Abstract
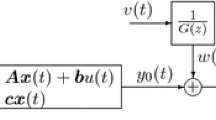
Identification of the Wiener system composed of an infinite impulse response (IIR) linear subsystem followed by a static nonlinearity is considered. The recursive estimates for unknown coefficients of the linear subsystem and for the values of the nonlinear function at any fixed points are given by the stochastic approximation algorithms with expanding truncations (SAAWET). With the help of properties of the Markov chain connected with the linear subsystem, all estimates derived in the paper are proved to be strongly consistent. In comparison with the existing results on the topic, the method presented in the paper simplifies the convergence analysis and requires weaker conditions. A numerical example is given, and the simulation results are consistent with the theoretical analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhu Y. Distillation column identification for control using Wiener model. In: Proceedings of American Control Conference, San Diego, 1999. 55: 3462–3466
Kalafatis A, Arifin N, Wang L, et al. A new approach to the identification of pH processes based on the Wiener model. Chem Eng Sci, 1995, 50: 3693–3701
Hunter I W, Korenberg M J. The identification of nonlinear biological systems: Wiener and Hammerstein cascade models. Bio Cybern, 1986, 55: 136–144
Bai E W. Frequency domain identification of Wiener models. Automatica, 2003, 39: 1521–1530
Boyd S, Chua L O. Fading memory and the problem of approximating nonlinear operators with Volterra series. IEEE Trans Circ Syst, 1985, 32: 1150–1161
Chen H F. Recursive identification for Wiener model with discontinuous piece-wise linear function. IEEE Trans Autom Control, 2006, 51: 390–400
Greblicki W. Nonparametric approach to Wiener system identification. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst-I: Fundam Theory Appl, 1997, 44: 538–545
Hagenblad A, Ljung L, Wills A. Maximum likelihood identification of Wiener models. Automatica, 2008, 44: 2697–2705
Hu X L, Chen H F. Strong consistence of recursive identification forWiener systems. Automatica, 2005, 41: 1905–1916
Hu X L, Chen H F. Identification for Wiener systems with RTF subsystems. European J Control, 2006, 6: 581–594
Nordsjö A E, Zetterberg L H. Identification of certain time-varying nonlinear Wiener and Hammerstein systems. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2001, 49: 577–592
Verhaegen M, Westwick D. Identifying MIMO Wiener systems in the context of subspace model identificatin methods. Int J Control, 1996, 63: 331–349
Vörös J. Parameter identification of Wiener systems with discontinuous nonlinearities. Syst Control Lett, 2001, 44: 363–372
Wigren T. Convergence analysis of recursive algorithms based on the nonlinear Wiener model. IEEE Trans Autom Control, 1994, 39: 2191–2206
Chen H F, Guo L. Identification and Stochastic Adaptive Control. Boston: Birkhäuser, 1991
Fan J Q, Yao Q. Nonlinear Time Series: Nonparametric and Parametric Approach. New York: Springer-Verlag, 2003
Ljung L. System Identification: Theory for Users. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall, 1987
Zhao W X, Chen H F, Zheng W X. Recursive identification for nonlinear ARX systems based on stochastic approximation algorithm. IEEE Trans Autom Control, 2010, 55: 1287–1299
Bussgang J J. Crosscorrelation functions of amplitude-distorted Gaussian signals. Technical Report 216. MIT Research Laboratory of Electronics, 1952
Song Q J, Chen H F. Identification of errors-in-variables systems with ARMA observation noise. Syst Control Lett, 2008, 57: 420–424
Ciarlet P G. Introduction to Numerical Linear Algebra and Optimisation. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1989
Meyn S P, Tweedie R L. Markov Chains and Stochastic Stability. London: Springer-Verlag, 1993
Davydov Yu A. Mixing conditions for Markov chains. SIAM Probability Appl, 1973, 18: 312–328
Nummelin E. General Irreducible Markov Chains and Non-negative Operators. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1984
Tong H. Nonlinear Time Series. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1990
Masry E, Györfi L. Strong consistency and rates for recursive probability density estimators of stationary processes. J Multivariate Analysis, 1987, 22: 79–93
Chen H F. Stochastic Approximation and Its Applications. Dordrecht: Kluwer, 2002
Song Q J, Chen H F. Identification of Wiener systems with internal noise. J Syst Sci Complex, 2008, 21: 378–393
Hirschman I I, Widder D V. The Convolution Transform. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 1955
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, W., Chen, H. Markov chain approach to identifying Wiener systems. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 55, 1201–1217 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-012-4582-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-012-4582-y