Abstract
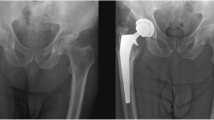
Heterotopic bone (HO), a rare association with total hip arthroplasty (THA), has recently been shown to be more of a problem with resurfacing hip arthroplasty (RHA). It has been speculated to be the result of greater soft tissue dissection required for this procedure. HO most commonly develops in males and patients with bilateral disease. To better understand if this problem does occur in RHA, groups of patients with RHA on one side and conventional THA on the other were evaluated. We retrospectively identified 45 patients that had RHA on one side and conventional cemented THA on the other. Follow-up has been up to 25 years. HO was graded at every clinical visit using the Brooker Classification. In the RHA group, there were 32 hips without evidence of HO, ten with grade 1, and three with grades 2 or 3. In the THA group, there were 36 hips without any HO, eight with grade 1, and one with grade 2. There was no statistical difference between either types of hip arthroplasty in HO formation overall or in the development of more severe grades. Motion was not significantly affected with the more severe grades. Our data obtained from a bilateral patient model suggests that RHA does not predispose to a greater development of HO. In doing a RHA, one should be aware that there might be an increased likelihood of HO in males with bilateral disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahrengart L, Periarticular heterotopic ossification after total hip arthroplasty. Risk factors and consequences. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1991; 263: 49–58
Ahrengart L, Lindgren U, Heterotopic bone after hip arthroplasty. Defining the patient at risk. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1993; 293: 153–159
Neal B, Gray H, MacMahon S, Dunn L, Incidence of heterotopic bone formation after major hip surgery. ANZ J. Surg. 2002; 7211: 808–821
Bischoff R, Dunlap J, Carpenter L, DeMouy E, Barrack R, Heterotopic ossification following uncemented total hip arthroplasty. Effect of the operative approach. J. Arthroplast. 1994; 9: 641–644
Rama KR, Vendittoli PA, Ganapathi M, Borgmann R, Roy A, Lavigne M, Heterotopic ossification after surface replacement arthroplasty and total hip arthroplasty: a randomized study. J. Arthroplast. 2009; 24: 256–262
Ritter MA, Vaughan RB, Ectopic ossification after total hip arthroplasty. Predisposing factors, frequency, and effect on results. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1977; 59: 345–351
Ritter MA, Gioe TJ, Conventional versus resurfacing total hip arthroplasty. A long-term prospective study of concomitant bilateral implantation of prostheses. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1986; 68: 216–225
Amstutz HC, Thomas BJ, Jinnah R, Kim W, Grogan T, Yale C, Treatment of primary osteoarthritis of the hip. A comparison of total joint and surface replacement arthroplasty. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1984; 66: 228–241
Treacy RB, McBryde CW, Pynsent PB, Birmingham hip resurfacing arthroplasty. A minimum follow-up of five years. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 2005; 87(2): 167–170
Grigoris P, Roberts P, Panousis K, Bosch H, The evolution of hip resurfacing arthroplasty. Orthop. Clin. North Am. 2005; 36: 125–134, vii
Grecula MJ, Resurfacing arthroplasty in osteonecrosis of the hip. Orthop. Clin. North Am. 2005; 36: 231–242, x
Wagner H, Surface replacement arthroplasty of the hip. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1978; 134: 102–130
Brooker AF, Bowerman JW, Robinson RA, Riley LH, Jr, Ectopic ossification following total hip replacement. Incidence and a method of classification. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1973; 55: 1629–1632
Capello WN, Ireland PH, Trammell TR, Eicher P, Conservative total hip arthroplasty: a procedure to conserve bone stock. Part I: analysis of sixty-six patients. Part II: analysis of failures. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1978; 134: 59-74
Riegler HF, Harris CM, Heterotopic bone formation after total hip arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1976; 117: 209–216
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Each author certifies that he or she has no commercial associations (e.g., consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc.) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Each author certifies that his or her institution has approved the reporting of these cases, that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research, and that informed consent for participating in the study was obtained.
Level of Evidence:
Level III: Therapeutic Study: Retrospective Review with Comparative Group.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ritter, M.A., Galley, M. Heterotopic Bone Formation Following Resurfacing Total Hip Arthroplasty. HSS Jrnl 7, 41–43 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11420-010-9163-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11420-010-9163-2