Abstract
Objectives
To investigate whether plasma cell-free DNA (cfDNA) or its integrity could differentiate prostate cancer from benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH) in patients with serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) ≥ 4 ng/ml.
Methods
Ninety-six patients with prostate cancer and 112 patients with BPH were enrolled. cfDNA levels in plasma before prostate biopsy were quantified by real-time PCR amplification of ALU gene (product size of 115 bp), and quantitative ratio of ALU (247 bp) to ALU (115 bp) reflected the integrity of cfDNA.
Results
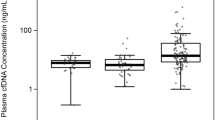
In patients with serum PSA ≥ 4 ng/ml, there were significant differences in plasma cfDNA or its integrity between the patients with prostate cancer (19.74 ± 4.43, 0.34 ± 0.05) and patients with BPH (7.36 ± 1.58, 0.19 ± 0.03; P < 0.001, P < 0.001). Prostate cancer could be differentiated with a sensitivity of 73.2 % and a specificity of 72.7 % by cfDNA (AUC = 0.864). The integrity of cfDNA had a sensitivity of 81.7 % and a specificity of 78.8 % for the distinguishing prostate cancer from BPH (AUC = 0.910).
Conclusions
cfDNA and its integrity could be applied to differentiate prostate cancer from BPH in patients with serum PSA ≥ 4 ng/ml.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E (2010) Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin 60:277–300
Strope SA, Andriole GL (2010) Prostate cancer screening: current status and future perspectives. Nat Rev Urol 7:487–493
Porcaro AB, Migliorini F, Romano M et al (2010) Investigative clinical study on prostate cancer: on the role of the pretreatment total PSA to free testosterone ratio in selecting different biology groups of prostate cancer patients. Int Urol Nephrol 42:673–681
Heijnsdijk EA, der Kinderen A, Wever EM et al (2009) Overdetection, overtreatment and costs in prostate-specific antigen screening for prostate cancer. Br J Cancer 101:1833–1838
Wang BG, Huang HY, Chen YC et al (2003) Increased plasm DNA integrity in cancer patients. Cancer Res 63:3966–3968
Schwarzenbach H, Hoon DS, Pantel K (2011) Cell-free nucleic acids as biomarkers in cancer patients. Nat Rev Cancer 11:426–437
Schwarzenbach H, Alix-Panabières C, Müller I et al (2009) Cell-free tumor DNA in blood plasma as a marker for circulating tumor cells in prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 15:1032–1038
Umetani N, Giuliano AE, Hiramatsu SH et al (2006) Prediction of breast tumor progression by integrity of free circulating DNA in serum. J Clin Oncol 24:4270–4276
Gui-Zhong L, Libo M, Guanglin H et al (2011) The correlation of extent and grade of inflammation with serum PSA levels in patients with IV prostatitis. Int Urol Nephrol 43:295–301
Heidenreich A, Aus G, Bolla M et al (2008) Eau guidelines on prostate cancer. Eur Urol 53:68–80
Strittmatter F, Stieber P, Nagel D et al (2011) Detection of prostate cancer with complexed PSA and complexed/total PSA ratio—is there any advantage? Eur J Med Res 16:445–450
Ellinger J, Wittkamp V, Albers P et al (2009) Cell-free circulating DNA: diagnostic value in patients with testicular germ cell cancer. J Urol 181:363–371
Kumar S, Guleria R, Singh V et al (2010) Efficacy of circulating plasma DNA as a diagnostic tool for advanced non-small cell lung cancer and its predictive utility for survival and response to chemotherapy. Lung Cancer 70:211–217
Gang F, Guorong L, An Z et al (2010) Prediction of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by integrity of cell-free DNA in serum. Urology 75:262–265
Wu TL, Zhang D, Chia JH et al (2002) Cell-free DNA: measurement in various carcinomas and establishment of normal reference range. Clin Chim Acta 321:77–87
Papadopoulou E, Davilas E, Sotiriou V et al (2004) Cell-free DNA in plasma as a new molecular marker for prostate cancer. Oncol Res 14:439–445
Altimari A, Grigioni AD, Benedettini E et al (2008) Diagnostic role of circulating free plasma DNA detection in patients with localized prostate cancer. Am J Clin Pathol 129:756–762
Boddy JL, Gal S, Malone PR et al (2005) Prospective study of quantitation of plasma DNA levels in the diagnosis of malignant versus benign prostate disease. Clin Cancer Res 11:1394–1399
Gordian E, Ramachandran K, Reis IM et al (2010) Serum free circulating DNA is a useful biomarker to distinguish benign versus malignant prostate disease. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 19:1984–1991
Hanley R, Rieger-Christ KM, Canes D et al (2006) DNA integrity assay: a plasma-based screening tool for the detection of prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 12:4569–4574
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Yijishan Hospital of Wannan Medical College (WK2011F26 and YR201112).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, J., Gang, F., Li, X. et al. Plasma cell-free DNA and its DNA integrity as biomarker to distinguish prostate cancer from benign prostatic hyperplasia in patients with increased serum prostate-specific antigen. Int Urol Nephrol 45, 1023–1028 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-013-0491-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-013-0491-2