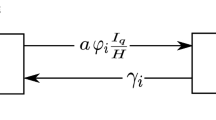Abstract
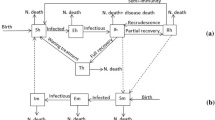
We develop a numerical method for estimating optimal parameters in a mathematical model of the within-host dynamics of malaria infection. The model consists of a quasilinear system of partial differential equations. Convergence theory for the computed parameters is provided. Following this analysis, we present several numerical simulations that suggest that periodic treatments that are in synchronization with the periodic bursting rate of infected erythrocytes are the most productive strategies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackleh, A. S. (1999). Parameter identification in size-structured population models with nonlinear individual rates. Math. Comput. Model., 30(9–10), 81–92.
Ackleh, A. S., & Thibodeaux, J. J. (2008). Parameter estimation in a structured erythropoiesis model. Math. Biosci. Eng., 5(4), 601–616.
Ackleh, A. S., Banks, H. T., Deng, K., & Hu, S. (2005). Parameter estimation in a coupled system of nonlinear size-structured populations. Math. Biosci. Eng., 2(2), 289–315.
Ackleh, A. S., Deng, K., Ito, K., & Thibodeaux, J. (2006). A structured erythropoiesis model with nonlinear cell maturation velocity and hormone decay rate. Math. Biosci., 204(1), 21–48.
Banks, H. T. (1988). Computational techniques for inverse problems in size-structured population models. In Lecture notes in control and info. science: Vol. 114. Proc. IFIP conf. on optimal control of systems governed by PDE (pp. 3–10), Santiago de Compostela, July 1987. Berlin: Springer.
Banks, H. T. (1994). Some remarks on estimation for size-structured population models. In S. Levin (Ed.), Lecture notes in biomathematics: Vol. 100. Frontiers of theoretical biology (pp. 609–623). Berlin: Springer.
Banks, H. T., & Fitzpatrick, B. G. (1991). Estimation of growth rate distributions in size structured population models. Q. Appl. Math., 49, 215–235.
Banks, H. T., & Kunisch, K. (1989). Estimation techniques for distributed parameter systems. Boston: Birkhauser.
Banks, H. T., Botsford, L., Kappel, F., & Wang, C. (1988). Modeling and estimation in size structured population models. In Proc. math. ecology (pp. 521–541), Trieste, 1986.
Banks, H. T., Botsford, L. W., Kappel, F., & Wang, C. (1991). Estimation of growth and survival in size-structured cohort data: an application to larval striped bass (Morone saxatilis). J. Math. Biol., 30(2), 125–150.
Banks, H. T., Cole, C. E., Schlosser, P. M., & Tran, H. T. (2004). Modeling and optimal regulation of erythropoiesis subject to benzene intoxication. Math. Biosci. Eng., 1(1), 15–48.
Bélair, J., & Mahaffy, J. M. (2001). Variable maturation velocity and parameter sensitivity in a model for hematopoiesis. IMA J. Math. Appl. Med. Biol., 18(2), 193–211.
Casals-Pascual, C., Kai, O., Cheung, J. O. P., Williams, S., Lowe, B., Nyanoti, M., Williams, T. N., Maitland, K., Molyneux, M., Newton, C. R. J. C., Peshu, N., Watt, S. M., & Roberts, D. J. (2006). Suppression of erythropoiesis in malarial anemia is associated with hemozoin in vitro and in vivo. Blood, 108(8), 2569–2577.
Chitnis, N., Cushing, J. M., & Hyman, J. M. (2006). Bifurcation analysis of a mathematical model for malaria transmission. SIAM J. Appl. Math., 67(1), 24–45.
Chiyaka, C., Garira, W., & Dube, S. (2007). Transmission model of endemic human malaria in a partially immune population. Math. Comput. Model., 46(5–6), 806–822.
Cho, K., & Kwon, Y. (1999). Parameter estimation in nonlinear age-dependent population dynamics. IMA J. Appl. Math., 62(3), 227–244.
De Leenheer, P., & Pilyugin, S. S. (2008). Immune response to a malaria infection: Properties of a mathematical model. J. Biol. Dyn., 2(2), 102–120.
Gurarie, D., & McKenzie, F. E. (2006). Dynamics of immune response and drug resistance in malaria infection. Malar. J., 5, 86.
Mahaffy, J. M., Polk, S. W., & Roeder, R. K. W. (1999). An age-structured model for erythropoiesis following a phlebotomy (Technical Report). Centre Recherches Mathématiques, Université de Montréal, CRM-2598.
NIH (2007). Understanding Malaria (Publication No. 07-7139).
Rundell, W. (1989). Determining the birth function for an age-structured population. Math. Popul. Stud., 1(4), 377–395.
Rundell, W. (1993). Determining the death rate for an age-structured population from census data. SIAM J. Appl. Math., 53(6), 1731–1746.
Sawyer, S. T., Krantz, S. B., & Goldwasser, E. (1987). Binding and receptor-mediated endocytosis of erythropoietin in friend virus infected erythroid cells. J. Biol. Chem., 262, 5554–5562.
Thibodeaux, J. J. (2010). Modeling erythropoiesis subject to malaria infection. Math. Biosci., 225(1), 59–67.
Tumwiine, J., Mugisha, J. Y. T., & Luboobi, L. S. (2008). On global stability of the intra-host dynamics of malaria and the immune system. J. Math. Anal. Appl., 341(2), 855–869.
White, N. J. (2004). Antimalarial drug resistance. J. Clin. Invest., 113(8), 1084–1092.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thibodeaux, J.J., Schlittenhardt, T.P. Optimal Treatment Strategies for Malaria Infection. Bull Math Biol 73, 2791–2808 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-011-9650-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-011-9650-8