic mixed cryoglobulinemia associated with chronic hepatitis C. J Clin Gastroenterol 2001, 33:137–140.
Mazzaro C, Zorat F, Caizzi M, et al.: Treatment with peg-interferon alfa-2b and ribavirin of hepatitis C virusassociated mixed cryoglobulinemia: a pilot study. J Hepatol 2005, 42:632–638.
Cacoub P, Saadoun D, Limal N, et al.: PEGylated interferon alfa-2b and ribavirin treatment in patients with hepatitis C virus-related systemic vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum 2005, 52:911–915.
Levine JW, Gota C, Fessler BJ, et al.: Persistent cryoglobulinemic vasculitis following successful treatment of hepatitis C virus. J Rheumatol 2005, 32:1164–1167. This study describes the absence of clinical improvement in four cryglobulinemic patients despite the eradication of HCV with antiviral therapy.
D’Amico E, Chincoli C, Cacciatore P, et al.: Effects of combined antiviral therapy on asymptomatic mixed cryoglobulinemia in naïve patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection: a preliminary study. Dig Dis Sci 2005, 50:2344–2347.
Niewold TB, Swedler WI: Systemic lupus erythematosus arising during interferon-alpha therapy for cryoglobulinemic vasculitis associated with hepatitis C. Clin Rheumatol 2005, 24:178–181.
Roccatello D, Baldovino S, Rossi D, et al.: Long-term effects of anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody treatment of cryoglobulinaemic glomerulonephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2004, 19:3054–3061. This study describes the efficacy and safety of rituximab in a series of six patients with HCV-related cryoglobulinemic glomerulonephritis. Both systemic manifestations and renal function improved without a significant change in viral load.
Sansonno D, De Re V, Lauletta G, et al.: Monoclonal antibody treatment of mixed cryoglobulinemia resistant to interferon alpha with an anti-CD20. Blood 2003, 101:3818–3826.
Chandesris MO, Gayet S, Schleinitz N, et al.: Infliximab in the treatment of refractory vasculitis secondary to hepatitis C-associated mixed cryoglobulinaemia [case report]. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2004, 43:532–533.
Bartolucci P, Ramanoelina J, Cohen P, et al.: Efficacy of the anti-TNF-alpha antibody infliximab against refractory systemic vasculitides: an open pilot study on 10 patients. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2002, 41:1126–1132.
Gladstone D, Golightly MG, Zamkoff KW: Severe, refractory type II essential mixed cryoglobulinemia treated with 2-chlorodeoxyadenosine and mycophenolate mofetil [case report]. Rheumatol Int 2005, 25:635–636.
Kaplanski G, Maisonobe T, Marin V, et al.: Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) plays a central role in the pathogenesis of severe forms of vasculitis due to hepatitis C-associated mixed cryoglobulinemia. J Hepatol 2005, 42:334–340.
Monti G, Pioltelli P, Saccardo F, et al.: Incidence and characteristics of non-Hodgkin lymphomas in a multicenter case file of patients with hepatitis C virus-related symptomatic mixed cryoglobulinemias. Arch Intern Med 2005, 165:101–105.
Negri E, Little D, Boiocchi M, et al.: B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and hepatitis C virus infection: a systematic review. Int J Cancer 2004, 111:1–8. This literature review documents the regional variability in the association between HCV and NHL, suggesting that there are environmental and host contributions.
Takeshita M, Sakai H, Okamura S, et al.: Prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in cases of B-cell lymphoma in Japan. Histopathology 2006, 48:189–198.
Giannini C, Giannelli F, Zignego AL: Association between mixed cryoglobulinemia, translocation (14;18), and persistence of occult HCV lymphoid infection after treatment [letter]. Hepatology 2006, 43:1166–1167.
Hermine O, Lefrere F, Bronowicki JP, et al.: Regression of splenic lymphoma with villous lymphocytes after treatment of hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med 2002, 347:89–94.
McGuire BM, Julian BA, Bynon JS, et al.: Glomerulonephritis in patients with hepatitis C cirrhosis undergoing liver transplantation. Ann Intern Med 2006, 144:735–741.
Tsui JI, Vittinghoff E, Shlipak MG, O’Hare AM: Relationship between hepatitis C and chronic kidney disease: results from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J Am Soc Nephrol 2006, 17:1168–1174.
Chadban SJ, Atkins RC: Glomerulonephritis. Lancet 2005, 365:1797–1806.
Sabry AA, Sobh MA, Sheaashaa HA, et al.: Effect of combination therapy (ribavirin and interferon) in HCVrelated glomerulopathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2002, 17:1924–1930.
Bruchfeld A, Lindahl K, Stahle L, et al.: Interferon and ribavirin treatment in patients with hepatitis C-associated renal disease and renal insufficiency. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2003, 18:1573–1580.
Rossi P, Bertani T, Balo P, et al.: Hepatitis C virus-related cryoglobulinemic glomerulonephritis: long-term remission after antiviral therapy. Kidney Int 2003, 63:2236–2241.
Hu SL, Jaber BL: Ribavirin monotherapy for hepatitis C virus-associated membranous nephropathy. Clin Nephrol 2005, 63:41–45.
Ojo AO, Held PJ, Port FK, et al.: Chronic renal failure after transplantation of a nonrenal organ. N Engl J Med 2003, 349:931–940.
Ozdemir BH, Ozdemir FN, Sezer S, et al.: De novo glomerulonephritis in renal allografts with hepatitis C virus infection. Transplant Proc 2006, 38:492–495.
Mohmous IM, Elhabashi AF, Elsawy E, et al.: The impact of hepatitis C virus viremia on renal graft and patient survival: a 9-year prospective study. Am J Kidney Dis 2004, 43:131–139.
Weiner SM, Thiel J, Berg T, et al.: Impact of in vivo complement activation and cryoglobulins on graft outcome of HCV-infected renal allograft recipients. Clin Transplant 2004, 18:7–13.
Rayhill SC, Kirby PA, Voigt MD, et al.: Positive serum cryoglobulin is associated with worse outcome after liver transplantation for chronic hepatitis C. Transplantation 2005, 80:448–456.
Fargion S, Francanzani A: Prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in porphyria cutanea tarda [review]. J Hepatol 2003. 39:635–638.
Gisbert J, Garcia-Buey L, Pajares J, et al.: Prevalence of hepatitis C virus in porphyria cutanea tarda: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hepatol 2003, 39:620–627.
Linde I, Harper P, Floderus Y, et al.: The prevalence of hepatitis C patients with porphyria cutanea tarda in Stockholm, Sweden. Acta Derm Venerol 2005, 85:164–166.
Okano J, Horie Y, Kawasaki H, et al.: Interferon treatment of porphyria cutanea tarda associated with chronic hepatitis type C. Hepatogastroenterology 1997, 44:525–528.
Sene D, Limal N, Messous D, et al.: Biological markers of liver fibrosis and activity as non-invasive alternatives to liver biopsy in patients with chronic hepatitis C and associated mixed cryoglobulinemia vasculitis. Clin Biochem. In press.
Protzer U, Ochsendorf FR, Leopolder-Ochsendorf A, Holtermuller KH: Exacerbation of lichen planus during interferon alfa-2a therapy for chronic active hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 1993, 104:903–905.
Doutre MS, Beylot C, Couzigou P, et al.: Lichen planus and hepatitis C virus: disappearance of lichen under interferon alfa therapy [letter]. Dermatology 1992, 184:229.
Dominguez M, Mateu A, Vieira R, et al.: Linear lichen planus and hepatitis C. Dermatol Online J 2006, 12:17.
Abdallah M, Ghozzi M, Monib H, et al.: Necrolytic acral erythema: a cutaneous sign of hepatitis C virus infection. J Am Acad Dermatol 2005, 53:247–251.
Khanna VJ, Shieh S, Benjamin J, et al.: Necrolytic acral erythema associated with hepatitis C: effective treatment with interferon alfa and zinc. Arch Dermatol 2000, 136:755–757.
Mason AL, Lau JY, Hoang N, et al.: Association of diabetes mellitus and chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 1999, 29:328–333.
Petit JM, Bour JB, Galland-Jos C, et al.: Risk factors for diabetes mellitus and early insulin resistance in chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol 2001, 35:279–283.
Hui JM, Sud A, Farrell GC, et al.: Insulin resistance is associated with chronic hepatitis C and virus infection fibrosis progression. Gastroenterology 2003, 125:1695–1704.
Papatheodoridis GV, Chrysanthos N, Savvas S, et al.: Diabetes mellitus in chronic hepatits B and C: prevalence and potential association with the extent of liver fibrosis. J Viral Hepat 2006, 13:303–310.
Mehta SH, Brancati FL, Strathdee SA, et al.: Hepatitis C virus infection and incident type 2 diabetes. Hepatology 2003, 38:50–56.
Fabris P, Betterle C, Greggio NA, et al.: Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus during alpha-interferon therapy for chronic viral hepatitis. J Hepatol 1998, 28:514–517.
Konrad T, Zeuzem S, Vicini P, et al.: Evaluation of factors controlling glucose tolerance in patients with HCV infection before and after 4 months therapy with interferonalpha. Eur J Clin Invest 2000, 30:111–121.
Ramos-Casals M, Font J: Extrahepatic manifestations in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection [review]. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2005, 17:447–455.
Wu C, Xu X, Tian G, et al.: [Serum autoantibodies of patients with chronic hepatitis C and the significance thereof in infection of hepatitis C virus] [Chinese]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2006, 86:390–393.
Antonelli A, Ferri C, Pampana A, et al.: Thyroid disorders in clinical hepatitis C. Am J Med 2004, 117:10–13.
Marazuela M, Garcia-Buey L, Gonzalez-Fernandez B, et al.: Thyroid autoimmune disorders in patients with chronic hepatitis C before and during inteferon-alpha therapy. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1996, 44:635–642.
Pawlotsky JM, Bouvier M, Fromont P, et al.: Hepatitis C infection and autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura. J Hepatol 1995, 23:635–639.
Sakuraya M, Murakami H, Uchiumi H, et al.: Steroidrefractory chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura assoicated with hepatitis C virus infection. Eur J Haematol 2002, 68:49–53.
Ramos-Casals M, Loustaud-Ratti V, De Vita S, et al.: Sjögren syndrome associated with hepatitis C virus: a multicenter analysis of 137 cases. Medicine (Baltimore) 2005, 84:81–89.
Ramos-Casals M, Mana J, Nardi N, et al.: Sarcoidosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection: analysis of 68 cases. Medicine (Baltimore) 2005, 84:69–80.
Halfon P, Levy M, San Marco M, et al.: Myasthenia gravis and hepatitis C virus infection. J Viral Hepat 1996, 3:329–332.
Weegink CJ, Chamuleau RA, Reesink HW, Molenaar DS: Development of myasthenia gravis during treatment of chronic hepatitis C with interferon-alpha and ribavirin [letter]. J Gastroenterol 2001, 36:723–724.
Ferri C, Bertozzi M, Zignego A: Erectile dysfunction and hepatitis C virus infection [letter]. JAMA 2002, 288:698–699.
Ali Y, Ghafouri M, Weitzman M, et al.: Refractory scleritis in a patient with cryoglobulinemia and hepatitis C [letter]. J Clin Rheumatol 1999, 5:371.
Moazami G, Auran JD, Florakis GJ, et al.: Inteferon treatment of Mooren’s ulcers associated with hepatitis C. Am J Ophthalmol 1995, 119:365–366.
Kawano T, Shigehira M, Uto H, et al.: Retinal complications during interferon therapy for chronic hepatitis C. Am J Gastroenterol 1996. 91:309–313.
d’Alteroche L, Majzoub S, Lecuyer A, et al.: Ophthalmologic side effects during alpha-inteferon therapy for viral hepatitis. J Hepatol 2006, 44:56–61.
Morgello S: The nervous system and hepatitis C virus. Semin Liver Dis 2005, 25:118–121.
Cai F, Ahern M, Smith M: Treatment of cryoglobulinemia associated peripheral neuropathy with rituximab. J Rheumatol 2006, 33:1197–1198.
Bolay H, Soylemezoglu F, Nurlu G, et al.: PCR detected hepatitis C virus genome in the brain of a case with progressive encephalomyelitis with rigidity. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 1996, 98:305–308.
Forton DM, Thomas HC, Taylor-Robinson SD: Central nervous system involvement in hepatitis C virus infection. Metab Brain Dis 2004, 19:383–391.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, N., Reau, N. Extrahepatic manifestations of HCV infection: A brief review and update. Curr hepatitis rep 5, 133–141 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11901-006-0022-z
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11901-006-0022-z