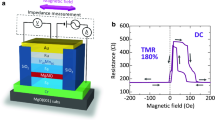
Abstract
Spintronics has received a great attention and significant interest within the past decades, and provided considerable and remarked applications in industry and electronic information etc. In spintronics, the MgO based magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) is an important research advancement because of its physical properties and excellent performance, such as the high TMR ratio in MgO based MTJs. We present an overview of more than a decade development in MgO based MTJs. The review contains three main sections. (1) Research of several types of MgO based MTJs, including single-crystal MgO barrier based-MTJs, double barrier MTJs, MgO based MTJs with interlayer, novel electrode material MTJs based on MgO, novel barrier based MTJs, novel barrier MTJs based on MgO, and perpendicular MTJs. (2) Some typical physical effects in MgO based MTJs, which include six observed physical effects in MgO based MTJs, namely spin transfer torque (STT) effect, Coulomb blockade magnetoresistance (CBMR) effect, oscillatory magnetoresistance, quantum-well resonance tunneling effect, electric field assisted magnetization switching effect, and spincaloric effect. (3) In the last section, a brief introduction of some important device applications of MgO based MTJs, such as GMR & TMR read heads and magneto-sensitive sensors, both field and current switching MRAM, spin nano oscillators, and spin logic devices, have been provided.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Julliere M. Tunneling between ferromagnetic films. Phys Lett A, 1975, 54: 225–226
Baibich M N, Broto J M, Fert A, et al. Giant magnetoresistance of (001)Fe/(001)Cr magnetic superlattices. Phys Rev Lett, 1988, 61: 2472–2475
Binasch G, Grunberg P, Saurenbach F, et al. Enhanced magnetoresistance in layered magnetic structures with antiferromagnetic interlayer exchange. Phys Rev B, 1989, 39: 4828–4830
Miyazaki T, Tezuka N. Giant magnetic tunneling effect in Fe/Al2O3/Fe junction. J Magn Magn Mater, 1995, 139: L231–L234
Moodera J S, Kinder L R, Wong T M, et al. Large magnetoresistance at RT in ferromagnetic thin film tunnel junctions. Phys Rev Lett, 1995, 74: 3273–3276
Han X F, Oogane M, Kubota H, et al. Fabrication of high-magnetoresistance tunnel junctions using Co75Fe25 ferromagnetic electrodes. Appl Phys Lett, 2000, 77: 283–285
Han X F, Miyazaki T. Effects of annealing on high-magnetoresistance tunnel junctions with Co75Fe25 ferromagnetic electrodes. J Mater Sci Technol, 2000, 16: 549–553
Wei H X, Qin Q H, Ma M, et al. 80% tunneling magnetoresistance at RT for thin Al-O barrier magnetic tunnel junction with CoFeB as free and reference layers. J Appl Phys, 2007, 101: 09B501
Yuasa S, Djayaprawira D D. Giant tunnel magnetoresistance in magnetic tunnel junctions with a crystalline MgO(001) barrier. J Phys D-Appl Phys, 2007, 40: R337
Butler W, Zhang X G, Schulthess T C, et al. Spin-dependent tunneling conductance of FeMgOFe sandwiches. Phys Rev B, 2011, 63: 054416
Mathon J, Umerski A. Theory of tunneling magnetoresistance of an epitaxial Fe/MgO/Fe(001) junction. Phys Rev B, 2001, 63: 220403 (R)
Parkin S S P, Kaiser C, Panchula A, et al. Giant tunnelling magnetoresistance at RT with MgO(100) tunnel barriers. Nat Mater, 2004, 3: 862–867
Yuasa S, Nagahama T, Fukushima A, et al. Giant room-temperature magnetoresistance in single-crystal Fe/MgO/Fe magnetic tunnel junctions. Nat Mater, 2004, 3: 868–871
Ikeda S, Hayakawa J, Ashizawa Y, et al. Tunnel magnetoresistance of 604% at 300 K by suppression of Ta diffusion in CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB pseudo-spin-valves annealed at high temperature. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 93: 082508
Du G X, Wang S G, Ma Q L, et al. Spin-dependent tunneling spectroscopy for interface characterization of epitaxial Fe/MgO/Fe MTJs. Phys Rev B, 2010, 81: 064438
Feng J F, Chen J Y, Venkatesan M, et al. Superparamagnetism in MgO-based MTJs with a thin pinned ferromagnetic electrode. Phys Rev B, 2010, 81: 205212
Heinonen O G, Singleton E W, Karr B W, et al. Review of the physics of magnetoresistive readers. IEEE Trans Magn, 2008, 44: 2465–2471
Slaughter J M. Materials for magnetoresistive random access memory. Ann Rev Mater Res, 2009, 39: 277–296
Hayakawa J, Ikeda S, Lee Y M, et al. Effect of high annealing temperature on giant tunnel magnetoresistance ratio of CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB magnetic tunnel junctions. App Phys Lett, 2006, 89: 232510
Djayaprawira D D, Tsunekawa K, Nagai M, et al. 230% room-temperature magnetoresistance in CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB magnetic tunnel junctions. Appl Phys Lett, 2005, 86: 092502
Lee Y M, Hayakawa J, Ikeda S, et al. Effect of electrode composition on the tunnel magnetoresistance of pseudo-spin-valve magnetic tunnel junction with a MgO tunnel barrier. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 90: 212507
Yan W. Spin-dependent Transport Theory and First-principles Calculation of MgO-based Magnetic Tunnel Junctions. Dissertation for the Doctoral Degree. Beijing: Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2009
Yuasa S. Giant tunneling magnetoresistance in MgO-based magnetic tunnel junctions. J Phys Soc Jap, 2008, 77: 031001
Mathon J, Umerski A. Theory of resonant tunneling in an epitaxial Fe/Au/MgO/Au/Fe(001) junction. Phys Rev B, 2005, 71: 220402 (R)
Yavorsky B Y, Mertig I. Noncollinear interface magnetism and ballistic transport in Fe/FeO/MgO/Fe tunnel junctions: Ab initio calculations using the KKR method. Phys Rev B, 2006, 74: 174402
Miura Y, Uchida H, Oba Y, et al. Half-metallic interface and coherent tunneling in Co2YZ/MgO/Co2YZ (YZ=MnSi,CrAl) magnetic tunnel junctions: A first-principles study. Phys Rev B, 2008, 78: 064416
Bose P, Ernst A, Mertig I, et al. Large reduction of the magnetoresistance in Fe/MgO/Fe tunnel junctions because of small oxygen concentrations at a single FeO interface layer: A first-principles study. Phys Rev B, 2008, 78: 092403
Nozaki T, Tezuka N, Inomata K. Quantum oscillation of the tunneling conductance in fully epitaxial double barrier magnetic tunnel junctions. Phys Rev Lett, 2006, 96: 027208
Wang Y, Lu Z Y, Zhang X G, et al. First-principles theory of quantum well resonance in double barrier magnetic tunnel junctions. Phys Rev Lett, 2006, 97: 087210
Wang Y, Han X F, Zhang X G. Effect of Co interlayers in Fe/MgO/Fe magnetic tunnel junctions. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 93: 172501
Zhang J, Wang Y, Zhang X G, et al. Inverse and oscillatory magnetoresistance in Fe(001)/MgO/Cr/Fe magnetic tunnel junctions. Phys Rev B, 2010, 82: 134449
Wang Y, Zhang J, Zhang X G, et al. First-principles study of Fe/MgO based magnetic tunnel junctions with Mg interlayers. Phys Rev B, 2010, 82: 054405
Yuasa S, Fukushima A, Nagahama T, et al. High tunnel magnetoresistance at RT in fully epitaxial Fe/MgO/Fe tunnel junctions because of coherent spin-polarized tunneling. J Appl Phys, 2004, 43: L588–L590
Yu G Q, Feng J F, Kurt H, et al. Field sensing in MgO double barrier MTJs with a superparamagnetic Co50Fe50 free layer. J Appl Phys, 2012, 111: 113906
Zeng Z M, Han X F, Zhan W S, et al. Oscillatory tunnel magnetoresistance in double barrier magnetic tunnel junctions. Phys Rev B, 2005, 72: 054419
Yakushiji K, Mitani S, Takanashi K, et al. Tunnel magnetoresistance oscillations in current perpendicular to plane geometry of CoAlO granular thin films. J Appl Phys, 2002, 91: 7038–7040
Yuasa S, Nagahama T, Suzuki Y. Spin-polarized resonant tunneling in magnetic tunnel junctions. Science, 2002, 297: 234–237
Niizeki T, Tezuka N, Inomata K. Enhanced tunnel magnetoresistance because of spin dependent quantum well resonance in specific symmetry states of an ultrathin ferromagnetic electrode. Phys Rev Lett, 2008, 100: 047207
Nozaki T, Hirohata A, Tezuka N, et al. Bias voltage effect on tunnel magnetoresistance in fully epitaxial MgO double-barrier magnetic tunnel junctions. Appl Phys Lett, 2005, 86: 082501
Gan H D, Ikeda S, Shiga W, et al. Tunnel magnetoresistance properties and film structures of double MgO barrier magnetic tunnel junctions. Appl Phys Lett, 2010, 96: 192507
Heiliger C, Zahn P, Mertig I. Microscopic origin of magnetoresistance. Mater Today, 2006, 9: 46–53
Waldron D, Liu L, Guo H. Ab initio simulation of magnetic tunnel junctions. Nanotechnology, 2007, 18: 424026
Ikeda S, Hayakawa J, Lee Y M, et al. Magnetic tunnel junctions for spintronic memories and beyond. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2007, 54: 991–1002
Velev J P, Dowben P A, Tsymbal E Y, et al. Interface effects in spin-polarized metal/insulator layered structures. Surf Sci Rep, 2008, 63: 400–425
Tsunekawa K, Djayaprawira D D, Nagai M, et al. Giant tunneling magnetoresistance effect in low-resistance CoFeB/MgO(001)/CoFeB magnetic tunnel junctions for read-head applications. Appl Phys Lett, 2005, 87: 072503
Miao G, Chetry K B, Gupta A, et al. Inelastic tunneling spectroscopy of magnetic tunnel junctions based on CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB with Mg insertion layer. J Appl Phys, 2006, 99: 08T305
Moriyama T, Ni C, Wang W G, et al. Tunneling magnetoresistance in (001)-oriented FeCo/MgO/FeCo magnetic tunneling junctions grown by sputtering deposition. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 88: 222503
Read J C, Mather P G, Buhrman R A. X-ray photoemission study of CoFeB/MgO thin film bilayers. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 90: 132503
Cha J J, Read J C, Buhrman R A, et al. Spatially resolved electron energy-loss spectroscopy of electron-beam grown and sputtered CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB magnetic tunnel junctions. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 91: 062516
Lu Y, Deranlot C, Vaurès A, et al. Effects of a thin Mg layer on the structural and magnetoresistance properties of CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB magnetic tunnel junctions. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 91: 222504
Huang J C A, Hsu C Y, Chen W H, et al. Effects of submonolayer Mg on CoFe-MgO-CoFe magnetic tunnel junctions. J Appl Phys, 2008, 104: 073909
Ye L, Lee C, Syu J, et al. Effect of annealing and barrier thickness on MgO-based Co/Pt and Co/Pd multilayered perpendicular magnetic tunnel junctions. IEEE Trans Magn, 2008, 44: 3601–3604
Zhang X G, Butler W H, Bandyopadhyay A. Effects of the iron-oxide layer in Fe-FeO-MgO-Fe tunneling junctions. Phys Rev B, 2003, 68: 092402
Tusche C, Meyerheim H L, Jedrecy N, et al. Oxygen-induced symmetrization and structural coherency in Fe/MgO/Fe(001) magnetic tunnel junctions. Phys Rev Lett, 2005, 95: 176101.
Heiliger C, Zahn P, Yavorsky B Y, et al. Influence of the interface structure on the bias dependence of tunneling magnetoresistance. Phys Rev B, 2005, 72: 180406 (R)
Waldron D, Timoshevskii V, Hu Y, et al. First principles modeling of tunnel magnetoresistance of Fe/MgO/Fe trilayers. Phys Rev Lett, 2006, 97: 226802
Heiliger C, Zahn P, Mertig I. Influence of interface oxidation on the TMR ratio of Fe/MgO/Fe tunnel junctions. J Magn Magn Mater, 2007, 316: 478–480
Matsumoto R, Fukushima A, Yakushiji K, et al. Spin-dependent tunneling in epitaxial Fe/Cr/MgO/Fe magnetic tunnel junctions with an ultrathin Cr(001) spacer layer. Phys Rev B, 2009, 79: 174436
Žutić I, Fabian J, Das Sarma S. Spintronics: Fundamentals and applications. Rev Mod Phys, 2004, 76: 323–410
de Groot R A, Mueller F M, van Engen P G, et al. New class of materials: Half-metallic ferromagnets. Phys Rev Lett, 1983, 50: 2024–2027
Felser C, Fecher G H, Balke B. Spintronics: A challenge for material science and solid-state chemistry. Angew Chem-Int Edit, 2007, 46: 668–699
Ishida S, Fujii S, Kashiwagi S, et al. Search for half-metallic compounds in Co2MnZ (Z=IIIb, IVb, Vb Element). J Phys Soc Jpn, 1995, 64: 2152–2157
Picozzi S, Continenza A, Freeman A J. Co2MnX (X=Si, Ge, Sn) Heusler compounds: An ab initio study of their structural, electronic, and magnetic properties at zero and elevated pressure. Phys Rev B, 2002, 66: 094421
Galanakis I, Dederichs P H, Papanikolaou N. Slater-Pauling behavior and origin of the half-metallicity of the full-Heusler alloys. Phys Rev B, 2002, 66: 174429
Webster P J. Magnetic and chemical order in Heusler alloys containing cobalt and manganese. J Phys Chem Solids, 1971, 32: 1221–1231
Inomata K, Okamura S, Goto R, et al. Large tunneling magnetoresistance at RT using a Heusler alloy with the B2 structure. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2003, 42: L419–L422
Kämmerer S, Thomas A, Hütten A, et al. Co2MnSi Heusler alloy as magnetic electrodes in magnetic tunnel junctions. Appl Phys Lett, 2004, 85: 79–81
Kubota H, Nakata J, Oogane M, et al. Large magnetoresistance in magnetic tunnel junctions using Co-Mn-Al full Heusler alloy. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2004, 43: L984–L986
Marukame T, Kasahara T, Matsuda K-I, et al. Fabrication of fully epitaxial magnetic tunnel junctions using full-Heusler alloy Co2Cr0.6Fe0.4Al thin film and MgO tunnel barrier. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2005, 44: L521–L524
Ishikawa T, Marukame T, Kijima H, et al. Spin-dependent tunneling characteristics of fully epitaxial magnetic tunneling junctions with a full-Heusler alloy Co2MnSi thin film and a MgO tunnel barrier. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 89: 192505
Sakuraba Y, Hattori M, Oogane M, et al. Giant tunneling magnetoresistance in Co2MnSi/Al-O/Co2MnSi magnetic tunnel junctions. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 88: 192508
Tezuka N, Ikeda N, Mitsuhashi F, et al. Improved tunnel magnetoresistance of magnetic tunnel junctions with Heusler Co2FeAl0.5Si0.5 electrodes fabricated by molecular beam epitaxy. Appl Phys Lett, 2009, 94: 162504
Yakushiji K, Saito K, Mitani S, et al. Current-perpendicular-to-plane magnetoresistance in epitaxial Co2MnSi/Cr/Co2MnSi trilayers. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 88: 222504
Furubayashi T, Kodama K, Sukegawa H, et al. Current-perpen-dicular-to-plane giant magnetoresistance in spin-valve structures using epitaxial Co2FeAl0.5Si0.5/Ag/Co2FeAl0.5Si0.5 trilayers. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 93: 122507
Sakuraba Y, Iwase T, Saito K, et al. Enhancement of spin-asymmetry by L21-ordering in Co2MnSi/Cr/Co2MnSi current-perpendicular-to-plane magnetoresistance devices. Appl Phys Lett, 2009, 94: 012511
Nikolaev K, Kolbo P, Pokhil T, et al. All-Heusler alloy current-perpendicular-to-plane giant magnetoresistance. Appl Phys Lett, 2009, 94: 222501
Dong X Y, Adelmann C, Xie J Q, et al. Spin injection from the Heusler alloy Co2MnGe into Al0.1Ga0.9As/GaAs heterostructures. Appl Phys Lett, 2005, 86: 102107
Hickey M C, Damsgaard C D, Farrer I, et al. Spin injection between epitaxial Co2.4Mn1.6Ga and an InGaAs quantum well. Appl Phys Lett, 2005, 86: 252106
Tezuka N, Ikeda N, Sugimoto S, et al. Giant tunnel magnetoresistance at RT for junctions using full-Heusler Co2FeAl0.5Si0.5 electrodes. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2007, 46: L454–L456
Tsunegi S, Sakuraba Y, Oogane M, et al. Large tunnel magnetoresistance in magnetic tunnel junctions using a Co2MnSi Heusler alloy electrode and a MgO barrier. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 93: 112506
Ikeda S, Hayakawa J, Lee Y M, et al. Dependence of tunnel magnetoresistance in MgO based magnetic tunnel junctions on Ar pressure during MgO sputtering. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2005, 44: L1442–L1445
Yamamoto M, Ishikawa T, Taira T, et al. Effect of defects in Heusler alloy thin films on spin-dependent tunnelling characteristics of Co2MnSi/MgO/Co2MnSi and Co2MnGe/MgO/Co2MnGe magnetic tunnel junctions. J Phys-Condes Matter, 2010, 22: 164212
Ishikawa T, Hakamata S, Matsuda K-I, et al. Fabrication of fully epitaxial Co2MnSi/MgO/Co2MnSi magnetic tunnel junctions. J Appl Phys, 2008, 103: 07A919
Ishikawa T, Itabashi N, Taira T, et al. Critical role of interface states for spin-dependent tunneling in half-metallic Co2MnSi-based magnetic tunnel junctions investigated by tunneling spectroscopy. Appl Phys Lett, 2009, 94: 092503
Bonell F, Andrieu S, Tiusan C, et al. Influence of misfit dislocations on the magnetoresistance of MgO-based epitaxial magnetic tunnel junctions. Phys Rev B, 2010, 82: 092405
Liu D P, Han X F, Guo H. Junction resistance, tunnel magnetoresistance ratio, and spin-transfer torque in Zn-doped MTJs. Phys Rev B, 2012, 85: 245436
Sukegawa H, Xiu H, Ohkubo T, et al. Tunnel magnetoresistance with improved bias voltage dependence in lattice-matched Fe/spinel MgAl2O4/Fe(001) junctions. Appl Phys Lett, 2010, 96: 212505
Shan R, Sukegawa H, Wang W, et al. Demonstration of half-metallicity in Fermi-level-tuned Heusler alloy Co2FeAl0.5Si0.5 at RT. Phys Rev Lett, 2009, 102: 246601
Liu H F, Ma Q L, Rizwan S, et al. Tunnel magnetoresistance effect in CoFeB/MgAlO/CoFeB magnetic tunnel junctions. IEEE Trans Magn, 2011, 47: 2716–2719
Mavropoulos P, Papanikolaou N, Dederichs P H. Complex band structure and tunneling through ferromagnet/insulator/ferromagnet junctions. Phys Rev Lett, 2000, 85: 1088–1091
Stewart D A. New type of magnetic tunnel junction based on spin filtering through a reduced symmetry oxide: FeCo/Mg3B2O6/FeCo. Nano Lett, 2010, 10: 263–267
Zhang J, Zhang X G, Han X F. Spinel oxides: Δ1 spin-filter barrier for a class of magnetic tunnel junctions. Appl Phys Lett, 2012, 100: 222401
Wei S H, Zhang S B. First-principles study of cation distribution in eighteen closed-shell AIIB2 IIIO4 and AIVB2 IIO4 spinel oxides. Phys Rev B, 2001, 63: 045112
Mangin S, Ravelosona D, Katine J A, et al. Current-induced magnetization reversal in nanopillars with perpendicular anisotropy. Nat Mater, 2006, 5: 210–215
Meng H, Wang J P. Spin transfer in nanomagnetic devices with perpendicular anisotropy. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 88: 172506
Law R, Sbiaa R, Liew T, et al. Effects of Ta seed layer and annealing on magnetoresistance in CoFe/Pd-based pseudo-spin-valves with perpendicular anisotropy. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 91: 242504
Kishi T, Yoda H, Kai T, et al. Lower-current and fast switching of a perpendicular TMR for high speed and high density spin-transfertorque MRAM. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting. San Francisco, USA, 2008. 309–312
Yoshikawa M, Kitagawa E, Nagase T, et al. Tunnel magnetoresistance over 100% in MgO-based magnetic tunnel junction films with perpendicular magnetic L10-FePt electrodes. IEEE Trans Magn, 2008, 44: 2573–2576
Nakayama M, Kai T, Shimomura N, et al. Spintransfer switching in TbCoFe/CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB/TbCoFe magnetic tunnel junctions with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy. J Appl Phys, 2008, 103: 07A710
Ohmori H, Hatori T, Nakagawa S. Perpendicular magnetic tunnel junction with tunneling magnetoresistance ratio of 64% using MgO(100) barrier layer prepared at RT. J Appl Phys, 2008, 103: 07A911
Kim G, Sakuraba Y, Oogane M, et al. Tunneling magnetoresistance of magnetic tunnel junctions using perpendicular magnetization L10-CoPt electrodes. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 92: 172502
Watanabe D, Mizukami S, Oogane M, et al. Fabrication of MgO-based magnetic tunnel junctions with CoCrPt perpendicularly magnetized electrodes. J Appl Phys, 2009, 105: 07C911
Park J H, Ikeda S, Yamamoto H, et al. Perpendicular magnetic tunnel junctions with CoFe/Pd multilayer electrodes and an MgO barrier. IEEE Trans Magn, 2009, 45: 3476–3479
Mizunuma K, Ikeda S, Park J H, et al. MgO barrier-perpendicular magnetic tunnel junctions with CoFe/Pd multilayers and ferromagnetic insertion layers. Appl Phys Lett, 2009, 95: 232516
Miyajima T, Ibusuki T, Umehara S, et al. Transmission electron microscopy study on the crystallization and boron distribution of CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB magnetic tunnel junctions with various capping layers. Appl Phys Lett, 2009, 94: 122501
Karthik S V, Takahashi Y K, Ohkubo T, et al. Transmission electron microscopy investigation of CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB pseudospin valves annealed at different temperatures. J Appl Phys, 2009, 106: 023920
Ikeda S, Miura K, Yamamoto H, et al. A perpendicular-anisotropy CoFeB-MgO magnetic tunnel junction. Nat Mater, 2010, 9: 721–724
Wang W X, Yang Y, Naganuma H, et al. The perpendicular anisotropy of Co40Fe40B20 sandwiched between Ta and MgO layers and its application in CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB tunnel junction. Appl Phys Lett, 2011, 99: 012502
Sato H, Yamanouchi M, Miura K, et al. Junction size effect on switching current and thermal stability in CoFeB/MgO perpendicular magnetic tunnel junctions. Appl Phys Lett, 2011, 99: 042501
Slonczewski J C. Current-driven excitation of magnetic multilayers. J Magn Magn Mater, 1996, 159: L1–L7
Katine J A, Albert F J, Buhrman R A, et al. Current-driven magnetization reversal and spin-wave excita-tion in Co/Cu/Co pillars. Phys Rev Lett, 2000, 84: 3149–3152
Grollier J, Cros V, Hamzic A, et al. Spin-polarized current induced switching in Co/Cu/Co pillars. Appl Phys Lett, 2001, 78: 3663–3665
Berger L. Emission of spin waves by a magnetic multilayer traversed by a current. Phys Rev B, 1996, 54: 9353–9358
Sun J Z, Monsma D J, Abraham D W, et al. Batch fabricated spin-injection magnetic switches. Appl Phys Lett, 2002, 81: 2202–2204
Rippard W H, Pufall M R, Kaka S, et al. Current-driven microwave dynamics in magnetic point contacts as a function of applied field angle. Phys Rev B, 2004, 70: 100406 (R)
Bazaliy Y B, Jones B A, Zhang S C. Modification of the Landau-Lifshitz equation in the presence of a spin-polarized current in colossal- and giant-magnetoresistive materials. Phys Rev B, 1998, 57: R3213–R3216
Tsoi M, Jansen A G M, Bass J, et al. Excitation of a magnetic multilayer by an electric current. Phys Rev Lett, 1998, 80: 4281–4284; Tsoi M, Jansen A G M, Bass J, et al. Erratum: Excitation of a magnetic multilayer by an electric current. Phys Rev Lett, 1998, 81: 493–493
Sun J Z. Current-driven magnetic switching in manganite trilayer junctions. J Magn Magn Mater, 2009, 202: 157–162
Myers E B, Ralph D C, Katine J A, et al. Current-induced switching of domains in magnetic multilayer devices. Science, 1999, 285: 867–870
Slaughter J M, Dave R W, Durlam M, et al. High speed toggle MRAM with MgO-based tunnel junctions. Technical Digest of IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, Washington DC, USA, 2005. 873–876
Chen E, Apalkov D, Diao Z, et al. Advances and future prospects of spin-transfer torque random access memory. IEEE Trans Magn, 2010, 46: 1873–1878
Nam K-T, Oh S C, Lee J E, et al. Switching properties in spin transper torque MRAM with sub-50 nm MTJ size. Proceedings of IEEE 7th Annual Non-Volatile Memory Technology Symposium. San Mateo: IEEE, 2006. 49–51
Fuchs G D, Katine J A, Kiselev S I, et al. Spin torque, tunnel-current spin polarization, and magnetoresistance in MgO magnetic tunnel junctions. Phys Rev Lett, 2006, 96: 186603
Huai Y M, Apalkov D, Diao Z, et al. Structure, materials and shape optimization of magnetic tunnel junction devices: Spin-transfer switching current reduction for future magnetoresistive random access memory application. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2006, 45: 3835–3841
Diao Z T, Panchula A, Ding Y, et al. Spin transfer switching in dual MgO magnetic tunnel junctions. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 90: 132508
Finocchio G, Consolo G, Carpentieri M, et al. Trends in spin-transfer-driven magnetization dynamics of CoFe/AlO/Py and CoFe/MgO/Py magnetic tunnel junctions. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 89: 262509
Kubota H, Fukushima A, Yakushiji K, et al. Quantitative measuremnet of voltage dependence of spin-trnasfer torque in MgO-based magnetic tunnel junctions, Nat Phys, 2008, 4: 37–41
Deac A M, Fukushima A, Kubota H, et al. Bias-driven high-power microwave emission from MgO-based tunnel magnetoresistance devices. Nat Phys, 2008, 4: 803–809
Helmer A, Cornelissen S, Devolder T, et al. Quantized spin-wave modes in magnetic tunnel junction nanopillars. Phys Rev B, 2010, 81: 094416
Wada T, Yamane T, Seki T, et al. Spin-transfer-torque-induced rf oscillations in CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB magnetic tunnel junctions under a perpendicular magnetic field. Phys Rev B, 2010, 81: 104410
Jung M H, Park S, You C-Y, et al. Bias dependences of in-plane and out-of-plane spin-transfer torques in symmetric MgO-based magnetic tunnel junctions. Phys Rev B, 2010, 81: 134419
Zeng Z M, Cheung K H, Jiang H W, et al. Evolution of spin-wave modes in magnetic tunnel junction nanopillars. Phys Rev B, 2010, 82: 100410 (R)
Worledge D C, Hu G, Abraham D W, et al. Spin torque switching of perpendicular Ta/CoFeB/MgO-based magnetic tunnel junctions. Appl Phys Lett, 2011, 98: 022501
Fukami S, Suzuki T, Nakatani Y, et al. Current-induced domain wall motion in perpendicularly magnetized CoFeB nanowire. Appl Phys Lett, 2011, 98: 082504
Diao Z, Apalkov D, Pakala M, et al. Spin transfer switching and spin polarization in magnetic tunnel junctions with MgO and AlOx barriers. Appl Phys Lett, 2005, 87: 232502
Takahashi S, Maekawa S. Effect of coulomb blockade on magnetoresistance in ferromagnetic tunnel junctions. Phys Rev Lett, 1998, 80: 1758–1761
Barnas J, Weymann I. Spin effects in single-electron tunneling. J Phys-Condes Matter, 2008, 20: 423202
Zhang X G, Wen Z C, Wei H X, et al. Giant Coulomb blockade magnetoresistance in magnetic tunnel junctions with a granular layer. Phys Rev B, 2010, 81: 155122
Weisheit M, Fähler S, Marty A, et al. Electric field-induced modification of magnetism in thin-film ferromagnets. Science, 2007, 315: 349–351
Endo M, Kanai S, Ikeda S, et al. Electric-field effects on thickness dependent magnetic anisotropy of sputtered MgO/Co40Fe40B20/Ta structures. Appl Phys Lett, 2010, 96: 212503
Chiba D, Chiba D, Fukami S, et al. Electrical control of the ferromagnetic phase transition in cobalt at RT. Nat Mater, 2011, 10: 853–856
Chu Y H, Chu Y H, Martin L W, et al. Electric-field control of local ferromagnetism using a magnetoelectric multiferroic. Nat Mater, 2008, 7: 478–482
Maruyama T, Shiota Y, Nozaki T, et al. Large voltage-induced magnetic anisotropy change in a few atomic layers of iron. Nat Nanotechnol, 2009, 4: 158–161
Ha S S, Kim B H, Lee S, et al. Voltage induced magnetic anisotropy change in ultrathin Fe80Co20/MgO junctions with Brillouin light scattering. Appl Phys Lett, 2010, 96: 142512
Shiota Y, Maruyama T, Nozaki T, et al. Voltage-assisted magnetization switching in ultrathin Fe80Co20 alloy layers. Appl Phys Express, 2009, 2: 063001
Nozaki T, Shiota Y, Shiraishi M, et al. Voltage-induced perpendicular magnetic anisotropy change in magnetic tunnel junctions. Appl Phys Lett, 2010, 96: 022506
Wang W G, Li M G, Hageman S, et al. Electric-field-assisted switching in magnetic tunnel junctions. Nat Mater, 2012, 11: 64–68
Meng H, Sbiaa R, Akhtar M A K, et al. Electric field effects in low resistance CoFeB-MgO magnetic tunnel junctions with perpendicular anisotropy. Appl Phys Lett, 2012, 100: 122405
Bauer G E W, MacDonald A H, Maekawa S, et al. Spin caloritronics. Solid State Commun, 2010, 150: 459–552
Bauer G E W. Spin caloritronics. Nat Mater, 2012, 11: 391–399
Uchida K, Takahashi S, Harii K, et al. Observation of the spin Seebeck effect. Nature, 2008, 455: 778–781
Uchida K, Xiao J, Adachi H, et al. Spin seebeck insulator. Nat Mater, 2010, 9: 894–897
Jaworski C M, Yang J, Mack S, et al. Observation of the spin-Seebeck effect in a ferromagnetic. Nat Mater, 2010, 9: 898–903
Huang S Y, Wang W G, Lee S F, et al. Intrinsic spin-dependent thermal transport. Phys Rev Lett, 2011, 107: 216604
Jansen R, Deac A M, Saito H, et al. Thermal spin current and magnetothermopower by Seebeck spin tunneling. Phys Rev B, 2012, 85: 094401
Lin W W, Hehn M, Chaput L, et al. Giant spin-dependent thermoelectric effect in magnetic tunnel. Nat Commun, 2012, 3: 744
Flipse J, Bakker F L, Slachter A, et al. Direct observation of the spin-dependent Peltier effect. Nat Nanotechnol, 2012, 7: 166–168
Czerner M, Bachmann M, Heiliger C, et al. Spin caloritronics in magnetic tunnel junctions: Ab initio studies. Phys Rev B, 2011, 83: 132405
Jia X T, Xia K, Bauer G E W, et al. Thermal spin transfer in Fe-MgO-Fe tunnel junctions. Phys Rev Lett, 2011, 107: 176603
Walter M, Walowski J, Zbarsky V, et al. Seebeck effect in magnetic tunnel junctions. Nat Mater, 2011, 10: 742–746
Liebing N, Serrano-Guisan S, Rott K, et al. Tunneling magnetothermopower in magnetic tunnel junction nanopillars. Phys Rev Lett, 2011, 107: 177201
Liebing N, Serrano-Guisan S, Rott K, et al. Determination of spin-dependent Seebeck coefficients of CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB magnetic tunnel junction nanopillars. J Appl Phys, 2012, 111: 07C520
Bosu S, Sakuraba Y, Uchida K, et al. Spin Seebeck effect in thin films of the Heusler compound Co2MnSi. Phys Rev B, 2011, 83: 224401
Grancharov S G, Zeng H, Sun S, et al. Bio-functionalization of monodisperse magnetic nanoparticles and their use as biomolecular labels in a magnetic tunnel junction based sensor. J Phys Chem B, 2005, 109: 13030–13035
Cardoso F A, Ferreira H A, Conde J P, et al. Diode/magnetic tunnel junction cell for fully scalable matrix-based biochip. J Appl Phys, 2006, 99: 08B307
Shen W, Schrag B D, Carter M J, et al. Detection of DNA labeled with magnetic nanoparticles using MgO-based magnetic tunnel junction sensors. J Appl Phys, 2008, 103: 07A306
Chen J Y, Feng J F, Coey J M D. Tunable linear magnetoresistance in MgO magnetic tunnel junction sensors using two pinned CoFeB electrodes. Appl Phys Lett, 2012, 100: 142407
Shen W, Schrag B D, Carter M J, et al. Quantitative detection of DNA labeled with magnetic nanoparticles using arrays of MgO-based magnetic tunnel junction sensors. Appl Phys Lett, 2005, 93: 033903
Chaves R C, Freitas P P, Ocker B, et al. MgO based picotesla field sensors. J Appl Phys, 2008, 103: 07E931
Duan H, Tseng H W, Li Y, et al. Improvement of the low-frequency sensitivity of MgO-based magnetic tunnel junctions by annealing. J Appl Phys, 2011, 109: 113917
Martins V C, Germano J, Cardoso F A, et al. Challenges and trends in the development of a magnetoresistive biochip portable platform. J Magn Magn Mater, 2010, 322: 1655–1663
Ma Q L, Liu H F, Han X F. Fabrication methods and application of magnetic multi layers in linear magnetic sensors. PCT Patent, 2011/150665, 2011-12-08
Wu H, Feng J F, Chen J Y, et al. Fabrication methods and application of magnetic multi layers in magnetic sensors. PRC Patent, 201210285542.
Lei Z Q, Li L, Li G J, et al. Liver cancer immunoassay with magnetic nanoparticles and MgO-based magnetic tunnel junction sensors. J Appl Phys, 2012, 111: 07E505
Kawahara T, Takemura R, Miura K, et al. 2 Mb SPRAM (SPin-transfer torque RAM) with bit-by-bit bi-directional current write and parallelizing-direction current read. IEEE J Solid-State Circuit, 2008, 43: 109–120
Zhu J G. Magnetoresistive random access memory: The path to com-petitiveness and scalability. Proc IEEE, 2008, 96: 1786–1798
Katine J A, Fullerton E E. Device implications of spin-transfer torques. J Magn Magn Mater, 2008, 320: 1217–1226
Sbiaa R, Meng H, Piramanayagam S N. Materials with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy for magnetic random access memory. Phys Status Solidi-Rapid Res Lett, 2001, 5: 413–419
Han X F, Wen Z C, Wei H X. Nanoring magnetic tunnel junction and its application in magnetic random access memory demo devices with spin-polarized current switching (invited). J Appl Phys, 2008, 103: 07E933
Wei H X, He J X, Wen Z C, et al. Effects of current on nanoscale ring-shaped magnetic tunnel junctions. Phys Rev B, 2008, 77: 134432
Wei H X, Hickey M C, Anderson G I R, et al. Current-induced magnetization switching in a microscale ring-shaped MTJ. Phys Rev B, 2008, 77: 132401
Wen Z C, Wang Y, Yu G Q, et al. Patterned nanoscale magnetic tunnel junctions with differenct geometry structures. Spin, 2011, 1: 109–114
Han X F, Wen Z C, Wang Y, et al. Nanoelliptic ring-shaped magnetic tunnel junction and its application in MRAM design with spinpolarized current switching. IEEE Trans Magn, 2011, 47: 2957–2961
Kiselev S I, Sankey J C, Krivorotov I N, et al. Microwave oscillations of a nanomagnet driven by a spin-polarized current. Nature, 2003, 425: 380–383
Rippard W H, Pufall M R, Kaka S, et al. Direct-current induced dynamics in Co90Fe10/Ni80Fe20 point contacts. Phys Rev Lett, 2004, 92: 027201
Kaka S, Pufall M R, Rippard W H, et al. Mutual phase-locking of microwave spin torque nano-oscillators. Nature, 2005, 437: 389–392
Mancof F B, Rizzo N D, Engel B N, et al. Phase-locking in double-point-contact spin-transfer devices. Nature, 2005, 437: 393–395
Ruotolo A, Cros V, Georges B, et al. Phase-locking of magnetic vortices mediated by antivortices. Nature Nanotechnol, 2009, 4: 528–532
Georges B, Grollier J, Cros V, et al. Impact of the electrical connection of spin transfer nano-oscillators on their synchronization: an analytical study. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 92: 232504
Georges B, Grollier J, Darques M, et al. Coupling efficiency for phase locking of a spin transfer oscillator to a microwave current. Phys Rev Lett, 2008, 101: 017201
Georges B, Grollier J, Cros V, et al. Origin of the spectral linewidth in non linear spin transfer oscillators based on MgO tunnel junctions. Phys Rev B, 2009, 80: 060404 (R)
Dussaux A, Georges B, Grollier J, et al. Large microwave generation from current-driven magnetic vortex oscillators in magnetic tunnel junctions. Nat Commun, 2010, 1: 8
Katsoprinakis G E, Katsoprinakis G E, Polis M, et al. Quantum random number generator based on spin noise. Phys Rev A, 2008, 77: 054101
Seagate Technology LLC. Magnetic precession based true random number generator. US Patent, 2010/0174, 766, 2010-07-08
Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba. Random number generator. US Patent, 2012/0026, 784, 2012-02-22
Wolf S A, Awschalom D D, Buhrman R A, et al. Spintronics: A spin-based electronics vision for the future. Science, 2001, 294: 1488–1495
Nikonov D E, Bourianoff G I, Gargini P A. Power dissipation in spintronic devices out of thermodynamic equilibrium. J Supercond Nov Magn, 2006, 19: 497–513
Datta S, Das B. Electronic analog of the electro-optic modulator. Appl Phys Lett, 1990, 56: 665–667
Behin-Aein B, Salahuddin S, Datta S. Switching energy of ferromagnetic logic bits. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol, 2009, 8: 505–514
Johnson M. Bipolar spin switch. Science, 1993, 260: 320–323
Monsma D J, Lodder J C, Popma T J A, et al. Perpendicular hot rlectron spin-valve effect in a new magnetic field sensor: The spin-valve transistor. Phys Rev Lett, 1995, 74: 5260–5263
Dijken S van, Jiang C, Parkin S S P, et al. Room temperature operation of a high output current magnetic tunnel transistor. Appl Phys Lett, 2002, 80: 3364–3366
Sugahara S, Tanaka M. A spin metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor using half-metallic-ferromagnet contacts for the source and drain. Appl Phys Lett, 2004, 84: 2307–2309
Sugahara S. Spin metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (spin MOSFETs) for integrated spin electronics. IEE Proc Circuits Devices Syst, 2005, 152: 355–365
Shuto Y, Nakane R, Wang W H, et al. A new spin-functional metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor based on magnetic tunnel junction technology: Pseudo-spin-MOSFET. Appl Phys Express, 2010, 3: 013003
Chua L O. Memristor—The missing circuit element. IEEE Trans Circuit Theory, 1971, CT18: 507–519
Strukov D B. The missing memristor found. Nature, 2008, 453: 80–83
Krzysteczko P. Memristive switching of MgO based magnetic tunnel junctions. Appl Phys Lett, 2009, 95: 112508
Slaughter J M, Rizzo N D, Janesky J, et al. High density ST-MRAM technology. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Electron Device Meeting. San Francisco, USA, 2012
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, X., Ali, S.S. & Liang, S. MgO(001) barrier based magnetic tunnel junctions and their device applications. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 56, 29–60 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-012-4977-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-012-4977-1