Abstract
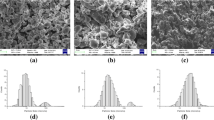
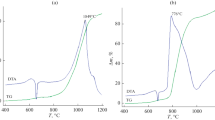
The effect of particle size and shape on the sintering response of aluminum powder has been examined. Spherical 3-, 5-, and 15-μm powders and irregularly shaped 6-, 7-, and 15-μm powders from two manufacturers were mixed with 4 wt pct Sn, poured into a crucible, and sintered for 2 hours under argon at 620 °C. The particle shape appears to be a critical characteristic governing the sintering characteristics. The particle size and size distribution, the tap density, the oxide film thickness, the surface chemistry, and the impurity concentration had little influence. The irregular particles sintered to a final density of 88 to 91 pct, whereas the spherical particles reached a density of only 65 to 73 pct. It is suggested that the differential thermal expansion between the aluminum particle and its oxide film may cause the oxide to fracture and that the fracture characteristics are different between the two powder morphologies.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
LECO is a trademark of LECO Corporation, St. Joseph, MI.
PHILIPS is a trademark of Philips Electronics Instruments Corp., Mahwah, NJ.
References
C. Lall: Int. J. Powder Metall., 1991, 27: 315–18
L.S. Darken, R.W. Gurry: Physical Chemistry of Metals, McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, 1953
S.W. Ip, M. Kucharski, J.M. Toguri: J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 1993, 12: 1699–702
Y. Liu, Z. He, G. Dong, Q. Li: J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 1992, 11: 896–98
D.T. Livey and P. Murray: Paper presented at the 2nd Plansee Seminar, Reutte/Tirol, 1955
J.-G. Li: Ceram. Int., 1994, 20: 391–412
Z.A. Munir: J. Mater. Sci., 1979, 17: 2733–40
Z.A. Munir: Powder Metall., 1981, 24: 177–80
R. Lumley, T.B. Sercombe, G.B. Schaffer: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1999, 30A: 457–63
T. Pieczonka, T. Schubert, S. Baunack, and B. Kieback: Paper presented at Sintering 05, Grenoble, France, 2005
G.B. Schaffer, B.J. Hall, S.J. Bonner, S.H. Huo, T.B. Sercombe: Acta Mater., 2006, 54: 131–38
G.B. Schaffer, B.J. Hall: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2002, 33A: 3279–84
I. E. Anderson, J.C. Foley: Surf. Interface Analysis, 2001, 31: 599–608
Alloy Phase Diagrams, ASM Handbook, ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1992, vol. 3
C.A. Harper: Handbook of Ceramics, Glasses and Diamond, McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, 2001
Acknowledgments
Financial support from the Australian Research Council, the Aluminum Powder Company, and Cooltemp Pty Ltd is gratefully acknowledged. The XPS data were collected and analyzed by Dr. Barry Wood, Brisbane Surface Analysis Facility, The University of Queensland.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted January 24, 2007.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Sercombe, T. & Schaffer, G. The Effect of Particle Shape on the Sintering of Aluminum. Metall Mater Trans A 38, 1351–1357 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-007-9153-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-007-9153-2