Abstract
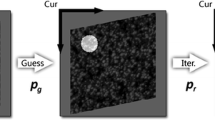
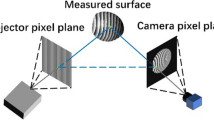
One of the necessary techniques for constructing a virtual museum is to estimate the surface normal and the albedo of the artwork which has high specularity. In this paper, we propose a novel photometric stereo method which is robust to the specular reflection of the object surface. Our method can also digitize the artwork arranged inside a glass or acrylic display case without bringing the artwork out of the display case. Our method treats the specular reflection at the object surface or at the display case as an outlier, and finds a good surface normal evading the influence of the outliers. We judiciously design the cost function so that the outlier will be automatically removed under the assumption that the object’s shape and color are smooth. At the end of this paper, we also show some archived 3D data of Segonko Tumulus and objects in the University Museum at The University of Tokyo that were generated by applying the proposed method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adobe Photoshop (2009). http://www.adobe.com/products/photoshop/ (ADOBE).
Agrawal, A. K., Raskar, R., & Chellappa, R. (2006). What is the range of surface reconstructions from a gradient field? In Proceedings of European conference on computer vision (pp. 578–591).
Alldrin, N., Zickler, T., & Kriegman, D. (2008). Photometric stereo with non-parametric and spatially-varying reflectance. In Proceedings of IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition.
Barsky, S., & Petrou, M. (2003). The 4-source photometric stereo technique for three-dimensional surfaces in the presence of highlights and shadows. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 25(10), 1239–1252.
Basri, R., Jacobs, D., & Kemelmacher, I. (2007). Photometric stereo with general, unknown lighting. International Journal of Computer Vision, 72(3), 239–257.
Belhumeur, P. N., Kriegman, D. J., & Yuille, A. L. (1999). The bas-relief ambiguity. International Journal of Computer Vision, 35(1), 33–44.
Birkbeck, N., Cobzas, D., Sturm, P., & Jagersand, M. (2006). Variational shape and reflectance estimation under changing light and viewpoints. In Proceedings of European conference on computer vision (pp. 536–549).
Chandraker, M., Agarwal, S., & Kriegman, D. (2007). ShadowCuts: Photometric stereo with shadows. In Proceedings of IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition.
Chen, C. P., & Chen, C. S. (2006). The 4-source photometric stereo under general unknown lighting. In Proceedings of European conference on computer vision (pp. 72–83).
Coleman, E. N. Jr. & Jain, R. (1982). Obtaining 3-dimensional shape of textured and specular surfaces using four-source photometry. Computer Graphics and Image Processing, 18(4), 309–328.
Courant, R., & Hilbert, D. (1953). Methods of mathematical physics. New York: Wiley (560 p.).
Drew, M. S. (1995). Reduction of rank-reduced orientation-from-color problem with many unknown lights to two-image known-illuminant photometric stereo. In Proceedings of international symposium on computer vision (pp. 419–424).
Eisemann, E., & Durand, F. (2004). Flash photography enhancement via intrinsic relighting. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 23(3), 673–678.
Farid, H., & Adelson, E. H. (1999). Separating reflections from images by use of independent component analysis. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 16(9), 2136–2145.
Fischler, M. A., & Bolles, R. C. (1981). Random sample consensus: A paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Communications of the ACM, 24(6), 381–395.
Fua, P., & Leclerc, Y. G. (1995). Object-centered surface reconstruction: combining multi-image stereo and shading. International Journal of Computer Vision, 16(1), 35–56.
Georghiades, A. S. (2003). Incorporating the Torrance and Sparrow model of reflectance in uncalibrated photometric stereo. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on computer vision (pp. 816–825).
Goldman, D., Curless, B., Hertzmann, A., & Seitz, S. M. (2005). Shape and spatially-varying BRDFs from photometric stereo. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on computer vision (pp. 341–348).
Hahn, D. V., Duncan, D. D., Baldwin, K. C., Cohen, J. D., & Purnomo, B. (2006). Digital Hammurabi: design and development of a 3D scanner for cuneiform tablets. Proceedings of SPIE, 6056, 130–141.
Hayakawa, H. (1994). Photometric stereo under a light source with arbitrary motion. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 11(11), 3079–3089.
Hertzmann, A., & Seitz, S. M. (2005). Example-based photometric stereo: Shape reconstruction with general, varying BRDFs. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 27(8), 1254–1264.
Horn, B. K. P. (1986). Robot vision. Cambridge: MIT Press (509 p.).
Ikeuchi, K. (1984). Reconstructing a depth map from intensity maps. In Proceedings of international conference on pattern recognition (pp. 736–738).
Kim, B., & Burger, P. (1991). Depth and shape from shading using the photometric stereo method. Image Understanding, 54(3), 416–427 (Proc. of CVGIP).
Klinker, G. J., Shafer, S. A., & Kanade, T. (1988). The measurement of highlights in color images. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2(1), 7–32.
Konica Minolta VIVID 910 (2009). http://www.minolta3d.com/products/vi910-en.asp (MINOLTA3D).
Levin, A., & Weiss, Y. (2004). User assisted separation of reflections from a single image using a sparsity prior. In Proceedings of European conference on computer vision (pp. 602–613).
Levin, A., Zomet, A., & Weiss, Y. (2004). Separating reflections from a single image using local features. In Proceedings of IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 306–313).
Li, Y., Sun, J., Tang, C. K., & Shum, H. Y. (2004). Lazy snapping. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 23(3), 303–308.
Lim, J., Ho, J., Yang, M. H., & Kriegman, D. (2005). Passive photometric stereo from motion. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on computer vision (pp. 1635–1642).
Lu, C., & Drew, M. S. (2006). Practical scene illuminant estimation via flash/no-flash pairs. In Proceedings of color imaging conference.
Lu, J., & Little, L. (1995). Reflectance function estimation and shape recovery from image sequence of a rotating object. In Proceedings of international conference on computer vision (pp. 80–86).
Magda, S., Kriegman, D. J., Zickler, T., & Belhumeur, P. N. (2001). Beyond Lambert: reconstructing surfaces with arbitrary BRDFs. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on computer vision (pp. 391–398).
Mukaigawa, Y., Ishii, Y., & Shakunaga, T. (2007). Analysis of photometric factors based on photometric linearization. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 24(10), 3326–3334.
Narasimhan, S. G., Nayar, S. K., Sun, B., & Koppal, S. J. (2005). Structured light in scattering media. In Proceedings of IEEE of international conference on computer vision (pp. 420–427).
Nayar, S. K., Ikeuchi, K., & Kanade, T. (1990). Determining shape and reflectance of hybrid surface by photometric sampling. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 6(4), 418–431.
Nayar, S. K., Ikeuchi, K., & Kanade, T. (1991a). Shape from interreflections. International Journal of Computer Vision, 6(3), 173–195.
Nayar, S. K., Ikeuchi, K., & Kanade, T. (1991b). Surface reflection: Physical and geometrical perspectives. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 13(7), 6119–634.
Nayar, S. K., Krishnan, G., Grossberg, M. D., & Raskar, R. (2006). Fast separation of direct and global components of a scene using high frequency illumination. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 25(3), 935–944.
Oishi, T., Nakazawa, A., Kurazume, R., & Ikeuchi, K. (2005). Fast simultaneous alignment of multiple range images using index images. In Proceedings of international conference on 3-D digital imaging and modeling (pp. 476–483).
Oo, T., Kawasaki, H., Ohsawa, Y., & Ikeuchi, K. (2007). The separation of reflected and transparent layers from real-world image sequence. Machine Vision and Applications, 18(1), 17–24.
Petschnigg, G., Agrawala, M., Hoppe, H., Szeliski, R., Cohen, M., & Toyama, K. (2004). Digital photography with flash and no-flash image pairs. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 23(3), 664–672.
Press, W. H. et al. (1997). Numerical recipes in C: the art of scientific computing. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press (994 p.).
Ragheb, H., & Hancock, E. R. (2004). Surface normals and height from non-Lambertian image data. In Proceedings of international symposium on 3D data processing, visualization and transmission (pp. 18–25).
Raskar, R., Tan, K. H., Feris, R., Yu, J., & Turk, M. (2004). Non-photorealistic camera: Depth edge detection and stylized rendering using multi-flash imaging. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 23(3), 679–688.
Rother, C., Kolmogorov, V., & Blake, A. (2004). GrabCut: Interactive foreground extraction using iterated graph cuts. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 23(3), 309–314.
Sarel, B., & Irani, M. (2004). Separating transparent layers through layer information exchange. In Proceedings of European conference on computer vision (pp. 328–341).
Sarel, B., & Irani, M. (2005). Separating transparent layers of repetitive dynamic behaviors. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on computer vision (pp. 26–32).
Sato, Y., & Ikeuchi, K. (1995). Reflectance analysis under solar illumination. In Proceedings of IEEE workshop on physics-based modeling and computer vision (pp. 180–187).
Sato, I., Okabe, T., Yu, Q., & Sato, Y. (2007). Shape reconstruction based on similarity in radiance changes under varying illumination. In Proceedings of international conference on computer vision.
Schechner, Y. Y., & Shamir, J. (2000). Polarization and statistical analysis of scenes containing a semireflector. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 17(2), 276–284.
Schechner, Y. Y., Kiryati, N., & Basri, R. (2000). Separation of transparent layers using focus. International Journal of Computer Vision, 39(1), 25–39.
Seitz, S. M., Matsushita, Y., & Kutulakos, K. N. (2005). A theory of inverse light transport. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on computer vision (pp. 1440–1447).
Shen, L., Machida, T., & Takemura, H. (2005). Efficient photometric stereo technique for three-dimensional surfaces with unknown BRDF. In Proceedings of conference on recent advances in 3-D digital imaging and modeling (pp. 326–333).
Simakov, D., Frolova, D., & Basri, R. (2003). Dense shape reconstruction of a moving object under arbitrary, unknown lighting. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on computer vision (pp. 1202–1209).
Solomon, F., & Ikeuchi, K. (1996). Extracting the shape and roughness of specular lobe objects using four light photometric stereo. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 18(4), 449–454.
Sun, J., Li, Y., Kang, S. B., & Shum, H. Y. (2006). Flash matting. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 25(3), 772–778.
Sun, J., Smith, M., Smith, L., Midha, S., & Bamber, J. (2007). Object surface recovery using a multi-light photometric stereo technique for non-Lambertian surfaces subject to shadows and specularities. Image and Vision Computing, 25(7), 1050–1057.
Szeliski, R., Avidan, S., & Anandan, P. (2000). Layer extraction from multiple images containing reflections and transparency. In Proceedings of IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 246–253).
Tan, P., Lin, S., & Quan, L. (2006) Resolution-enhanced photometric stereo. In Proceedings of European conference on computer vision (pp. 58–71).
Tan, P., Mallick, S. P., Quan, L., Kriegman, D. J., & Zickler, T. (2007). Isotropy, reciprocity and the generalized bas-relief ambiguity. In Proceedings of IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition.
Tang, K., Tang, C., & Wong, T. (2005). Dense photometric stereo using tensorial belief propagation. In Proceedings of IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 132–139).
Tominaga, S., Nakagawa, M., & Tanaka, N. (2004). Image rendering of art paintings-total archives considering surface properties and chromatic adaptation. In Proceedings of color imaging conference (pp. 70–75).
Tsai, R. Y. (1986). An efficient and accurate camera calibration technique for 3D machine vision. In Proceedings of IEEE Computer Society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 364–374).
Tu, P., & Mendonca, P. R. S. (2003). Surface reconstruction via Helmholtz reciprocity with a single image pair. In Proceedings of IEEE Computer Society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition.
Wada, T., Ukida, H., & Matsuyama, T. (1997). Shape from shading with interreflections under a proximal light source: Distortion-free copying of an unfolded book. International Journal of Computer Vision, 24(2), 125–135.
Woodham, R. J. (1980). Photometric method for determining surface orientation from multiple images. Optical Engineering, 19(1), 139–144.
Woodham, R. J., Iwahori, Y., & Barman, R. A. (1991). Photometric stereo: Lambertian reflectance and light sources with unknown direction and strength. Technical report.
Wu, T. P., & Tang, C. K. (2005). Dense photometric stereo using a mirror sphere and graph cut. In Proceedings of IEEE Computer Society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 140–147).
Wu, T. P., & Tang, C. K. (2006). Dense photometric stereo by expectation maximization. In Proceedings of European conference on computer vision (pp. 159–172).
Wu, T. P., Tang, K. L., Tang, C. K., & Wong, T. T. (2006). Dense photometric stereo: a Markov random field approach. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 28(11), 1830–1846.
Yang, J., Zhang, D., Ohnishi, N., & Sugie, N. (1997). Determining a polyhedral shape using interreflections. In Proceedings of IEEE Computer Society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 110–115).
Yuille, A. L., Snow, D., Epstein, R., & Belhumeur, P. N. (1999). Determining generative models of objects under varying illumination: Shape and albedo from multiple images using SVD and integrability. International Journal of Computer Vision, 35(3), 203–222.
Zhang, L., Curless, B., Hertzmann, A., & Seitz, S. M. (2003). Shape and motion under varying illumination: Unifying structure from motion, photometric stereo, and multi-view stereo. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on computer vision (pp. 618–625).
Zickler, T., Belhumeur, P. N., & Kriegman, D. J. (2002). Helmholtz stereopsis: Exploiting reciprocity for surface reconstruction. International Journal of Computer Vision, 215–227.
Zickler, T. E., Belhumeur, P. N., & Kriegman, D. J. (2003). Toward a stratification of Helmholtz stereopsis. In Proceedings of IEEE Computer Society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyazaki, D., Hara, K. & Ikeuchi, K. Median Photometric Stereo as Applied to the Segonko Tumulus and Museum Objects. Int J Comput Vis 86, 229–242 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-009-0262-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-009-0262-9