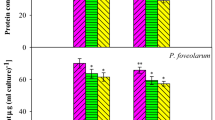
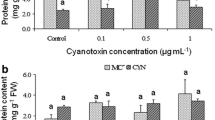
Abstract
The presence of cyanotoxins, mainly microcystins (MCs), in surface freshwater represents a serious health risk to aquatic organisms living in the water body, as well as terrestrial animals and plants that are in contact with contaminated water. Consequently, the use of MCs contaminated water for irrigation represents a hazard for cultivated plants and could induce severe economical losses due to crops’ yield reduction. The experimental approach undertaken in this work was exposing Vicia faba seedlings (inoculated with a Rhizobium strain resistant to MCs), to water supplemented with cyanobacterial crude extract containing total microcystins at a concentration of 50 and 100 μg/L (environmental relevant concentrations of MCs dissolved in the raw irrigation water from Lalla Takerkoust Lake-Marrakesh region). After chronic MCs exposure (2 months), biological and physiological parameters (plant growth, nitrogen uptake, mineral assimilation, and oxidative defense mechanisms) were evaluated. The results obtained showed evidence that chronic exposure to cyanobacterial bloom extract containing MCs strongly affected the physiological and biological plants activities; reduction of dry matter, photosynthetic activity, nodule number, and nitrogen assimilation. At the same time, an increase of oxidative stress was observed, as deduced from a significant increase of the activities of peroxidase, catalase, polyphenoloxidase, and phenylalanine ammonia lyase in leaves, roots, and nodules of faba bean plants exposed to cyanotoxins, especially at 100 μg/L of MCs. This experimentation constitutes a simulation of the situation related to cyanotoxins chronic exposure of seedlings—plants via the contaminated irrigation water. For this reason, once should take into consideration the possibility of contamination of agricultural crops and the quality of irrigation water should be by the way monitored for cyanotoxins biohazard.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- Fv/Fm:
-
Ratio of variable to maximum fluorescence–the quantum efficiency of open photosystem II centers
- Fm:
-
Maximum fluorescence
- F0:
-
Minimum fluorescence yield
- HPLC-PDA:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography coupled to a photodiode array detector
- MC:
-
Microcystins
- MC-LR:
-
Microcystin-LR
- NN:
-
Number of nodules
- NDW:
-
Nodule dry weight
- PAL:
-
L-phenylalanine ammonia lyase
- POD:
-
Peroxidase
- PPO:
-
Polyphenoloxidase
- PSII:
-
Photosystem II
- RDW:
-
Root dry weight
- RL:
-
Root length
- TPC:
-
Total polyphenols content
References
Abe T, Lawson T, Weyers JDB, Codd GA (1996) Microcystin-LR inhibits photosynthesis of Phaseolus vulgaris primary leaves: implications for current spray irrigation practice. New Phytol 133:651–658. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1996.tb01934.x
Ali SF, Rawat LS, Meghvansi MK, Mahna SK (2009) Selection of stress-tolerant rhizobial isolates of wild legumes growing in dry regions of Rajasthan, India. ARPN J Agric Biol Sci 4(1):13–18, http://www.arpnjournals.com/jabs/research_papers/rp_2009/jabs_0109_105.pdf
Archana S, Prabakar K, Raguchander T, Hubballi M, Valarmathi P, Prakasam V (2011) Defense response of grapevine to Plasmopara viticola induced by Azoxystrobin and Pseudomonas fluorescens. Int J Sustain Agric 3(1):30–38, http://idosi.org/ijsa/3(1)11/6.pdf
Bianco C, Defez R (2009) Medicago truncatula improves salt tolerance when nodulated by an indole-3-acetic acid-overproducing Sinorhizobium meliloti strain. J Exp Bot 60:3097–3107. doi:10.1093/jxb/erp140
Bláha L, Babica P, Maršálek B (2009) Toxins produced in cyanobacterial water blooms—toxicity and risks. Interdiscip Toxicol 2(2):36–41. doi:10.2478/v10102-009-0006-2
Bond DA, Lawes DA, Hawtin GC, Saxena MC, Stephens JS (1985) In: Summerfield RJ, Roberts EH (eds) Grain legume crops. Collins, London, pp 199–265
Boo HO, Heob B, Gorinsteinc S, Chond S (2011) Positive effects of temperature and growth conditions on enzymatic and antioxidant status in lettuce plants. Plant Sci 181:479–484. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2011.07.013
Boudet AM (2007) Evolution and current status of research in phenolic compounds. Phytochemistry 68:2722–2735. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2007.06.012
Camm EC, Towers GHN (1973) Phenylalanine ammonia lyase. Phytochemistry 12:961–973. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(73)85001-0
Chen J, Song L, Dai J, Gan N, Liu Z (2004) Effects of microcystins on the growth and the activity of superoxide dismutase and peroxidase of rape (Brassica napus L.) and rice (Oryza sativa L.). Toxicon 43:393–400. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2004.01.011
Dary M, Chamber-Pérez MA, Palomares AJ, Pajuelo E (2010) “In situ” phytostabilisation of heavy metal polluted soils using Lupinus luteus inoculated with metal resistant plant-growth promoting rhizobacteria. J Hazard Mater 177:323–330. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.12.035
Du Z, Bramlage WJ (1994) Superoxide dismutase activities in senescing apple fruit (Malus domestica Borkh). J Food Sci 59:581–584. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.1994.tb05567.x
El Ghazali I, Saqrane S, Saker M, Youness O, Oudra B, Vasconcelos V, Del Campo FF (2011) Caractérisation biochimique et moléculaire d’efflorescences à cyanobactéries toxiques dans le réservoir Lalla Takerkoust (Maroc). Rev Sci l’eau 24(2):117–128. doi:10.7202/1006106ar (In french)
El Khalloufi F, Oufdou K, Lahrouni M, El Ghazali I, Saqrane S, Vasconcelos V, Oudra B (2011) Allelopatic effects of cyanobacteria extracts containing microcystins on Medicago sativa–rhizobia symbiosis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:431–438. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2010.10.006
Esterbauer H, Schaur RJ, Zollner H (1991) Chemistry and biochemistry of 4-hydroxynonrnal, malonaldehyde and related aldehydes. Free Radic Biol Med 11:81–128
Geider RJ, Osborne BA (1992) Algal photosynthesis. Chapman & Hall, New York, OCLC 23082055
Gong Y, Toivonen P, Lau OL, Wiersma PA (2001) Antioxidant system level in Braeburn apple is related to its browning disorder. Bot Bull Acad Sin 42:259–264, http://ejournal.sinica.edu.tw/bbas/content/2001/4/bot424-04.html
Järvenpää S, Lundberg-Niinistö C, Spoof L, Sjövall O, Tyystjärvi E, Meriluoto J (2007) Effects of microcystins on broccoli and mustard, and analysis of accumulated toxin by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Toxicon 49:865–874. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2006.12.008
Jiang AL, Tian SP, Xu Y (2002) Effects of controlled atmospheres with high-O2 or high-CO2 concentrations on post harvest physiology and storability of “Napoleon” sweet cherry. Acta Bot Sin 44:925–930, http://www.jipb.net/pubsoft/content/2/2313/X010590(PS2).pdf
Johnson GN, Young AJ, Scholes JD, Horton P (1993) The dissipation of excess excitation energy in British plant species. Plant Cell Environ 16(6):673–679. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.1993.tb00485.x
Kinnear SHW, Fabbro LD, Duivenvoorden LJ (2008) Variable growth responses of water thyme (Hydrilla verticillata) to whole-cell extracts of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 54:187–194. doi:10.1007/s00244-007-9026-0
Kós P, Gorzó G, Surányi G, Borbély G (1995) Simple and efficient method for isolation and measurement of cyanobacterial hepatotoxins by plant tests (Sinapis alba L.). Anal Biochem 225:49–53. doi:10.1006/abio.1995.1106
Ksouri R, Megdiche W, Debez A, Falleh H, Grignon C, Abdelly C (2007) Salinity effects on polyphenol content and antioxidant activities in leaves of the halophyte Cakile maritima. Plant Physiol Biochem 45:244–249. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2007.02.001
Lahrouni M, Oufdou K, Faghire M, Peix A, El Khalloufi F, Vasconcelos V, Oudra B (2012) Cyanobacterial extracts containing microcystins affect the growth, nodulation process and nitrogen uptake of faba bean (Vicia faba L., Fabaceae). Ecotoxicology 21:681–687. doi:10.1007/s10646-011-0826-7
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) Chlorophylls and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Methods Enzymol 148:350–382. doi:10.1016/0076-6879(87)48036-1
MADRPM/DERD (2006) Statistiques du Ministère de l’Agriculture, du Développement Rural et des Pêches Maritimes, Maroc. http://www.madrpm.gov. (In french)
Maxwell K, Johnson GN (2000) Chlorophyll fluorescence—a practical guide. J Exp Bot 51(345):659–668. doi:10.1093/jexbot/51.345.659
McElhiney J, Lawton LA, Leifert C (2001) Investigations into the inhibitory effects of Microcystins on plant growth, and the toxicity of plant tissues following exposure. Toxicon 39:1411–1420. doi:10.1016/S0041-0101(01)00100-3
Mitrovic SM, Pflugmacher S, James KJ, Furey A (2004) Anatoxin-a elicits an increase in peroxidase and glutathione S-transferase activity in aquatic plant. Aquat Toxicol 68:185–192. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2004.03.017
Oudra B, Loudiki M, Sbiyyaa B, Martins R, Vasconcelos V, Namikoshi M (2001) Isolation, characterization and quantification of microcystins (heptapeptides hepatotoxins) in Microcystis aeruginosa dominated bloom of Lalla Takerkoust lake reservoir (Morocco). Toxicon 39:1375–1381. doi:10.1016/S0041-0101(01)00093-9
Oudra B, Loudiki M, Sbiyyaa B, Sabour B, Amorim A, Martins R, Vasconcelos V (2002) Detection and variation of microcystin contents of Microcystis blooms in eutrophic Lalla Takerkoust lake (Morocco). Lakes Reserv Res Manag 7:35–44. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1770.2002.00165.x
Peuthert A, Chakrabarti S, Pflugmacher S (2007) Uptake of microcystins-LR and -LF (cyanobacterial toxins) in seedlings of several important agricultural plant species and the correlation with cellular damage (lipid peroxidation). Environ Toxicol 22(4):436–442. doi:10.1002/tox.20266
Pflugmacher S, Wiegand C, Oberemm A, Beattie KA, Krause E, Codd GA, Steinberg CEW (1998) Identification of an enzymatically formed glutathione conjugate of the cyanobacterial hepatotoxin microcystin-LR: the first step of detoxication. Biochim Biophys Acta 1425(3):527–533
Pflugmacher S (2004) Promotion of oxidative stress in the aquatic macrophyte Ceratophyllum demersum during biotransformation of the cyanobacterial toxin Microcystin-LR. Aquat Toxicol 70:169–178. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2004.06.010
Pflugmacher S, Jung K, Lundvall L, Neumann S, Peuthert A (2006) Effects of cyanobacterial toxins and cyanobacterial cell-free crude extract on germination of alfalfa (Medicago sativa) and induction of oxidative stress. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:2381–2387
Pflugmacher S, Aulhorn M, Grimm B (2007) Influence of a cyanobacterial crude extract containing microcystin-LR on the physiology and antioxidative defense systems of different spinach variants. New Phytol 175:482–489. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.02144.x
Pichardo S, Pflugmacher S (2010) Study of the antioxidant response of several bean variants to irrigation with water containing MC-LR and cyanobacterial crude extract. Environ Toxicol 26:300–306. doi:10.1002/tox.20622
Prieto A, Campos A, Cameàn A, Vasconcelos V (2011) Effects on growth and oxidative stress status of rice plants (Oryza sativa) exposed to two extracts of toxin-producing cyanobacteria (Aphanizomenon ovalisporum and Microcystis aeruginosa). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:1973–1980. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.06.009
Reichman S (2007) The potential use of the legume–rhizobium symbiosis for the remediation of arsenic contaminated sites. Soil Biol Biochem 39:2587–2593. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2007.04.030
Rigaud J, Puppo A (1975) Indole-3-acetic acid catabolism by soybean bacteroids. J Gen Microbiol 88:223–228, http://mic.sgmjournals.org/content/88/2/223.full.pdf
Sakihama Y, Cohen MF, Grace SC, Yamasaki H (2002) Plant phenolic antioxidant and pro-oxidant activities: phenolics-induced oxidative damage mediated by metals in plants. Toxicology 177:67–80. doi:10.1016/S0300-483X(02)00196-8
Saqrane S, Oudra B (2009) CyanoHAB occurrence and water irrigation cyanotoxins contamination: ecological impacts and potential health risks. Toxins 1:113–122. doi:10.3390/toxins1020113
Saqrane S, El Ghazali I, Ouahid Y, El Hassani M, El Hadrami I, Oudra B, Bouarab L, del Campo FF, Vasconcelos V (2007) Phytotoxic effects of cyanobacteria extract on the aquatic plant Lemna gibba: microcystin accumulation, detoxification and oxidative stress induction. Aquat Toxicol 83:284–294. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2007.05.004
Saqrane S, Ouahid Y, El Ghazali I, Oudra B, Bouarab L, Del Campo FF (2009) Physiological changes in Triticum durum, Zea mays, Pisum sativum and Lens esculenta cultivars, caused by irrigation with water contaminated with microcystins: a laboratory experimental approach. Toxicon 53:786–796. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2009.01.028
Singla R, Garg N (2006) The legume–rhizobia symbiosis under salt stress—a review. Agric Rev 27(1):1–21, http://arccjournals.com/pdf/Reviews/ar-27-1/ar-27-1-001.pdf
Singleton VL, Rossi JA (1965) Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic phospholungistic acid reagents. Am J Enol Vitic 16:144–158, http://ajevonline.org/content/16/3/144.full.pdf
Vassilakaki M, Pflugmacher S (2007) Oxidative stress response of Synechocystis sp. (PCC 6803) due to exposure to microcystin-LR and cell-free cyanobacterial crude extract containing microcystin-LR. J Appl Phycol 20:219–225. doi:10.1007/s10811-007-9222-3
Venisse JS, Gullner G, Brisset MN (2001) Evidence for the involvement of an oxidative stress in the initiation of infection of pear by Erwinia amylovora. Plant Physiol 125:2164–2172. doi:10.1104/pp.125.4.2164
Wani PA, Khan MS, Zaidi A (2008) Chromium-reducing and plant growth-promoting Mesorhizobium improves chickpea growth in chromium-amended soil. Biotechnol Lett 30(1):159–163. doi:10.1007/s10529-007-9515-2
Zhou Y, Dahler JM, Underhill SJR, Wills RBH (2003) The enzymes associated with blackheart development in pineapple. Food Chem 80:565–572. doi:10.1016/S0308-8146(02)00375-8
Zurawell RW, Chen H, Burke JM, Prepas EE (2005) Hepatotoxic cyanobacteria: a review of the biological importance of microcystins in freshwater environments. J Toxicol Environ Health 68:1–3. doi:10.1080/10937400590889412
Acknowledgments
This study is financially supported by the International Foundation for Sciences (IFS project F/2826-3F). This work is also carried out within the framework of the Morocco-Spanish collaboration (AECID project n° A1/035873/11).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lahrouni, M., Oufdou, K., El Khalloufi, F. et al. Physiological and biochemical defense reactions of Vicia faba L.–Rhizobium symbiosis face to chronic exposure to cyanobacterial bloom extract containing microcystins. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20, 5405–5415 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1535-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1535-y