Abstract
Objective
The study aimed to evaluate whether the inflammatory marker “high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP)” level was associated with impaired heart rate recovery at 1 min after exercise termination (HRR-1) in middle-aged patients with severe obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
Methods
Thirty middle-aged male patients (40–64 years old) with severe OSA (apnea–hypopnea index [AHI] ≥ 30 h−1) and 30 subjects without OSA (AHI < 5 h−1), matched with age and body mass index (BMI), were recruited. All subjects underwent an overnight polysomnography and completed a symptom-limited maximal exercise test. Cardiopulmonary parameters included peak oxygen consumption (VO2peak) and heart rate response during and immediately after exercise. Fasting blood samples were drawn for hsCRP analysis.
Result
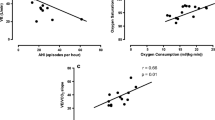
Patients with severe OSA had significantly higher hsCRP levels (0.18 vs. 0.07 mg/dl, P < 0.01), lower reduced HRR-1, peak heart rate, and VO2peak values than those in the controls. The hsCRP levels significantly correlated with HRR-1 in the OSA group (r = −0.69, P < 0.01) after adjustment for VO2peak (r = −0.66, P < 0.01). Furthermore, stepwise multiple regression analysis showed that HRR-1 and AHI were significant predictors of hsCRP levels in all participants (adjusted R 2 = 0.53, P < 0.01).
Conclusions
Blunted HRR was shown in middle-aged men with severe OSA, and it was associated with high hsCRP levels significantly.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Punjabi NM, Shahar E, Redline S, Gottlieb DJ, Givelber R, Resnick HE (2004) Sleep-disordered breathing, glucose intolerance, and insulin resistance: the Sleep Heart Health Study. Am J Epidemiol 160:521–530
Somers VK, Dyken ME, Clary MP, Abboud FM (1995) Sympathetic neural mechanisms in obstructive sleep apnea. J Clin Invest 96:1897–1904
Narkiewicz K, Montano N, Cogliati C, van de Borne PJ, Dyken ME, Somers VK (1998) Altered cardiovascular variability in obstructive sleep apnea. Circulation 98:1071–1077
Ryan S, Taylor CT, McNicholas WT (2005) Selective activation of inflammatory pathways by intermittent hypoxia in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Circulation 112:2660–2667
Hedner J, Darpo B, Ejnell H, Carlson J, Caidahl K (1989) Reduction in sympathetic activity after long-term CPAP in sleep apnea: cardiovascular implications. Eur Respir J 8:222–229
Cole CR, Blackstone EH, Pashkow FJ, Snader CE, Lauer MS (1999) Heart rate recovery immediately after exercise as a predictor of mortality. N Engl J Med 341:1351–1357
Arena R, Guazzi M, Myers J, Peberdy MA (2006) Prognostic value of heart rate recovery in patients with heart failure. Am Heart J 151:e7–e13
Imai K, Sato H, Hori M, Kusuoka H, Ozaki H, Yokoyama H, Takeda H, Inoue M, Kamada T (1994) Vagally mediated heart rate recovery after exercise is accelerated in athletes but blunted in patients with chronic heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 24:1529–1535
Jae SY, Ahn ES, Heffernan KS, Woods JA, Lee MK, Park WH, Fernhall B (2007) Relation of heart rate recovery after exercise to C-reactive protein and white blood cell count. Am J Cardiol 99:707–710
Lanza GA, Sgueglia GA, Cianflone D, Rebuzzi AG, Angeloni G, Sestito A, Infusino F, Crea F, Maseri A, SPAI (Stratificazione Prognostica dell'Angina Instabile) Investigators (2006) Relation of heart rate variability to serum levels of C-reactive protein in patients with unstable angina pectoris. Am J Cardiol 97:1702–1706
Sloan RP, McCreath H, Tracey KJ, Sidney S, Liu K, Seeman T (2007) RR interval variability is inversely related to inflammatory markers: the CARDIA study. Mol Med 13:178–184
Lampert R, Bremner JD, Su S, Miller A, Lee F, Cheema F, Goldberg J, Vaccarino V (2008) Decreased heart rate variability is associated with higher levels of inflammation in middle-aged men. Am Heart J 156:759.e1–759.e7
Vieira VJ, Valentine RJ, McAuley E, Evans E, Woods JA (2007) Independent relationship between heart rate recovery and C-reactive protein in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc 55:747–751
Tracey KJ (2002) The inflammatory reflex. Nature 420:1622–1673
Shamsuzzaman AS, Winnicki M, Lanfranchi P, Wolk R, Kara T, Accurso V, Somers VK (2002) Elevated C-reactive protein in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Circulation 105:2462–2464
Hargens TA, Guill SG, Zedalis D, Gregg JM, Nickols-Richardson SM, Herbert WG (2008) Heart rate recovery following exercise testing in overweight young men with untreated obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep 31:104–110
Maeder MT, Münzer T, Rickli H, Schoch OD, Korte W, Hürny C, Ammann P (2008) Association between heart rate recovery and severity of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep Med 9:753–761
Maeder MT, Ammann P, Münzer T, Schoch OD, Korte W, Hürny C, Myers J, Rickli H (2009) Continuous positive airway pressure improves exercise capacity and heart rate recovery in obstructive sleep apnea. Int J Cardiol 132:75–83
Kaleth AS, Chittenden TW, Hawkins BJ, Hargens TA, Guill SG, Zedalis D, Gregg JM, Herbert WG (2007) Unique cardiopulmonary exercise test responses in overweight middle-aged adults with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Med 8:160–168
Vanhecke TE, Franklin BA, Zalesin KC, Sangal RB, deJong AT, Agrawal V, McCullough PA (2008) Cardiorespiratory fitness and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in morbidly obese patients. Chest 134:539–545
Lee P, Su YN, Yu CJ, Yang PC, Wu HD (2009) PHOX2B mutation-confirmed congenital central hypoventilation syndrome in a Chinese family: presentation from newborn to adulthood. Chest 135:537–544
American Academy of Sleep Medicine (1999) Sleep-related breathing disorders in adults: recommendations for syndrome definition and measurement techniques in clinical research. The Report of an American Academy of Sleep Medicine Task Force. Sleep 22:667–689
John MW (1991) A new method for measuring daytime sleepiness: the Epworth sleepiness scale. Sleep 14:540–545
Roberts WL, Moulton L, Law TC, Farrow G, Cooper-Anderson M, Savory J, Nader R (2001) Evaluation of nine automated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein methods: implications for clinical and epidemiological applications. Part 2. Clin Chem 47:418–425
Pollock ML, Graves JE, Mahar MT (1988) Reliability and validity of bioelectrical impedance in determining body composition. J Appl Physiol 64:529–534
Lukaski HC, Bolonchuk WW, Hall CB, Siders WA (1986) Validation of tetrapolar bioelectrical impedance method to assess human body composition. J Appl Physiol 60:1327–1332
Gupta N, Balasekaran G, Govindaswamy VV, Hwa CY, Shun LM (2011) Comparison of body composition with bioelectric impedance (BIA) and dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) among Singapore Chinese. J Sci Med Sports 14:33–35
American College of Sports Medicine (2006) ACSM's guidelines for exercise testing and prescription, 7th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Bosquet L, Gamelin FX, Berthoin S (2008) Reliability of postexercise heart rate recovery. Int J Sports Med 29:238–243
Lauer MS, Francis GS, Okin PM, Pashkow FJ, Snader CE, Marwick TH (1999) Impaired chronotropic response to exercise stress testing as a predictor of mortality. JAMA 281:524–529
Maeder MT, Duerring C, Engel RP, Boesch C, Pfisterer ME, Myers J, Müller-Brand J, Zellweger MJ (2010) Predictors of impaired heart rate recovery: a myocardial perfusion SPECT study. Eur J Cardivasc Prev Rehabil 17:303–308
Pickering TG, Hall JE, Appel LJ, Falkner BE, Graves J, Hill MN, Jones DW, Kurtz T, Sheps SG, Roccella EJ (2005) Recommendations for blood pressure measurement in humans and experimental animals. Part I: blood pressure measurement in humans: statement for professionals from the Subcommittee of Professional and Public Education of the American Heart Association Council on High Blood Pressure Research. Circulation 111:697–716
Ridker PM, Cushman M, Stampfer MJ, Tracy RP, Hennekens CH (1998) Plasma concentration of C-reactive protein and risk of developing peripheral vascular disease. Circulation 97:425–428
Ridker PM, Cushman M, Stampfer MJ, Tracy RP, Hennekens CH (1997) Inflammation, aspirin, and the risk of cardiovascular disease in apparently health men. N Engl J Med 336:973–979
Lui MM, Lam JC, Mak HK, Xu A, Ooi C, Lam DC, Mak JC, Khong PL, Ip MS (2009) C-reactive protein is associated with obstructive sleep apnea independent of visceral obesity. Chest 135:950–956
Sharma SK, Mishra HK, Sharma H, Goel A, Sreenivas V, Gulati V, Tahir M (2008) Obesity, and not obstructive sleep apnea, is responsible for increased serum hs-CRP levels in patients with sleep-disordered breathing in Delhi. Sleep Med 9:149–156
Taheri S, Austin D, Lin L, Nieto FJ, Young T, Mignot E (2007) Correlates of serum C-reactive protein (CRP)—no association with sleep duration or sleep disordered breathing. Sleep 30:991–996
Lin CC, Hsieh WY, Chou CS, Liaw SF (2006) Cardiopulmonary exercise testing in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 150:27–34
Alonso-Fernandez A, Garcia-Rio F, Arias MA, Mediano O, Pino JM, Martinez I (2006) Obstructive sleep apnoea–hypoapnoea syndrome reversibly depresses cardiac response to exercise. Eur Heart J 27:207–215
Grote L, Kraiczi H, Hender J (2000) Reduced alpha- and beta-adrenergic vascular response in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Crit Care Med 162:1480–1487
Carlson JT, Hender JA, Sellgren J, Elam M, Wallin BC (1996) Depressed baroreflex sensitivity in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 154:1490–1496
Bonsignore MR, Parati G, Insalaco G, Castiglioni P, Marrone O, Romano S, Salvaggio A, Mancia G, Bonsignore G, Di Rienzo M (2006) Baroreflex control of heart rate during sleep in severe obstructive sleep apnoea: effects of acute CPAP. Eur Respir J 27:128–135
Lombardi C, Parati G, Cortelli P, Provini F, Vetrugno R, Plazzi G, Vignatelli L, Di Rienzo M, Lugaresi E, Mancia G, Montagna P, Castiglioni P (2008) Daytime sleepiness and neural cardiac modulation in sleep-related breathing disorders. J Sleep Res 17:263–270
Rennie KL, Hemingway H, Kumari M, Brunner E, Malik M, Marmot M (2003) Effects of moderate and vigorous physical activity on heart rate variability in a British study of civil servants. Am J Epidemiol 157:135–143
Jae SY, Heffernan KS, Yoon ES, Lee MK, Fernhall B, Park WH (2009) The inverse association between cardiorespiratory fitness and C-reactive protein is mediated by autonomic function: a possible role of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. Mol Med 15:291–296
Czura CJ, Tracey KJ (2005) Autonomic neural regulation of immunity. J Intern Med 257:156–166
Jüttler E, Tarabin V, Schwaninger M (2002) Interleukin-6 (IL-6): a possible neuromodulator induced by neuronal activity. Neuroscientist 8:268–275
Ruzek MC, Miller AH, Opal SM, Pearce BD, Biron CA (1997) Characterization of early cytokine responses and an interleukin (IL)-6-depenednet pathway of endogenous glucocorticoid induction during murine cytomegalovirus infection. J Exp Med 185:1185–1192
Acknowledgement
The authors thank the National Science Council (Taiwan) for the financial support (NSC 96-2314-B-002-022-MY3).
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors has a financial relationship with a commercial entity that has an interest in the subject of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Clinical trial registration
ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT00813852
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chien, MY., Lee, P., Tsai, YF. et al. C-reactive protein and heart rate recovery in middle-aged men with severe obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath 16, 629–637 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-011-0549-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-011-0549-2