Abstract
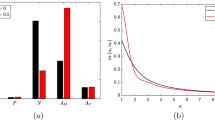
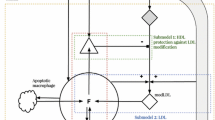
Atherosclerosis is a chronic disease of the large arteries, characterized by fatty cholesterol-filled streaks and plaque build-up within the artery wall. Within the past decade, inflammation has been determined as a crucial factor in all stages of lesion formation, however, many of the mechanisms involved are not yet fully understood. We present a simplified ODE model that explores the role of inflammation in atherosclerosis. The model incorporates two of the main lesion constituents, cholesterol-carrying modified Low Density Lipoproteins (LDLs) and macrophage foam cells. Their complex interactions are combined into general functions, and the long-term model behaviour is investigated through phase plane analysis and simulations. Our results indicate that the underlying mechanisms of macrophage uptake of modified LDL can have a deep impact on the cellular dynamics in the lesion. Our model demonstrates that it is macrophage proliferation and constant signalling to the endothelial cells, rather than an increasing influx of modified LDL, that drives lesion instability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cobbold, C.A., Sherratt, J.A., Maxwell, S.R.J., 2002. Lipoprotein oxidation and its significance for atherosclerosis: a mathematical approach. Bull. Math. Biol. 64, 65–95.
Girn, H.R.S., Orsi, N.M., Homer-Vanniasinkam, S., 2007. An overview of cytokine interactions in atherosclerosis and implications for peripheral arterial disease. Vasc. Med. 12(4), 299–309.
Hansson, G.K., 2005. Mechanisms of disease: Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 352, 1685–1695.
Hansson, G.K., Libby, P., 2006. The immune response in atherosclerosis: a double-edged sword. Nature Immunology 6, 508–519.
Ibragimov, A.I., McNeal, C.J., Ritter, L.R., Walton, J.R., 2005. A mathematical model of atherogenesis as an inflammatory response. Math. Med. Biol. 22, 305–333.
Kharbanda, R., MacAllister, R., 2005. The atherosclerosis time-line and the role of the endothelium. Curr. Med. Chem. 5, 47–52.
Kreisberg, R.A., Oberman, A., 2002. Lipids and atherosclerosis: Lessons learned from randomized controlled trials of lipid lowering and other relevant studies. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 87(2), 423–437.
Kunjathoor, V.V., Febbraio, M., Podrez, E.A., Moore, K.J., Andersson, L., Koehn, S., Rhee, J.S., Silverstein, R., Hoff, H.F., Freeman, M.W., 2002. Scavenger receptors class A-I/II and CD36 are the principal receptors responsible for the uptake of modified low density lipoprotein leading to lipid loading in macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 277(51), 49982–49988.
Lendon, C.L., Davies, M.J., Born, G.V.R., Richardson, P.D., 1991. Atherosclerotic plaque caps are locally weakened when macrophages density is increased. Atherosclerosis 87(1), 87–90.
Libby, P., 2002. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature 420, 868–874.
Libby, P., Aikawa, M., 2002. Stabilization of atherosclerotic plaques: New mechanisms and clinical targets. Nat. Med. 8(11), 1257–1262.
Libby, P., Ridker, P.M., 2006. Inflammation and atherothrombosis: from population biology and bench research to clinical practice. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 48, A33–46.
Libby, P., Ridker, P.M., Maseri, A., 2002. Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation 105, 1135–1143.
Liu, H., Shi, B., Huang, C.-C., Eksarko, P., Pope, R.M., 2008. Transcriptional diversity during monocyte to macrophage differentiation. Immunol. Lett. 117(1), 70–80.
Llodrá, J., Angeli, V., Liu, J., Trogan, E., Fisher, E.A., Randolph, G.J., 2004. Emigration of monocyte-derived cells from atherosclerotic lesions characterizes regressive, but not progressive plaques. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101(32), 11779–11784.
Lusis, A.J., 2000. Atherosclerosis. Nature 407.
Nicholson, A.C., Han, J., Febbraio, M., Silverstein, R.L., Hajjar, D.P., 2001. Role of CD36, the macrophage class B scavenger receptor, in atherosclerosis. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 947(1), 224–228.
Perko, L., 1991. Differential Equations and Dynamical Systems, 1st edn. Texts in Applied Mathematics, vol. 7, Springer, Berlin.
Plank, M.J., Comerford, A., Wall, D.J.N., David, T., 2007. Modelling the early stages of atherosclerosis. In: Deutsch, A., Brusch, L., Byrne, H., de Vries, G., Herzel, H. (Eds.), Mathematical Modelling of Biological Systems, vol. 1, pp. 263–274. Birkhauser, Boston. Chap. 23.
Prosi, M., Zunino, P., Perktold, K., Quarteroni, A., 2005. Mathematical and numerical models for transfer of low-density lipoproteins through the arterial walls: a new methodology for the model set up with applications to the study of disturbed lumenal flow. J. Biomech. 38, 903–917.
Resnick, N., Yahav, H., Shay-Salit, A., Shushy, M., Schubert, S., Zilberman, M., Chen, L., Wofovitz, E., 2003. Fluid shear stress and the vascular endothelium: for better and for worse. Progress Biophys. Molecular Biol. 81, 177–199(23).
Ross, R., 1999. Atherosclerosis—an inflammatory disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 340(2), 115–126.
Williams, K.J., Feig, J.E., Fisher, E.A., 2008. Rapid regression of atherosclerosis: insights from the clinical and experimental literature. Nat. Clinical Practice Cardiovasc. Med. 5(2), 91–102.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ougrinovskaia, A., Thompson, R.S. & Myerscough, M.R. An ODE Model of Early Stages of Atherosclerosis: Mechanisms of the Inflammatory Response. Bull. Math. Biol. 72, 1534–1561 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-010-9509-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-010-9509-4