Abstract
Background
Ghrelin is secreted mainly in the stomach and plays a role in food intake regulation. Morbidly obese (MO) individuals report a decline in appetite after sleeve gastrectomy (SG), presumably due, in part, to ghrelin cell removal. Ghrelin cell distribution and expression were determined in three areas of resected stomach specimens from MO patients subjected to SG.
Methods
Resected stomach specimens from 20 MO patients undergoing SG were analyzed. Real-time polymerase chain reaction of ghrelin mRNA and immunohistostaining for ghrelin cells in three stomach regions (fundus, body, and pre-antral areas) were performed. Body mass index (BMI) and total plasma ghrelin levels were obtained before and 3 months postoperatively.
Results
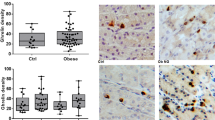
Ghrelin mRNA was detected throughout the stomach, its expression decreasing from the fundus towards the antrum. The relative quantification for ghrelin mRNA expression was 0.043, 0.026, and 0.015 at the fundus, body, and pre-antral region, respectively (P = 0.05, fundus vs. pre-antral region). Average ghrelin cell counts declined from 60 ± 40 to 45 ± 20 and 39 ± 13 cells/high power fields in the fundus, body, and pre-antral region, respectively. Three months after surgery, total plasma ghrelin levels decreased from 1,676 ± 470 to 1,179 ± 188 pg/ml (P < 0.00001) and BMI dropped from 46 ± 6 to 38 ± 5 kg/m2 (P < 0.00001).
Conclusions
Distribution and expression of ghrelin-secreting cells throughout the stomach were defined, emphasizing the importance of meticulous resection of the fundus during SG for maximal ghrelin cell removal.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ariyasu H, Takaya K, Tagami T, et al. Stomach is a major source of circulating ghrelin, and feeding state determines plasma ghrelin-like immunoreactivity levels in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86:4753–8.
Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, et al. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature. 1999;402:656–60.
Tschop M, Wawarta R, Riepl RL, et al. Post-prandial decrease of circulating human ghrelin levels. J Endocrinol Invest. 2001;24:RC19–21.
Date Y, Murakami N, Toshinai K, et al. The role of the gastric afferent vagal nerve in ghrelin-induced feeding and growth hormone secretion in rats. Gastroenterology. 2002;123:1120–8.
Cummings DE, Purnell JQ, Frayo RS, et al. A preprandial rise in plasma ghrelin levels suggests a role in meal initiation in humans. Diabetes. 2001;50:1714–9.
Shiiya T, Nakazato M, Mizuta M, et al. Plasma ghrelin levels in lean and obese humans and the effect of glucose on ghrelin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:240–4.
Date Y, Kojima M, Hosoda H, et al. Ghrelin, a novel growth hormone-releasing acylated peptide, is synthesized in a distinct endocrine cell type in the gastrointestinal tracts of rats and humans. Endocrinology. 2000;141:4255–61.
Simonsson M, Eriksson S, Hakanson R, et al. Endocrine cells in the human oxyntic mucosa. A histochemical study. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1988;23:1089–99.
Roa PE, Kaidar-Person O, Pinto D, et al. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy as treatment for morbid obesity: technique and short-term outcome. Obes Surg. 2006;16:1323–6.
Yehoshua RT, Eidelman LA, Stein M, et al. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy—volume and pressure assessment. Obes Surg. 2008;18:1083–8.
Bohdjalian A, Langer FB, Shakeri-Leidenmuhler S, et al. Sleeve gastrectomy as sole and definitive bariatric procedure: 5-year results for weight loss and ghrelin. Obes Surg. 2010;20:535–40.
Cummings DE, Weigle DS, Frayo RS, et al. Plasma ghrelin levels after diet-induced weight loss or gastric bypass surgery. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1623–30.
Langer FB, Reza Hoda MA, Bohdjalian A, et al. Sleeve gastrectomy and gastric banding: effects on plasma ghrelin levels. Obes Surg. 2005;15:1024–9.
Frezza EE, Chiriva-Internati M, Wachtel MS. Analysis of the results of sleeve gastrectomy for morbid obesity and the role of ghrelin. Surg Today. 2008;38:481–3.
Telejko B, Kuzmicki M, Zonenberg A, et al. Ghrelin in gestational diabetes: serum level and mRNA expression in fat and placental tissue. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2010;118:87–92.
Gnanapavan S, Kola B, Bustin SA, et al. The tissue distribution of the mRNA of ghrelin and subtypes of its receptor, GHS-R, in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:2988.
Tanaka-Shintani M, Watanabe M. Distribution of ghrelin-immunoreactive cells in human gastric mucosa: comparison with that of parietal cells. J Gastroenterol. 2005;40:345–9.
Himpens J, Dobbeleir J, Peeters G. Long-term results of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy for obesity. Ann Surg. 2010;252:319–24.
Goitein D, Goitein O, Feigin A, et al. Sleeve gastrectomy: radiologic patterns after surgery. Surg Endosc. 2009;23:1559–63.
Iannelli A, Schneck AS, Noel P, et al. Re-sleeve gastrectomy for failed laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy: a feasibility study. Obes Surg. 2010;21(7):832–5.
Zhang JV, Ren PG, Avsian-Kretchmer O, et al. Obestatin, a peptide encoded by the ghrelin gene, opposes ghrelin’s effects on food intake. Science. 2005;310:996–9.
Weiner RA, Weiner S, Pomhoff I, et al. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy—influence of sleeve size and resected gastric volume. Obes Surg. 2007;17:1297–305.
Givon-Madhala O, Spector R, Wasserberg N, et al. Technical aspects of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy in 25 morbidly obese patients. Obes Surg. 2007;17:722–7.
Baltasar A, Serra C, Perez N, et al. Re-sleeve gastrectomy. Obes Surg. 2006;16:1535–8.
Gagner M. Leaks after sleeve gastrectomy are associated with smaller bougies: prevention and treatment strategies. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2010;20:166–9.
Conflict of Interest
David Goitein MD, Doron Lederfein PhD, Ronit Zioni MA, Haim Berkenstadt MD, Moris Venturero MD, and Moshe Rubin MD have no conflict of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goitein, D., Lederfein, D., Tzioni, R. et al. Mapping of Ghrelin Gene Expression and Cell Distribution in the Stomach of Morbidly Obese Patients—a Possible Guide for Efficient Sleeve Gastrectomy Construction. OBES SURG 22, 617–622 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-011-0585-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-011-0585-9