Abstract
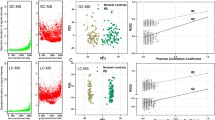
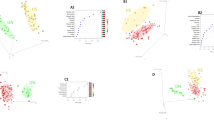
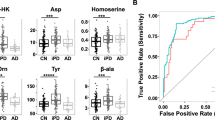
Objective To investigate the metabolic profile of serum and urine samples from 23 female patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD) and 23 age and sex-matched controls. Methods We used gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry to detect metabolites (approximately 1,600 in total), then supervised statistical analysis (using projection to latent structures discriminant analysis) to study the differences between control and PD samples. Results Supervised statistical analysis yielded models that possessed statistically significant predictive value for blind samples on the basis of the metabolic profile of urine but not of serum. However, whilst no individual biomarkers were identified, suggesting that any metabolic disturbance associated with PD is comparatively minor, a multivariate metabolic signature associated with PD was identified in urine. Interpretation There is a relatively subtle, yet distinct, metabolic signature of PD present in the urine of patients with early disease. The signature may itself act as a useful biomarker for PD, although larger studies will be required to validate our present findings.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdi, F., Quinn, J. F., Jankovic, J., McIntosh, M., Leverenz, J. B., Peskind, E., Nixon, R., Nutt, J., Chung, K., Zabetian, C., Samii, A., Lin, M., Hattan, S., Pan, C., Wang, Y., Jin, J., Zhu, D., Li, G. J., Liu, Y., Waichunas, D., Montine, T. J., & Zhang, J. (2006). Detection of biomarkers with a multiplex quantitative proteomic platform in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with neurodegenerative disorders. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, 9(3), 293–348.
Bohnen, N. I., Kaufer, D. I., Ivanco, L. S., Lopresti, B., Koeppe, R. A., Davis, J. G., Mathis, C. A., Moore, R. Y., & DeKosky, S. T. (2003). Cortical cholinergic function is more severely affected in parkinsonian dementia than in Alzheimer disease: An in vivo positron emission tomographic study. Archives of Neurology, 60, 1745–1748. doi:10.1001/archneur.60.12.1745.
Braak, H., Del Tredici, K., Rub, U., de Vos, R. A., Jansen Steur, E. N., & Braak, E. (2003). Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiology of Aging, 24, 197–211. doi:10.1016/S0197-4580(02)00065-9.
Brindle, J. T., Antti, H., Holmes, E., Tranter, G., Nicholson, J. K., Bethell, H. W., Clarke, S., Schofield, P. M., McKilligin, E., Mosedale, D. E., & Grainger, D. J. (2002). Rapid and noninvasive diagnosis of the presence and severity of coronary heart disease using 1H-NMR-based metabonomics. Nature Medicine, 8, 1439–1444. doi:10.1038/nm802.
Brindle, J. T., Nicholson, J. K., Schofield, P. M., Grainger, D. J., & Holmes, E. (2003). Application of chemometrics to 1H NMR spectroscopic data to investigate a relationship between human serum metabolic profiles and hypertension. Analyst, 128, 32–36. doi:10.1039/b209155k.
Burn, D. J., & Lees, A. J. (2002). Progressive supranuclear palsy: Where are we now? Lancet Neurology, 1, 359–369. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(02)00161-8.
Di Monte, D. A. (2003). The environment and Parkinson’s disease: Is the nigrostriatal system preferentially targeted by neurotoxins? Lancet Neurology, 2, 531–538. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(03)00501-5.
Dunn, W. B., Bailey, N. J., & Johnson, H. E. (2005). Measuring the metabolome: Current analytical technologies. Analyst, 130, 606–625. doi:10.1039/b418288j.
Dunne, V. G., Bhattachayya, S., Besser, M., Rae, C., & Griffin, J. L. (2005). Metabolites from cerebrospinal fluid in aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage correlate with vasospasm and clinical outcome: A pattern-recognition 1H NMR study. NMR in Biomedicine, 18, 24–33. doi:10.1002/nbm.918.
Edwards, L. L., Quigley, E. M., & Pfeiffer, R. F. (1992). Gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease: Frequency and pathophysiology. Neurology, 42, 726–732.
Fearnley, J. M., & Lees, A. J. (1991). Ageing and Parkinson’s disease: Substantia nigra regional selectivity. Brain, 114(Pt 5), 2283–2301. doi:10.1093/brain/114.5.2283.
Foltynie, T., Brayne, C., & Barker, R. A. (2002). The heterogeneity of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Journal of Neurology, 249, 138–145. doi:10.1007/PL00007856.
Gavaghan, C. L., Holmes, E., Lenz, E., Wilson, I. D., & Nicholson, J. K. (2000). An NMR-based metabonomic approach to investigate the biochemical consequences of genetic strain differences: Application to the C57BL10J and Alpk:ApfCD mouse. FEBS Letters, 484, 169–174. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(00)02147-5.
Ghauri, F. Y., Nicholson, J. K., Sweatman, B. C., Wood, J., Beddell, C. R., Lindon, J. C., & Cairns, N. J. (1993). NMR spectroscopy of human post mortem cerebrospinal fluid: Distinction of Alzheimer’s disease from control using pattern recognition and statistics. NMR in Biomedicine, 6, 163–167. doi:10.1002/nbm.1940060210.
Gibb, W. R., & Lees, A. J. (1988). The relevance of the Lewy body to the pathogenesis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 51, 745–752.
Griffin, J. L. (2003). Metabonomics: NMR spectroscopy and pattern recognition analysis of body fluids and tissues for characterisation of xenobiotic toxicity and disease diagnosis. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 7, 648–654. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2003.08.008.
Hughes, A. J., Daniel, S. E., Ben Shlomo, Y., & Lees, A. J. (2002). The accuracy of diagnosis of parkinsonian syndromes in a specialist movement disorder service. Brain, 125, 861–870. doi:10.1093/brain/awf080.
Hughes, A. J., Daniel, S. E., Kilford, L., & Lees, A. J. (1992). Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: A clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 55, 181–184.
Kirschenlohr, H. L., Griffin, J. L., Clarke, S. C., Rhydwen, R., Grace, A. A., Schofield, P. M., Brindle, K. M., & Metcalfe, J. C. (2006). Proton NMR analysis of plasma is a weak predictor of coronary artery disease. Nature Medicine, 12(6), 705–710. doi:10.1038/nm1432.
Lenz, E. M., Bright, J., Wilson, I. D., Hughes, A., Morrisson, J., Lindberg, H., & Lockton, A. (2004). Metabonomics, dietary influences and cultural differences: A 1H NMR-based study of urine samples obtained from healthy British and Swedish subjects. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 36, 841–849. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2004.08.002.
Lewis, S. J., Foltynie, T., Blackwell, A. D., Robbins, T. W., Owen, A. M., & Barker, R. A. (2005). Heterogeneity of Parkinson’s disease in the early clinical stages using a data driven approach. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 76, 343–348. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2003.033530.
Lindon, J. C., Nicholson, J. K., Holmes, E., Antti, H., Bollard, M. E., Keun, H., Beckonert, O., Ebbels, T. M., Reily, M. D., Robertson, D., Stevens, G. J., Luke, P., Breau, A. P., Cantor, G. H., Bible, R. H., Niederhauser, U., Senn, H., Schlotterbeck, G., Sidelmann, U. G., Laursen, S. M., Tymiak, A., Car, B. D., Lehman-McKeeman, L., Colet, J. M., Loukaci, A., & Thomas, C. (2003). Contemporary issues in toxicology the role of metabonomics in toxicology and its evaluation by the COMET project. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 187, 137–146. doi:10.1016/S0041-008X(02)00079-0.
Mauborgne, A., Javoy-Agid, F., Legrand, J. C., Agid, Y., & Cesselin, F. (1983). Decrease of substance P-like immunoreactivity in the substantia nigra and pallidum of parkinsonian brains. Brain Research, 268, 167–170. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(83)90403-1.
Mayeux, R., Chen, J., Mirabello, E., Marder, K., Bell, K., Dooneief, G., Cote, L., & Stern, Y. (1990). An estimate of the incidence of dementia in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Neurology, 40, 1513–1517.
Michell, A. W., Lewis, S. J., Foltynie, T., & Barker, R. A. (2004). Biomarkers and Parkinson’s disease. Brain, 127, 1693–1705. doi:10.1093/brain/awh198.
Michell, A. W., Luheshi, L. M., & Barker, R. A. (2005). Skin and platelet alpha-synuclein as peripheral biomarkers of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience Letters, 381, 294–298. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2005.02.030.
Mikolaenko, I., Pletnikova, O., Kawas, C. H., O’Brien, R., Resnick, S. M., Crain, B., & Troncoso, J. C. (2005). Alpha-synuclein lesions in normal aging, Parkinson disease, and Alzheimer disease: evidence from the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging (BLSA). Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology, 64, 156–162.
Nicholson, J. K., Connelly, J., Lindon, J. C., & Holmes, E. (2002). Metabonomics: A platform for studying drug toxicity and gene function. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 1, 153–161. doi:10.1038/nrd728.
Nicholson, J. K., & Wilson, I. D. (2003). Opinion: understanding ‘global’ systems biology: metabonomics and the continuum of metabolism. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2, 668–676. doi:10.1038/nrd1157.
O’Hagan, S., Dunn, W. B., Brown, M., Knowles, J. D., & Kell, D. B. (2005). Closed-loop, multiobjective optimization of analytical instrumentation: gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry of the metabolomes of human serum and of yeast fermentations. Analytical Chemistry, 77, 290–303. doi:10.1021/ac049146x.
Odunsi, K., Wollman, R. M., Ambrosone, C. B., Hutson, A., McCann, S. E., Tammela, J., Geisler, J. P., Miller, G., Sellers, T., Cliby, W., Qian, F., Keitz, B., Intengan, M., Lele, S., & Alderfer, J. L. (2005). Detection of epithelial ovarian cancer using 1H-NMR-based metabonomics. International Journal of Cancer, 113, 782–788. doi:10.1002/ijc.20651.
Olanow, C. W., & Tatton, W. G. (1999). Etiology and pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 22, 123–144. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.22.1.123.
Parkinson, J. (1817). An essay on the shaking palsy. London: Sherwood, Neely and Jones.
Poewe, W., & Wenning, G. (2002). The differential diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. European Journal of Neurology, 9(Suppl 3), 23–30. doi:10.1046/j.1468-1331.9.s3.3.x.
Raamsdonk, L. M., Teusink, B., Broadhurst, D., Zhang, N., Hayes, A., Walsh, M. C., Berden, J. A., Brindle, K. M., Kell, D. B., Rowland, J. J., Westerhoff, H. V., van Dam, K., & Oliver, S. G. (2001). A functional genomics strategy that uses metabolome data to reveal the phenotype of silent mutations. Nature Biotechnology, 19, 45–50. doi:10.1038/83496.
Ravasz, E., Somera, A. L., Mongru, D. A., Oltvai, Z. N., & Barabasi, A. L. (2002). Hierarchical organization of modularity in metabolic networks. Science, 297, 1551–1555. doi:10.1126/science.1073374.
Sato, S., Mizuno, Y., & Hattori, N. (2005). Urinary 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine levels as a biomarker for progression of Parkinson disease. Neurology, 64, 1081–1083.
Scatton, B., Javoy-Agid, F., Rouquier, L., Dubois, B., & Agid, Y. (1983). Reduction of cortical dopamine, noradrenaline, serotonin and their metabolites in Parkinson’s disease. Brain Research, 275, 321–328. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(83)90993-9.
Scherzer, C. R., Eklund, A. C., Morse, L. J., Liao, Z., Locascio, J. J., Fefer, D., Schwarzschild, M. A., Schlossmacher, M. G., Hauser, M. A., Vance, J. M., Sudarsky, L. R., Standaert, D. G., Growdon, J. H., Jensen, R. V., & Gullans, S. R. (2007). Molecular markers of early Parkinson’s disease based on gene expression in blood. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 104(3), 955–960. doi:10.1073/pnas.0610204104.
Taquet, H., Javoy-Agid, F., Hamon, M., Legrand, J. C., Agid, Y., & Cesselin, F. (1983). Parkinson’s disease affects differently Met5- and Leu5-enkephalin in the human brain. Brain Research, 280, 379–382. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(83)90071-9.
Tsuboi, Y., Ahlskog, J. E., Apaydin, H., Parisi, J. E., & Dickson, D. W. (2001). Lewy bodies are not increased in progressive supranuclear palsy compared with normal controls. Neurology, 57, 1675–1678.
Underwood, B. R., Broadhurst, D., Dunn, W. B., Ellis, D. I., Michell, A. W., Vacher, C., Mosedale, D. E., Kell, D. B., Barker, R. A., Grainger, D. J., & Rubinsztein, D. C. (2006). Huntington disease patients and transgenic mice have similar pro-catabolic serum metabolite profiles. Brain, 129, 877–886. doi:10.1093/brain/awl027.
Valafar, F. (2002). Pattern recognition techniques in microarray data analysis: A survey. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 980, 41–64.
Van, Q. N., Klose, J. R., Lucas, D. A., Prieto, D. A., Luke, B., Collins, J., Burt, S. K., Chmurny, G. N., Issaq, H. J., Conrads, T. P., Veenstra, T. D., & Keay, S. K. (2003). The use of urine proteomic and metabonomic patterns for the diagnosis of interstitial cystitis and bacterial cystitis. Disease Markers, 19, 169–183.
Van der, G. J., & McBurney, R. N. (2005). Innovation: Rescuing drug discovery: In vivo systems pathology and systems pharmacology. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 4, 961–967. doi:10.1038/nrd1904.
Vila, M., & Przedborski, S. (2004). Genetic clues to the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Nature Medicine, 10(Suppl), S58–S62. doi:10.1038/nm1068.
Visser, M., Marinus, J., Stiggelbout, A. M., & Van Hilten, J. J. (2004). Assessment of autonomic dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease: The SCOPA-AUT. Movement Disorders, 19, 1306–1312. doi:10.1002/mds.20153.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dave Broadhurst, Rick Dunn, Dave Ellis and Douglas Kell for assistance with the analyses. Funding: DJG is a British Heart Foundation Senior Research Fellow. AWM held a Parkinson’s Disease Society studentship and Sackler award.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
David J. Grainger and Roger A. Barker are the senior authors of this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Michell, A.W., Mosedale, D., Grainger, D.J. et al. Metabolomic analysis of urine and serum in Parkinson’s disease. Metabolomics 4, 191–201 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-008-0111-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-008-0111-9