Abstract
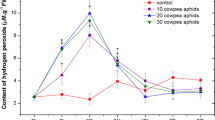
In response to Clostera anachoreta larvae attack, poplar (Populus simonii × P. pyramidalis ‘Opera 8277’) leaves produced a high level of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Histochemical localization revealed that H2O2 was mainly localized in herbivore-wounded zones and might spread through the veins. The activities of three H2O2-scavenging enzymes, i.e., peroxidase (POD), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), and catalase (CAT), were also enhanced in herbivore-wounded leaves, and exhibited an opposite pattern to the accumulation of H2O2. It was found that diphenylene iodonium chloride (DPI, a special inhibitor of NADPH oxidase) treatment significantly inhibited the accumulation of H2O2 induced by herbivory damage. Moreover, DPI treatment led to an obvious decrease in the activities of POD, APX, and CAT. The results indicated that NADPH oxidase contributed to the accumulation of H2O2 and the increase in activities of H2O2-scavenging enzymes in poplar leaves induced by herbivory damage. The balance between H2O2-production pathway and H2O2-scavenging enzymes led to the tolerable level of H2O2 acting in P. simonii × P. pyramidalis ‘Opera 8277’ cuttings in response to herbivory damage.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez ME, Pennell RI, Meijer PJ, Ishikawa A, Dixon RA, Lamb C (1998) Reactive oxygen intermediates mediate a systemic signal network in the establishment of plant immunity. Cell 92:773–784. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81405-1
Bi JL, Felton GW (1995) Foliar oxidative stress and herbivory damage-primary compounds, secondary metabolites, and reactive oxygen species as components of induced resistance. J Chem Ecol 21:1511–1530. doi:10.1007/BF02035149
Blee KA, Jupe SC, Richard G, Bolwell GP (2001) Molecular identification and expression of the peroxidase responsible for the oxidative burst in French bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and related members of the gene family. Plant Mol Biol 47:607–620. doi:10.1023/A:1012307324782
Bolwell GP, Bindschedler LV, Blee KA, Butt VS, Davies DR, Gardner SL, Gerrish C, Minibayeva F (2002) The apoplastic oxidative burst in response to biotic stress in plants: a three-component system. J Exp Bot 53:1367–1376. doi:10.1093/jexbot/53.372.1367
Dangl JL, Dietrich RA, Richberg MH (1996) Death don’t have no mercy: cell death programs in plant-microbe interactions. Plant Cell 8:1793–1807
Grant M, Brown I, Adams S, Knight M, Ainslie A, Mansfield J (2000) The RPM1 plant disease resistance gene facilitates a rapid and sustained increase in cytosolic calcium that is necessary for the oxidative burst and hypersensitive cell death. Plant J 23:441–450. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313x.2000.00804.x
Guan LM, Scandalios JG (2000) Hydrogen peroxide-mediated catalase gene expression in response to wounding. Free Radic Biol Med 28:1182–1190. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(00)00212-4
Hu Z, Yang D, Shen Y (2004) Difference in volatiles of poplar induced by various damages. J For Res 15:280–282. doi:10.1007/BF02844952
Jacks TJ, Davidonis GH (1996) Superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, and the respiratory burst of fungally infected plant cells. Mol Cell Biochem 158:77–79
Lamb C, Dixon RA (1997) The oxidative burst in plant disease resistance. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 48:251–275. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.48.1.251
Leitner M, Boland W, Mithöfer A (2005) Direct and indirect defences induced by piercing-sucking and chewing herbivores in Medicago truncatula. New Phytol 167:597–606. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2005.01426.x
Liu J, Lu B, Xu L (2000) An improved method for the determination of hydrogen peroxide in leaves. Prog Biochem Biophys 27:548–551
Maffei ME, Mithöfer A, Arimura G, Uchtenhagen H, Bossi S, Bertea CM, Cucuzz LS, Novero M, Volpe V, Quadro S, Boland W (2006) Effects of feeding Spodoptera littoralis on lima bean leaves. III. Membrane depolarization and involvement of hydrogen peroxide. Plant Physiol 140:1022–1035. doi:10.1104/pp.105.071993
Mittler R, Lam E, Shulaev V, Cohen M (1999) Signals controlling the expression of cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase during pathogen induced programmed cell death in tobacco. Plant Mol Biol 39:1025–1035. doi:10.1023/A:1006110223774
Mittler R, Vanderauwera S, Gollery M, Van Breusegem F (2004) Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. Trends Plant Sci 9:490–498. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2004.08.009
Mur L, Kenton P, Draper J (2005) In planta measurements of oxidative bursts elicited by avirulent and virulent bacterial pathogens suggests that H2O2 is insufficient to elicit cell death in tobacco. Plant Cell Environ 28:548–561. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2005.01301.x
Neill S, Desikan R, Hancock J (2002) Hydrogen peroxide signaling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:388–395. doi:10.1016/S1369-5266(02)00282-0
Orozco-Cárdenas ML, Ryan C (1999) Hydrogen peroxide is generated systemically in plant leaves by wounding and systemin via the octadecanoid pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:6553–6557. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.11.6553
Orozco-Cárdenas ML, Narváez-Vásquez J, Ryan CA (2001) Hydrogen peroxide acts as a second messenger for the induction of defense genes in tomato plants in response to wounding, systemin, and methyl jasmonate. Plant Cell 13:179–191
Romero-Puertas MC, Rodríguez-Serrano M, Corpas FJ, Gómez M, Del Río LA, Sandalio LM (2004) Cadmium-induced subcellular accumulation of O2 − and H2O2 in pea leaves. Plant Cell Environ 27:1122–1134. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2004.01217.x
Slesak I, Slesak H, Libik M, Miszalski Z (2008) Antioxidant response system in the short-term post-wounding effect in Mesembryanthemum crystallinum leaves. J Plant Physiol 165:127–137. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2007.03.015
Tenhaken R, Levine A, Brisson LF, Dixon RA, Lamb C (1995) Function of the oxidative burst in hypersensitive disease resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:4158–4163. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.10.4158
Vandenabeele S, Van Der Kelen K, Dat J, Gadjev I, Boonefaes T, Morsa S, Rottiers P, Slooten L, Van Montagu M, Zabeau M, Inzé D, Van Breusegem F (2003) A comprehensive analysis of hydrogen peroxide-induced gene expression in tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:16113–16118. doi:10.1073/pnas.2136610100
Venisse JS, Gullner G, Brisset MN (2001) Evidence for the involvement of an oxidative stress in the initiation of infection of pear by Erwinia amylovora. Plant Physiol 125:2164–2172. doi:10.1104/pp.125.4.2164
Vranová E, Inzé D, Van Breusegem F (2002) Signal transduction during oxidative stress. J Exp Bot 53:1227–1236. doi:10.1093/jexbot/53.372.1227
Watanabe T, Sakai S (1998) Effects of active oxygen species and methyl jasmonate on expression of the gene for a wound-inducible 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase in winter squash (Cucurbita maxima). Planta 206:570–576. doi:10.1007/s004250050434
Zhang X, Zhang L, Dong F, Gao J, Galbraith DW, Song C (2001) Hydrogen peroxide is involved in abscisic acid-induced stomatal closure in Vicia faba. Plant Physiol 126:1438–1448. doi:10.1104/pp.126.4.1438
Acknowledgments
This work was collectively supported by the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in Universities of China (PCSIRT0607), by the Key Science Program of the State Forestry Administration of China (2006-59) and National Key Project of Scientific and Technical Supporting Programs Funded by the Ministry of Science & Technology of China (2006BAD01A15; 2006BAD24B04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by B. Barna.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, ZH., Shen, YB., Shen, FY. et al. Effects of feeding Clostera anachoreta on hydrogen peroxide accumulation and activities of peroxidase, catalase, and ascorbate peroxidase in Populus simonii × P. pyramidalis ‘Opera 8277’ leaves. Acta Physiol Plant 31, 995–1002 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-009-0316-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-009-0316-1