Abstract
Aim
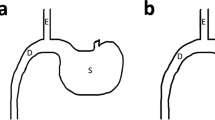
Sleeve gastrectomy (SG) and modified duodenal jejunal bypass (MDJB) were compared as procedures for glucose control. We aim to form the initial conclusions with respect to the possibility of (1) whether gastric fundus exclusion is essential for the control of diabetes and (2) application as a low morbidity procedure.
Materials and Methods
SG and MDJB were performed on 10- to 12-week-old Goto–Kakizaki rats that spontaneously develop type 2 diabetes. Rats were observed for 36 weeks after surgery, and glucose, insulin, glucagons-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), glucose tolerate, insulin sensitivity, cholesterol, triglycerides, and free fatty acid levels were measured.
Results
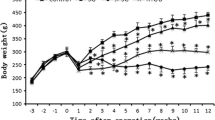
Apart from distinct weight loss of SG and MDJB after 1 month compared with sham-operated rats (P < 0.001), SG showed strikingly improved blood glucose levels and significantly decreased Ghrelin secretion (P < 0.001). Furthermore, SG resulted in a shorter operative time (P < 0.01) and postoperative recovery time (P < 0.01) than MDJB group.
Conclusions
SG shows better control in terms of glucose tolerance and other measurements. This study provides direct evidence that SG possesses better improvement of diabetes by reduction of Ghrelin.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SG:
-
Sleeve gastrectomy
- GK:
-
Goto–Kakizaki
- MDJB:
-
Modified duodenal jejunal bypass
- OGTT:
-
Oral glucose tolerance test
- ITT:
-
Insulin tolerance test
- GLP-1:
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1
References
Papadopoulos AA, Kontodimopoulos N, Frydas A, Ikonomakis E, Niakas D. Predictors of health-related quality of life in type II diabetic patients in Greece. BMC Public Health 2007;7:186.
King H, Aubert RE, Herman WH. Global burden of diabetes, 1995–2025: prevalence, numerical estimates, and projections. Diabetes Care 1998;21:1414–1431.
Chan BS, Tsang MW, Lee VW, Lee KK. Cost of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Hong Kong Chinese. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 2007;45:455–468.
Klein S, Fontana L, Young VL, Coggan AR, Kilo C, Patterson BW, Mohammed BS. Absence of an effect of liposuction on insulin action and risk factors for coronary heart disease. N Engl J Med 2004;350:2549–2557.
Kelley DE. Thermodynamics, liposuction, and metabolism. N Engl J Med 2004;350:2542–2544.
Kirchner H, Guijarro A, Meguid MM. Is a model useful in exploring the catabolic mechanisms of weight loss after gastric bypass in humans? Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 2007;10:463–474.
Pories WJ, Swanson MS, MacDonald KG, Long SB, Morris PG, Brown BM, Barakat HA, deRamon RA, Israel G, Dolezal JM. Who would have thought it? An operation proves to be the most effective therapy for adult-onset diabetes mellitus. Ann Surg 1995;222:339–352.
Detournay B, Cros S, Charbonnel B, Grimaldi A, Liard F, Cogneau J, Fagnani F, Eschwège E. Managing type 2 diabetes in France: the ECODIA survey. Diabetes Metab 2000;26:363–369.
Scopinaro N, Adami GF, Marinari GM, Gianetta E, Traverso E, Friedman D, Camerini G, Baschieri G, Simonelli A. Biliopancreatic diversion. World J Surg 1998;22:936–946.
Pereferrer FS, Gonzàlez MH, Rovira AF, Blasco SB, Rivas AM, del Castillo Déjardin D. Influence of sleeve gastrectomy on several experimental models of obesity: metabolic and hormonal implications. Obes Surg 2008;18(1):97–108.
Vidal J, Ibarzabal A, Romero F, Delgado S, Momblán D, Flores L, Lacy A. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and the metabolic syndrome following sleeve gastrectomy in severely obese subjects. Obes Surg 2008;18(9):1077–1082.
Rubino F, Marescaux J. Effect of duodenal-jejunal exclusion in a non-obese animal model of type 2 diabetes: a new perspective for an old disease. Ann Surg 2004;239:1–11.
Cohen RV, Schiavon CA, Pinheiro JS, Correa JL, Rubino F. Duodenal-jejunal bypass for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in patients with body mass index of 22–34 kg/m2: a report of 2 cases. Surg Obes Relat Dis 2007;3:195–197.
Rubino F, Gagner M. Potential of surgery for curing type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann Surg 2002;236:554–559.
Cowan GS Jr, Buffington CK. Significant changes in blood pressure, glucose, and lipids with gastric bypass surgery. World J Surg 1998;22:987–992.
Marceau P, Hould FS, Simard S, Lebel S, Bourque RA, Potvin M, Biron S. Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch. World J Surg 1998;22:947–954.
Schauer PR, Ikramuddin S, Gourash W, Ramanathan R, Luketich J. Outcomes after laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for morbid obesity. Ann Surg 2000;232:515–529.
Wittgrove AC, Clark GW. Laparoscopic gastric bypass, Roux-en-Y-500 patients: technique and results, with 3–60 month follow-up. Obes Surg 2000;10:233–239.
Pontiroli AE, Pizzocri P, Librenti MC, Vedani P, Marchi M, Cucchi E, Orena C, Paganelli M, Giacomelli M, Ferla G, Folli F. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding for the treatment of morbid (grade 3) obesity and its metabolic complications: a three-year study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002;87:3555–3561.
Scopinaro N, Gianetta E, Adami GF, Friedman D, Traverso E, Marinari GM, Cuneo S, Vitale B, Ballari F, Colombini M, Baschieri G, Bachi V. Biliopancreatic diversion for obesity at eighteen years. Surgery 1996;119:261–268.
Dixon JB, O’Brien PE. Health outcomes of severely obese type 2 diabetic subjects 1 year after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. Diabetes Care 2002;25:358–363.
Galli J, Li LS, Glaser A, Ostenson CG, Jiao H, Fakhrai-Rad H, Jacob HJ, Lander ES, Luthman H. Genetic analysis of non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus in the GK rat. Nat Genet 1996;12:31–37.
Inabnet WB 3rd, Milone L, Korner J, Durak E, Ahmed L, Pomrantz J, Harris PE, Bessler M. A rodent model of metabolic surgery for study of type 2 diabetes and positron emission tomography scanning of beta cell mass. Surg Obes Relat Dis 2009;5(2):212–217.
National Research Council. Public Health Service Policy and Government Principles regarding the care and use of animals. Appendix D. Guide for the care and use of animals. Washington, DC: National Academy, 1996, pp 116–118.
de Bona Castelan J, Bettiol J, d’Acampora AJ, Castelan JV, de Souza JC, Bressiani V, Giroldi SB. Sleeve gastrectomy model in Wistar rats. Obes Surg 2007;17(7):957–961.
Pories WJ, MacDonald KG Jr, Morgan EJ, Sinha MK, Dohm GL, Swanson MS, Barakat HA, Khazanie PG, Leggett-Frazier N, Long SD. Surgical treatment of obesity and its effect on diabetes: 10-y follow-up. Am J Clin Nutr 1992;55:582S–585S.
Patriti A, Aisa MC, Annetti C, Sidoni A, Galli F, Ferri I, Gullà N, Donini A. How the hindgut can cure type 2 diabetes. Ileal transposition improves glucose metabolism and beta-cell function in Goto-kakizaki rats through an enhanced Proglucagon gene expression and L-cell number. Surgery 2007;142:74–85.
Castagneto M, De Gaetano A, Mingrone G, Tacchino R, Nanni G, Capristo E, Benedetti G, Tataranni PA, Greco AV. Normalization of insulin sensitivity in the obese patient after stable weight reduction with biliopancreatic diversion. Obes Surg 1994;4:161–168.
MacDonald KG Jr, Long SD, Swanson MS, Brown BM, Morris P, Dohm GL, Pories WJ. The gastric bypass operation reduces the progression and mortality of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Gastrointest Surg 1997;1:213–220. discussion 220.
Meneghini LF. Impact of bariatric surgery on type 2 diabetes. Cell Biochem Biophys 2007;48:97–102.
Frezza EE, Wachtel MS, Chiriva-Internati M. The multiple faces of glucagons-like peptide 1-obesity, appetite, and stress: what is next? A review. Dig Dis Sci 2007;52:643–649.
Langer FB, Reza Hoda MA, Bohdjalian A, Felberbauer FX, Zacherl J, Wenzl E, Schindler K, Luger A, Ludvik B, Prager G. Sleeve gastrectomy and gastric banding: effects on plasma Ghrelin levels. Obes Surg 2005;15:1024–1029.
Näslund E, Backman L, Holst JJ, Theodorsson E, Hellström PM. Importance of small bowel peptides for the improved glucose metabolism 20 years after jejunoileal bypass for obesity. Obes Surg 1998;8:253–260.
Brzozowski T, Konturek PC, Drozdowicz D, Konturek SJ, Pawlik M, Sliwowski Z, Pawlik WW, Hahn EG. Role of central and peripheral ghrelin in the mechanism of gastric mucosal defence. Inflammopharmacology 2005;13:45–62.
Kotidis EV, Koliakos GG, Baltzopoulos VG, Ioannidis KN, Yovos JG, Papavramidis ST. Serum ghrelin, leptin and adiponectin levels before and after weight loss: comparison of three methods of treatment–a prospective study. Obes Surg 2006;16:1425–1432.
Pusztai P, Sarman B, Ruzicska E, Toke J, Racz K, Somogyi A, Tulassay Z. Ghrelin: a new peptide regulating the neurohormonal system, energy homeostasis and glucose metabolism. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2008;24:343–352.
Gentileschi P, Kini S, Catarci M, Gagner M. Evidence-based medicine: open and laparoscopic bariatric surgery. Surg Endosc 2002;16:736–744.
Schauer PR, Ikramuddin S. Laparoscopic surgery for morbid obesity. Surg Clin North Am 2001;81:1145–1179.
Lewis GF, Carpentier A, Adeli K, Giacca A. Disordered fat storage and mobilization in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Endocr Rev 2002;23:201–229.
Strader AD, Vahl TP, Jandacek RJ, Woods SC, D’Alessio DA, Seeley RJ. Weight loss through ileal transposition is accompanied by increased ileal hormone secretion and synthesis in rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2005;288:E447–E453.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, F., Zhang, G., Liang, J. et al. Sleeve Gastrectomy Provides a Better Control of Diabetes by Decreasing Ghrelin in the Diabetic Goto–Kakizaki Rats. J Gastrointest Surg 13, 2302–2308 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-009-0997-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-009-0997-1