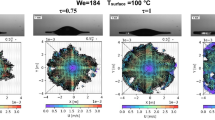
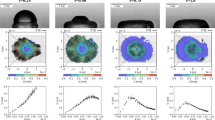
The spreading phenomena of particles during thermal spraying are quite difficult to observe given the kinetics of the process. In this work, the splat formation of glass and alumina is theoretically compared, showing that glass transition and low-thermal conductivity yield a higher ratio between cooling and flattening times, which strongly modifies their spreading behavior. Wipe tests show that splash—splat transition temperature can be modified by the glass composition and its subsequent hydrodynamic properties. The detection of peculiar remaining objects, such as fibers and wavelets shows the possibility of “freezing” some phenomena that are totally unobservable with crystalline oxides, except with high-velocity observations.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a,b:
-
Empirical flattening coefficients, dimensionless
- c:
-
Wavelets speed, m/s
- Cp:
-
Heat capacity of the particle in the liquid phase, J/kg.K
- D:
-
Initial diameter of the particle, m
- Dsplat :
-
Splat diameter, m
- e:
-
Flattened film thickness, m
- f:
-
Frequency of wavelets, s−1
- F:
-
Degree of fragmentation, dimensionless
- g:
-
Gravity constant, m/s2
- K:
-
Sommerfeld number, dimensionless
- l:
-
Wavelength, m
- lC :
-
Critical wavelength value before obtaining gravitational predominance, m
- L:
-
Latent heat of transformation, J/kg
- \( {\cal L}\) :
-
Travel distance of wavelets, m
- \( \ifmmode\expandafter\dot\else\expandafter\.\fi{m} \) :
-
Particles mass flow rate, kg/s
- N:
-
Number of impinging particles during ttransf
- Nu:
-
Nusselt number, dimensionless
- P:
-
Probability, dimensionless
- Re:
-
Reynolds number, dimensionless
- Ssplat :
-
Surface area of splat, m2
- Sexposed :
-
Substrate surface area exposed to impinging particles, m2
- Tg :
-
Glass transition temperature, °C
- Ts:
-
Substrate temperature, °C
- Tglazing :
-
Typical glazing temperature, °C
- Tparticle :
-
Particle temperature, °C
- Ttransformation :
-
Change of state temperature, °C
- \( {\cal T}\) :
-
Period between wavelets, s
- ttransf :
-
Cooling time, s
- tsplat :
-
Flattening time, s
- U:
-
Spreading velocity, m/s
- V:
-
Particle velocity, m/s
- Vi :
-
Volume of a size class of particles, m3
- Vtotal :
-
Total volume of particles, m3
- We:
-
Weber number, dimensionless
- ΔT:
-
Temperature gap between particle and transformation temperatures, °C
- ξ:
-
Spreading factor, dimensionless
- ρ:
-
Particle density, kg/m3
- λ:
-
Thermal conductivity, W/m K
- μ:
-
Particle viscosity, Pa.s
- σ:
-
Surface tension, N/m
- Ξ:
-
Ratio between cooling and flattening time, dimensionless
- Ψ:
-
Feedstock intrinsic prefactor for Ξ and ttransf
- Ω:
-
Wavelet pulsation, rad/s
References
D. Gawne, Y. Bao, and T. Zhang, The Effect of Substrate Temperature on the Adhesion of Plasma Sprayed Borosilicate Glass Coatings, Thermal Spray. A United Forum for Scientific and Technological Advances, C. Berndt, Ed., ASM International, Indianapolis, IN, 1997, p 467-472
D. Gawne, Z. Qiu, T. Zhang, Y. Bao, and K. Zhang, Abrasive Wear Resistance of Plasma Sprayed Glass-Composite Coatings, Thermal Spray: Surface Engineering Via Applied Research, C. Berndt, Ed., TSS, DVS and IIW, Montreal, Quebec, 2000, p 977-981
T. Zhang, Y. Bao, D.T. Gawne, Process Model of Plasma Enamelling, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 23 (2003) 1019-1026
Y. Bao, T. Zhang, and D. Gawne, Analysis of Residual Stress Generated During Plasma Spraying of Glass Coatings, ITSC 98, Nice, France
T. Zhang, Z. Qiu, Y. Bao, D. Gawne, and K. Zhang, Temperature Profiles and Thermal Stress Analysis of Plasma Sprayed Glass-Composite Coatings, Thermal Spray: Surface Engineering Via Applied Research, C. Berndt, Ed., TSS, DVS and IIW, Montreal, Quebec, 2000, p 355-361
T.M. Lee, E. Chang, B.C. Wang, C.Y. Yang, Characteristics of Plasma-Sprayed Bioactive Glass Coatings on Ti-6A1-4V Alloy: An In Vitro Study, Surf. Coat. Technol. 79 (1996) 170-177
E. Verne, M. Ferraris, A. Ventrella, L. Paracchini, Sintering, Plasma Spray Deposition of Bioactive Glass-Matrix Composites for Medical Applications, J. Eur. Cer. Soc., 18 (1998) 363-372
E. Verne, M. Ferraris, C. Jana, L. Paracchini, Bioverit1 I Base Glass/Ti Particulate Biocomposite: In Situ Vacuum Plasma Spray Deposition, J. Eur. Cer. Soc. 20 (2000) 473-479
G.Z. Komskii and G. Saakov, Forming Decorative Protective Coatings by Plasma Spraying, Steklo I keramika no. 4, p 22-24, Izdatel’stvo Lad’ia, Moscow, Russia, April 1991
V.S. Bessmertnyi, V.P. Krokhin, V.A. Panasenko, N.A. Drizhd, P.S. Dyumina, O.M. Kolchina, Plasma Rod Decorating of Household Glass. Glass Ceram., 2001, 58, 214-215
J. Tikkanen, M. Eerola, M. Rajala, Coating Glass by Flame Spraying, J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 178, 1994, p 220-226
G. Bolelli, V. Cannillo, L. Lusvarghi, Plasma-Sprayed Glass-Ceramic Coatings on Ceramic Tiles: Microstructure, Chemical Resistance, Mechanical Properties, J. Eur. Cer. Soc. 25(2005) 1835-1853
G. Bolelli, L. Lusvarghi, T. Manfredini, C. Siligardi, Influence of the Manufacturing Process on the Crystallization Behaviour of CZS Glass System, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 351 (2005) 2537-2546
T. Valente, C. Bartulli, and A. Loreto, Plasma Sprayed Nanostructured Glass Ceramic Matrix Composite Coatings from the CaO-SiO2-ZrO2 Eutectic System, ITSC 2004, Osaka, 10-12/05/2004
S.H. Leigh, C. Berndt, Quantitative Evaluation of Void Distributions Within a Plasma-Sprayed Ceramic, J. Am. Ceram. 82 17-21 (1999)
S. Deshpande, A. Kulkarni, S. Sampath, H. Herman, Application of Image Analysis for Characterization of Porosity in Thermal Spray Coatings and Correlation with Small Angle Neutron Scattering, Surf. Coat. Technol. 187 (2004) 6-16
A. Refke, D. Hawley, J. Doesburg, and R.K. Schmid, LPPS Thin Film Technology for the Application of TBC Systems, ITSC 2005, E. Lugscheider, Ed., May 2-4, 2005, Basel, Switzerland, 6 pages
V.S. Bessmertnyi, N.I. Min’ko, V.N. Glaz, P.S. Dyumina, V.P. Krokhin, M.A. Trubitsin, The Effect of Argon Plasma on Reduction of Variable-Valence Oxides in Synthesis of Minerals, Glass Ceram., 2004, 61(1-2), p 63-64
S. Dallaire, B. Arsenault, A. De Santis, Investigation of Plasma Sprayed Coatings for Bonding Glass to Metal in Hermetic Seal Applications, Surf. Coat. Technol., 53 (1992) 129-135
G. Bolelli, L. Lusvarghi, T. Manfredini, C. Siligardi, Influence of the Manufacturing Process on the Crystallization Behaviour of CZS Glass System, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 351 (2005) 2537-2546
G. Bayrak, S. Yilmaz, Crystallization Kinetics of Plasma Sprayed Basalt Coatings, Ceram. Int. 32 (2006) 441-446
G. Bolelli, V. Canillo, L. Lusvarghi, T. Manfredini, Glass-Alumina Composite Coatings by Plasma Spraying. Part I: Microstructural and Mechanical Characterization, Surf. Coat. Technol. 201 (2006) 458-473
G. Bolelli, V. Canillo, L. Lusvarghi, T. Manfredini, M. Montorsi, Glass-Alumina Composite Coatings by Plasma Spraying. Part II: Microstructure-Based Modeling of Mechanical Properties, Surf. Coat. Technol. 201 (2006) 474-486
V. Cannillo, T. Manfredini, M. Montorsi, C. Siligardi, A. Sola, Microstructure-Based Modelling and Experimental Investigation of Crack Propagation in Glass-Alumina Functionally Graded Materials, J. Eur. Cer. Soc. (2006) 26, 3067-3073
H. Zhang, X.Y. Wang, L.L. Zheng, X.Y. Jiang, Studies of Splat Morphology and Rapid Solidification During Thermal Spraying, Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 44 (2001) 4579-4592
D.R. Lide, Ed., CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, CRC press, London, 1995, p 12-182
P. Fauchais, M. Fukumoto, A. Vardelle, M. Vardelle, Knowledge Concerning Splat Formation: An Invited Review, JTST, 13(3) 2004 337-357
C.J. Li, H. Liao, P. Gougeon, G. Montavon, C. Coddet, Experimental Determination of the Relationship Between Flattening Degree and Reynolds Number for Spray Molten Droplets, Surf. Coat. Technol. 191 (2005) 375-383
K. Shinoda, T. Koseki, and T. Yoshida, Influence of Impact Parameters of Zirconia Droplets on Splat Formation and Morphology in Plasma Spraying, J. Appl. Phys., 2006, 100(7), Art. No. 074903
C. Escure, “Impact Study of Liquid Alumina Droplets onto a Hot Substrate or a Liquid Alumina Film,” Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Limoges, November 2000, 55-2000 (in french)
G.J. Browning, G.W. Bryant, H.J. Hurst, J.A. Lucas, T.F. Wall, An Empirical Method for the Prediction of Coal Ash Slag Viscosity, Energy Fuels 2003, 17, 731-737
M. Vardelle, A. Vardelle, A.C. Léger, and P. Fauchais, Dynamics of Splat Formation and Solidification in Thermal Spraying Processes, Proceedings of the 7th NTSC, 20-24/06/1994, Boston, MS, p 555-562
C. Kang, H. Ng, Splat Morphology and Spreading Behavior due to Oblique Impact of Droplets onto Substrates in Plasma Spray Coating Process, Surf. Coat. Technol. 200 (2006) 5462-5477
K. Shinoda, Y. Kojima, T. Yoshida, In Situ Measurement System for Deformation and Solidification Phenomena of Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia Droplets Impinging on Quartz Glass Substrate Under Plasma Spraying Conditions, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2005, 14 (4), p 511-517
T. Lakatos, Viscosity-Temperature Relations in Glasses Composed of SiO2-Al2O3-Na2O-K2O-Li2O-CaO-MgO-BaO-ZnO-PbO-B2O3, Glastecknisk Tidskrift, 31 (1976) 3, 51-54
T. Lakatos, The Effect of Some Glass Components on the Viscosity of Glass, Glastecknisk Tidskrift, 27 (1972) 2, 25-28
E. Tillotson, On the Surface Tension of Silicate and Borosilicate Glasses, J. Ind. Eng. Chem., 1912, 4(9) 651-652
A.G. Clare, D. Wing, L.E. Jones, A. Kucuk, Density and Surface Tension of Borate Containing Silicate Glass Melts, Glass Technol.—Eur. J. Glass Sci. Technol. Part A, 44(2), 2003, 59-62
X. Shi, Q. Wang, X. Niu, C. Li, K. Lu, An Examination of Surface Tension of Binary Lithium Borate Melts as a Function of Composition and Temperature, JACS, 89 (10) 3222-3228 (2006)
W.D. Kingery, H. Bowen, D.R. Uhlmann, Introduction to Ceramics, John Wiley & sons, New York, 1960, p 284
T. Seward, Modeling of Glass Making Processes for Improved Efficiency: Final Report, DE-FG07-96EE41262, 2003
A. Priven, General Method for Calculating the Properties of Oxide Glass Forming Melts from Their Composition and Temperature, Glass Technol., 2004, 45 (6) 244-54
B. Dussoubs, A. Vardelle, D. Gobin, and P. Fauchais, Solidification and Cooling of a Plasma Sprayed Droplet: Determination of Cooling Velocity, Journée SFT’95, Société Française de Thermique, Limoges, France, p 361-366 (in French)
H. Jones, Cooling, Freezing and Substrate Impact of Droplets Formed by Rotary Atomization, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys., 1971, 4, 1657
M. Fukumoto, S. Katoh, and I. Okane, Splat Behaviour of Plasma Sprayed Particles on Flat Substrate, Thermal Spraying: Current Status and Future Trends, A. Ohmori, Ed., High Temperature Society of Japan, Kobe, Japan, 1995, vol. 1, p 353-358
Z. Liu, R. Reitz, Modelling Fuel Spray Impingement and Heat Transfer Between Spray and Wall in Direct Injection Diesel Engines, Numer. Heat Transfer, Part A, 1995, 28, p 515-529
S. Schiaffino, A. Sonin, Molten Droplet Deposition and Solidification at Low Weber Numbers, Phys. Fluids, 9(11) (1997) p 3172-3187
X. Jiang, Y. Wan, H. Hermann, S. Sampath, Role of Condensates and Adsorbates on Substrate Surface on Fragmentation of Impinging Molten Droplets During Thermal Spraying, Thin Solid Films 385 (2001) 132
A. McDonald, M. Lamontagne, C. Moreau, S. Chandra, Impact of Plasma-Sprayed Metal Particles on Hot and Cold Glass Surfaces, Thin Solid Films, 2006, 514 (1-2), 212-222
L. Li, A. Vaidya, S. Sampath, H. Xiong, L. Zheng, Particle Characterization and Splat Formation of Plasma Sprayed Zirconia, JTST, 2006, 15(1), p 97-105
L. Bianchi, “Projection ar plasma d’arc et plasma inductif de dépôts céramiques: mécanisme de formation de la premièrecouche et relation avec les propriétés mécaniques des dépôts”, Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Limoges, January 1995, p 41-1995 (in French)
K. Shinoda, A. Yamada, M. Kambara, Y. Kojima, T. Yoshida, Deformation of Alumina Droplets on Micro-Patterned Substrates Under Plasma Spraying Conditions, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2007, 16(2), p 300-305
A. Navrotsky, Thermodynamic Properties of Minerals, Mineral Physics and Crystallography: A Handbook of Physical Constants, American Geophysical Union, Washington, DC, 1995, p 18-28
A. Kucuk, A.G. Clare, L.E. Jones, Differences Between the Surface and Bulk of Glass Melts. Part 2. Influence of Redox Ratio on the Surface Properties of Silicate Melts, Phys. Chem. Glasses—Eur. J. Glass Sci. Technol. Part B, 2000, 41(2), p 75-80
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Philippe Belleudy at Université Joseph Fourier (Grenoble), George « Bud » Homsy at University of California (Santa Barbara) and Marc Rabaud at Université Paris-Sud (Orsay) for their kind assessment about hydrodynamic aspects of wavelets in splats. Technical help from Pierre Bertrand and Pascale Hoog, and bibliographical help from Martine Coddet are also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poirier, T., Planche, M.P., Landemarre, O. et al. Particles Spreading Phenomena in the Case of Glass Thermal Spraying. J Therm Spray Tech 17, 564–573 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-008-9211-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-008-9211-3