Abstract
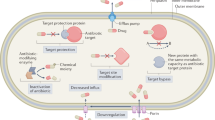
Since 1944, we have come a long way using aminoglycosides as antibiotics. Bacteria also have got them selected with hardier resistance mechanisms. Aminoglycosides are aminocyclitols that kill bacteria by inhibiting protein synthesis as they bind to the 16S rRNA and by disrupting the integrity of bacterial cell membrane. Aminoglycoside resistance mechanisms include: (a) the deactivation of aminoglycosides by N-acetylation, adenylylation or O-phosphorylation, (b) the reduction of the intracellular concentration of aminoglycosides by changes in outer membrane permeability, decreased inner membrane transport, active efflux, and drug trapping, (c) the alteration of the 30S ribosomal subunit target by mutation, and (d) methylation of the aminoglycoside binding site. There is an alarming increase in resistance outbreaks in hospital setting. Our review explores the molecular understanding of aminoglycoside action and resistance with an aim to minimize the spread of resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akram M., Shahid M. and Khan A.U., Etiology and antibiotic resistance patterns of community-acquired urinary tract infections in J N M C Hospital Aligarh, India. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 6: 4, 2007
Khan A.U., Musharraf A. (2004) Plasmid-mediated multiple antibiotic resistance in Proteus mirabilis isolated from patients with urinary tract infection. Med. Sci. Monit. 10:CR598–602
Marra A.R., Wey S.B., Castelo A. et al., Nosocomial bloodstream infections caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae: impact of extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) production on clinical outcome in a hospital with high ESBL prevalence.␣BMC Infect. Dis. 6: 24 doi:10.1186/1471-2334-6-24, 2006
Liou G.F., Yoshizawa S., Courvalin P., Galimand M. (2006) Aminoglycosides resistance by ArmA-mediated ribosomal 16S methylation in human bacterial pathogens. J. Mol. Biol. 359:358–364
Kotra L.P., Haddad J., Mobashery S. (2000) Aminoglycoside: perspectives on mechanisms of action and resistance and strategies to counter resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 44:3249–3256
Magnet S., Blanchard J.S. (2005) Molecular insights into aminoglycoside action and resistance. Chem. Rev. 105:477–497
Nikaido H. (2003) Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability revisited. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 67:593–656
Taber H.W., Mueller J.P., Miller P.F., Arrow A.S. (1987) Bacterial uptake of aminoglycoside antibiotics. Microbiol. Rev. 51:439–457
Magnet S., Courvalin P., Lambert T. (2001) Resistance-nodulation-cell division-type efflux pump involved in aminoglycoside resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii strain BM4454. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 45:3375–3380
Moore R.A., DeShazer D., Reckseidler S., Weissman A., Woods D.E. (1999) Efflux-mediated aminoglycoside and macrolide resistance in Burkholderia pseudomallei. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 43:465–470
Magnet S., Smith T.A., Zheng R., Nordmann P., Blanchard J.S. (2003) Aminoglycoside resistance resulting from tight drug binding to an altered aminoglycoside acetyltransferase. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 47:1577–1583
Menard R., Molinas C., Arthur M., Duval J., Courvalin P., Leclercq R. (1993) Overproduction of 3′-aminoglycoside phosphotransferase type I confers resistance to tobramycin in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 37:78–83
Musser J.M. (1995) Antimicrobial agent resistance in mycobacteria: molecular genetic insights. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 8:496–514
Skeggs P.A., Thompson J., Cundliffe E. (1985) Methylation of 16 S ribosomal RNA and resistance to aminoglycoside antibiotics in clones of Streptomyces lividans carrying DNA from Streptomyces tenjimariensis. Mol. Gen. Genet. 200:415–421
Cundliffe E. (1989) How antibiotic-producing organisms avoid suicide. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 43:207–233
Thompson J., Skeggs P.A., Cundliffe E. (1985) Methylation of 16 S ribosomal RNA and resistance to the aminoglycoside antibiotics gentamicin and kanamycin determined by DNA from the gentamicin producer, Micromonospora purpurea. Mol. Gen. Genet. 201:168–173
Gilbert D.N. (1985) Aminoglycosides. In: Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R, (eds). Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 4th ed. Churchill Livingstone, New York, NY, pp. 279–306
Mingeot-Leclercq M.P., Glupczynski Y., Tulkens P.M. (1999) Aminoglycosides: activity and resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 43:727–737
Sakon J., Liao H.H., Kanikula A.M., Benning M.M., Rayment I., Holden H.M. (1993) Molecular structure of kanamycin nucleotidyl transferase determined to 3 Å resolution. Biochemistry 32:11977–11984
Wybenga-Groot L.E., Draker K., Wright G.D., Berghuis A.M. (1999) Crystal structure of an aminoglycoside 6’-N-acetyltransferase: defining the GCN5-related N-acetyltransferase superfamily fold. Struct. Fold. Des. 7:497–507
Burk D.L., Hon W.C., Leung A.K., Berghuis A.M. (2001) Structural analyses of nucleotide binding to an aminoglycoside phosphotransferase. Biochemistry 40:8756–8764
Spelman D.W., McDonald M., Spice W.J. (1989) Aminoglycoside antibiotic agents: a review. Therapeutics 151:346–349
Hancock R.E., Farmer S.W., Li Z.S., Poole K. (1991) Interaction of aminoglycosides with the outer membranes and purified lipopolysaccharide and OmpF porin of E.␣coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 35:1309–1314
Bryan L.E., Kwan S. (1983) Roles of ribosomal binding, membrane potential, and electron transport in bacterial uptake of streptomycin and gentamicin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 23:835–845
Ban N., Nissen P., Hansen J., Moore P.B., Steitz T.A. (2000) The complete atomic structure of the large ribosomal subunit at 2.4 Å resolution. Science 289:905–920
Fourmy D., Yoshizawa S., Puglisi J.D. (1998) Paromomycin binding induces a local conformational change in the A-site of 16 S rRNA. J. Mol. Biol. 277:333–345
Noller H.F. (1991) Ribosomal RNA and translation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 60:191–227
Fourmy D., Recht M.I., Blanchard S.C., Puglisi J.D. (1996) Structure of the A-site of E.␣coli. 16 S rRNA complexed with an aminoglycoside antibiotic. Science 274:1367–1371
Recht M.I., Fourmy D., Blanchard S.C., Dahlquist K.D., Puglisi J.D. (1996) RNA sequence determinants for aminoglycoside binding to an A-site rRNA model oligonucleotide. J. Mol. Biol. 262:421–436
Cate J.H., Yusupov M.M., Yusupova G.Z., Earnest T.E., Noller H.F. (1999) X-ray crystal structure of 70S ribosome functional complexes. Science 285:2095–2104
Jiang L., Patel D.J. (1998) Solution structure of the tobramycin-RNA aptamer complex. Nat. Struct. Biol. 5:769–774
Xi H., Arya D.P. (2005) Recognition of triple helical nucleic acids by aminoglycosides. Curr. Med. Chem. Anticancer Agents 5:327–338
Hermann T., Westhoff E. (1998) Saccharide-RNA recognition. Biopolymers 48:155–165
Recht M.I., Douthwaite S., Puglisi J.D. (1999) Basis for prokaryotic specificity of action of aminoglycoside antibiotics. EMBO J 18:3133–3138
Michael K., Wang H., Tor Y. (1999) Enhanced RNA binding of dimerized aminoglycosides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 7:1361–1371
Welch K.T., Virga K.G., Whittemore N.A., Ozen C., Wright E., Brown C.L., Lee R.E., Serpersu E.H. (2005) Discovery of non-carbohydrate inhibitors of aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 13:6252–6363
Cho J., Hamasaki K., Rando R.R. (1998) The binding site of a specific aminoglycoside binding RNA molecule. Biochemistry 37:4985–4992
Pilch D.S., Kaul M., Barbieri C.M. (2005) Defining the basis for the specificity of aminoglycoside–rRNA recognition: a comparative study of drug binding to the A sites of Escherichia coli and human rRNA. J. Mol. Biol. 346:119–134
Hayashi S.F., Norcia L.J., Seibel S.B., Silvia A.M. (1997) Structure activity relationships of hygromycin A and its analogs: protein synthesis inhibition activity in a cell free system. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 50:514–521
Hotta K., Zhu C.B., Ogata T., Sunada A., Ishikawa J., Mizuno S., Kondo S. (1996) Enzymatic 2’-N-acetylation of arbekacin and antibiotic activity of its product. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 49:458–464
Shaw K.J., Rather P.N., Hare R.S., Miller G.H. (1993) Molecular genetics of aminoglycoside resistance genes and familial relationships of the aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes. Microbiol. Rev. 57:138–163
Llano-Sotelo B., Azucena E.F., Kotra L.P., Mobashery S., Chow C.S. (2002) Aminoglycosides modified by resistance enzymes display diminished binding to the bacterial ribosomal aminoacyl-tRNA site. Chem. Biol. 9:455–463
Mingeot-Leclercq M.-P., Glupczynski Y., Tulkens P.M. (1999) Aminoglycosides: activity and resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 43:727–737
Vakulenko S.B., Donabedian S.M., Voskresenskiy A.M., Zervos M.J., Lerner S.A., Chow J.W. (2003) Multiplex PCR for detection of aminoglycoside resistance genes in enterococci. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 47(4):1423–1426
Zarrilli R., Tripodi M., Di Popolo A. et al. (2005) Molecular epidemiology of high-level amino glycoside-resistant enterococci isolated from patients in a university hospital in southern Italy. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 56:827–835
Ahmed A.M., Shimamoto T. (2004) A plasmid-encoded class 1 integron carrying sat, a putative phosphoserine phosphatase gene and aadA2 from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli O159 isolated in Japan. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 235:243–248
Rather P.N., Munayyer H., Mann P.A., Hare R.S., Miller G.H., Shaw K.J. (1992) Genetic analysis of bacterial acetyltransferases: identification of amino acids determining the specificities of the aminoglycoside 69-Nacetyltransferase-Ib and IIa proteins. J. Bacteriol. 174:3196–3203
Wu H.Y., Miller G.H., Blanco M.G, Hare RS, Shaw K.J. (1997) Cloning and characterization of an aminoglycoside 69-N-acetyltransferase gene from Citrobacter freundii which confers an altered resistance profile. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 41:2439–2447
Aires J.R., Kohler T., Nikaido H., Plesiat P. (1999) Involvement of an active efflux system in the natural resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to aminoglycosides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 43:2624–2628
Masuda N., Sakagawa E., Ohya S., Gotoh N., Tsujimoto H., Nishino T. (2000) Substrate specificities of MexAB-OprM, MexCD-OprJ, and MexXY-OprM efflux pumps in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 44:3322–3327
Westbrock-Wadman S., Sherman D.R., Hickey M.J. et al. (1999) Characterization of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa efflux pump contributing to aminoglycoside impermeability. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 43:2975–2983
Livermore D.M. (2002) Multiple mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: our worst nightmare? Clin. Infect. Dis. 34:634–640
Poole K. (2005) Efflux-mediated antimicrobial resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 56:20–51
Maravic G. (2004) Macrolide resistance based on the Erm-mediated rRNA methylation. Curr. Drug Targets Infect. Disord. 4:193–202
Doi Y., Yokoyama K., Yamane K. et al. (2004) Plasmid-mediated 16S rRNA methylase in Serratia marcescens conferring highlevel resistance to aminoglycosides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 48:491–496
Galimand M., Sabtcheva S., Courvalin P., Lambert T. (2005) Worldwide disseminated armA aminoglycoside resistance methylase gene is borne by composite transposon Tn1548. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 49:2949–2953
Chow J.W. (2000) Aminoglycoside resistance in enterococci. Clin. Infect. Dis. 31:586–599
Lester C.H., Frimodt-Moller N., Hammerum A.M. (2004) Conjugal transfer of aminoglycoside and macrolide resistance between Enterococcus faecium isolates in the intestine of streptomycin-treated mice. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 235:385–389
Tomita H., Pierson C., Lim S.K., Clewell D.B., Ike Y. (2002) Possible connection between a widely disseminated conjugative gentamicin resistance (pMG1-like) plasmid and the emergence of vancomycin resistance in Enterococcus faecium. J. Clin. Microbiol. 40:3326–3333
Udo E.E., Al-Sweih N., John P., Jacob L.E., Mohanakrishnan S. (2004) Characterization of high-level aminoglycoside-resistant enterococci in Kuwait hospitals. Microb. Drug Resist. 10:139–145
Campo R.D., Ruiz-Garbajosa P., Sanchez-Moreno M.P. et al. (2003) Antimicrobial resistance in recent fecal enterococci from healthy volunteers and food handlers in Spain: genes and phenotypes. Microb. Drug Resist. 9:47–60
Donabedian S.M., Thal L.A., Hershberger E. et al. (2003) Molecular characterization of gentamicin-resistant enterococci in the United States: evidence of spread from animals to humans through food. J. Clin. Microbiol. 41:1109–1113
Rybak L.P., Whitworth C.A. (2005) Ototoxicity: therapeutic opportunities. Drug Discov. Today 10:1313–1321
Rougier F., Claude D., Maurin M., Maire P. (2004) Aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity. Curr. Drug Targets 4:153–162
Peloquin C.A., Berning S.E., Nitta A.T., Simone P.M., Goble M., Huitt G.A., Iseman M.D., Cook J.L., Curran-Everett D. (2004) Aminoglycoside toxicity: daily versus thrice weekly dosing for treatment of mycobacterial diseases. Clin. Infect. Dis. 38:1538–1544
Magnet S., Blanchard J.S. (2005) Molecular insights into aminoglycoside action and resistance. Chem. Rev. 105:477–497
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shakil, S., Khan, R., Zarrilli, R. et al. Aminoglycosides versus bacteria – a description of the action, resistance mechanism, and nosocomial battleground. J Biomed Sci 15, 5–14 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11373-007-9194-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11373-007-9194-y