Abstract
Objective
The objective of this study is to assess the risk of sleep-disordered breathing (SDB) in patients with Parkinson's disease (PD) in a cross-sectional survey of PD subjects and controls in a university-based movement disorders clinic.
Methods
One hundred thirty-four consecutive PD subjects and 94 control subjects without prior diagnosis of SDB were assessed. Participants were assessed with clinical history, Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale, Geriatric Depression Scale, Berlin Questionnaire to classify SDB risk, Epworth Sleepiness Scale, Parkinson's Disease Sleep Scale, and SF-36 to examine quality of life. The presence of risk for SDB was assessed by the Berlin Questionnaire.
Results
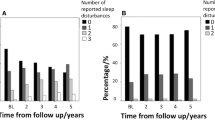
High risk for SDB was apparent in 66 (49.3%) of the PD patients and 32 (34.8%) of the controls. After adjustment for age, gender, and body mass index (BMI), PD subjects in comparison to controls showed higher risk for SBD (odds ratio = 2.81; 95% confidence interval, 1.36–5.82). Quality of life (physical component score) was significantly diminished in PD patients at high risk for SDB. PD severity did not correlate well with SDB risk. PD patients at high risk for SDB had higher BMIs and Epworth scores.
Conclusions
PD patients have features suggesting increased risk for SDB. This frequently undiagnosed sleep disorder may have a substantial impact on quality of life of PD patients.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Lau LM, Breteler MM (2006) Epidemiology of Parkinson's disease. Lancet Neurol 5:525–535
Strickland D, Bertoni JM (2004) Parkinson's prevalence estimated by a state registry. Mov Disord 19:318–323
Guttman M, Slaughter PM, Theriault M-E, DeBoer DP, Naylor CD (2003) Burden of parkinsonism: a population-based study. Mov Disord 18:313–319
Holroyd S, Currie LJ, Wooten GF (2005) Depression is associated with impairment of ADL, not motor function in Parkinson disease. Neurology 64:2134–2135
Schrag A (2006) Quality of life and depression in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Sci 248:151–157
Global Parkinson's Disease Survey Steering Committee (2002) Factors impacting on quality of life in Parkinson's disease: results from an international survey. Mov Disord 17:60–67
Aarsland D, Larsen JP, Tandberg E, Laake K (2000) Predictors of nursing home placement in Parkinson's disease: a population-based, prospective study. J Am Geriatr Soc 48:938–942
Pal PK, Thennarsu K, Fleming J, Schulzer M, Brown T, Calne SM (2004) Nocturnal sleep disturbances and daytime dysfunction in patients with Parkinson's disease and in their caregivers. Parkinsonism Rel Disord 10:157–168
Karslen KH, Larsen JP, Tandberg E, Maland JG (1998) Quality of life measurements in patients with Parkinson's disease; a community-base study. Eur J Neurol 5:443–450
Karslen KH, Larsen JP, Tandberg E, Maeland JG (1999) The influence of clinical and demographic variables on quality of life in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr 66:431–435
Lees AJ, Blackburn NA, Campbell VL (1988) The nighttime problems of Parkinson's disease. Clin Neuropharmacol 11:512–519
Nausieda PA, Weiner WS, Kaplan LR, Weber S, Kluwans HL (1982) Sleep disruption in the course of chronic levodopa therapy an early feature of levodopa psychosis. Clin Neuropharmacol 5:183–194
Tandberg E, Larsen JP, Karlsen K (1998) A community based study of sleep disorders in patients with Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 13:895–899
Gjerstad MD, Wentzel-Larsen T, Aarsland D, Larsen JP (2007) Insomnia in Parkinson's disease: frequency and progression over time. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr 78:476–479
Braga-Neto P, da Silva-Junior FP, Monte FS, De Bruin PFC, de Bruin VMS (2004) Snoring and excessive daytime sleepiness in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Sci 217:41–45
Chaudhuri KR (2003) Nocturnal symptom complex in PD and its management. Neurology 61:S17–S23
Garcia-Borreguero D, Larosa O, Bravo M (2003) Parkinson's disease and sleep. Sleep Med Rev 7:115–129
Factor SA, Mc Alarney T, Sanchez-Ramos JR, Weiner WJ (1990) Sleep disorders and sleep effect in Parkinson's disease. Mov Dis 5:280–285
Van Hilten JJ, Weggerman M, Van der Velde EA, Kerkhoff GA, Van Dijk JG, Roos RAC (1993) Sleep, excessive daytime sleepinessand fatigue in Parkinson's disease. J Neural Transm 5:235–244
Arnulf I, Konofal E, Merino-Andreu M et al (2002) Parkinson's disease and sleepiness: an integral part of PD. Neurology 58:1019–1024
Maria B, Sophia S, Michalis M et al (2003) Sleep breathing disorders in patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Resp Med 97:1151–1157
Diederich NJ, Vaillant M, Leischen M et al (2005) Sleep apnea syndrome in Parkinson's disease. A case-control study in 49 patients. Mov Disord 20:1413–1418
Schäfer D (2001) Schlafbezogene Atmungsstörungen bei Parkinsonsyndromen: Häufigkeit, Art und Behandlungsansätze. Somnologie 5:103–114
Chen H, Zhang SM, Hernán MA, Willett WC, Ascherio A (2003) Weight loss in Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol 53:676–679
Uc EY, Struck LK, Rodnitzky RL, Zimmerman B, Dobson J, Evans WJ (2006) Predictors of weight loss in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 21:930–936
Kish SJ (2003) Biochemistry of Parkinson's disease: is a brain serotonergic deficiency a characteristic of idiopathic Parkinson's disease? Adv Neuro 91:39–49
Kerenyi L, Ricaurte GA, Schretlen DJ et al (2003) Positron emission tomography of striatal serotonin transporters in Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 60:1223–1229
Albin RL, Koeppe RA, Bohnen NI, Wernette K, Kilbourn MA, Frey KA (2008) Spared caudal brainstem SERT binding in early Parkinson's disease. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 28:441–444
Kish SJ, Tong J, Hornykiewicz O et al (2008) Preferential loss of serotonin markers in caudate versus putamen in Parkinson's disease. Brain 131(Pt 1):120–131
Schiermeier S, Schäfer D, Schäfer T, Greulich W, Schläfke (2001) Breathing and locomotion in patients with Parkinson's disease. Eur J Physiol 443:67–71
Micieli G, Tosi P, Marcheselli S, Cavallini A (2003) Autonomic dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Neurol Sci 24:S32–S34
Cochen de Cock V, Abouda M, Smaranda L et al (2010) Is obstructive sleep apnea a problem in Parkinson's disease? Sleep Med 11:247–252
Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Kilford L, Lees AJ (1992) Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson's disease. A clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr 55:181–184
Fahn S, Elton RL, UPDRS program members (1987) Unified Parkinsons disease rating scale. In: Fahn S, Marsden CD, Goldstein M, Calne DB (eds) Recent developments in Parkinsons disease, vol 2. Macmillan Healthcare Information, Florham Park, pp 153–163
Netzer NC, Stoohs RA, Netzer CM, Clark K, Strohl KP (1999) Using the Berlin Questionnaire to identify patients at risk for the sleep apnea. Ann Intern Med 131:485–491
Chung F, Yegneswaran B, Liao P et al (2008) STOP Questionnaire: a tool to screen patients for obstructive sleep apnea. Anesthesiology 108:812–821
Gonsalves MA, Paiva T, Ramos E, Guilleminault C (2004) Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, sleepiness, and quality of life. Chest 125:2091–2096
Reimer MA, Flemons WW (2003) Quality of life in sleep disorders. Sleep Med Rev 7:335–349
Raizi A, Hobart JC, Lamping DL et al (2003) Using the SF-36 measure to compare the health impact of multiple sclerosis and Parkinson's disease with normal population health profiles. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74:710–714
Schrag A, Jahanshahi M, Quinn N (2000) How does Parkinson's disease affect quality of life? A comparison with quality of life in the general population. Mov Disord 15:1112–1118
Kuopio A, Marttila RJ, Helenius H, Toivonen M, Rinne UK (2000) The quality of life in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 15:216–223
Johns MW (1991) A new method for measuring daytime sleepiness: the Epworth sleepiness scale. Sleep 14:540–545
Chaudhuri KR, Pal S, Dimarco A et al (2002) The Parkinson's disease sleep scale: a new instrument for assessing sleep and nocturnal disability in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr 73:629–635
Sheikh JL, Yesavage JA (1986) Geriatric depression scale: recent evidence and development of a shorter version. In: Brink TL (ed) Clinical gerontology: a guide to assessment and intervention. Howarth, New York, pp 165–173
Weintraub D, Oehlberg KA, Katz IR, Stern MB (2006) Test characteristics of the 15-item geriatric depression scale and Hamilton depression rating scale in Parkinson disease. Am J Geriatr Psychiatr 14:169–175
Netzer N, Hoegel J, Loube D et al (2003) Prevalence of symptoms and risk of sleep apnea in primary care. Chest 124:1406–1414
Young T, Evans L, Finn L, Palta M (1997) Estimation of the clinically diagnosed proportion of sleep apnea syndrome in middle-aged men and women. Sleep 20:705–706
Quittenbaum BH, Grahn B (2004) Quality of life and pain in Parkinson's disease: a controlled cross-sectional study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 10:129–136
Gage H, Hendricks A, Zhang S, Kazis L (2003) The relative health related quality of life of veterans with Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr 74:163–169
Lugaresi E, Mondini S, Zucconi M, Montagna P, Cirignotta F (1983) Staging of heavy snorer's disease: a proposal. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir 19:590–594
Young T, Palta M, Dempsey J, Skatrud J, Weber S, Badr S (1993) The occurrence of sleep-disordered breathing among middle-aged adults. N Engl J Med 328:1230–1235
Ye L, Pien GW, Weaver TE (2009) Gender differences in the clinical manifestations of obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Med 10:1075–1084
Redline S, Kump K, Tishler PV, Browner I, Ferrette V (1994) Gender differences in sleep disordered breathing in a community-based sample. Am J Resp Crit Care Med 149:722–726
Young T, Hutton R, Finn L, Badr S, Palta M (1996) The gender bias is sleep apnea diagnosis. Are women missed because they have different symptoms? Arch Intern Med 156:2445–2451
Schafer D, Greulich W (2000) Effects of parkinsonian medication on sleep. J Neurol 247(Suppl 4):IV24–IV27
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the patients and staff of the University of Michigan Movement Disorders Clinic, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, for their participation and help in this survey; Dr. Ninith V. Kartha, Dr. Kelvin L. Chou, and Dr. Kirk A. Frey for their help in recruitment of the participants; and Brady T. West and Kenneth E. Guire for statistical consultation. Dr. Chotinaiwattarakul's effort was funded by Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand. This study was also supported by NS15655 and the Michael J. Fox Foundation. All authors had full access to all of the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chotinaiwattarakul, W., Dayalu, P., Chervin, R.D. et al. Risk of sleep-disordered breathing in Parkinson's disease. Sleep Breath 15, 471–478 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-010-0362-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-010-0362-3