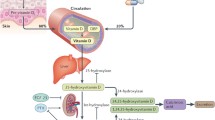
Abstract
Vitamin D deficiency results in abnormal mineralization of bones and has resulted in prevention programs for children with supplementation when they are breast fed. Further activities of vitamin D relate to defence of microbial infections, e.g. tuberculosis, prevention of cancer, contractility of muscle cells and counteraction of congestive heart failure. Given early reports in the 1960s on deleterious effects of vitamin D supplementation in rodents, that is ectopic media ossification of arterial vessels, a pro-atherogenic function had been anticipated for humans as well. However, cross-sectional studies reveal that vitamin D deficiency in humans is associated with elevated blood pressure and propagation of atherogenesis. These contradictory findings on the progression of atherosclerosis may be reconciled by dissecting the activation mechanism(s) of vitamin D in rodents versus humans. Notably, novel findings convincingly indicate that vitamin D exerts anti-inflammatory effects. In conclusion, vitamin D supplementation in adults may be regarded as simple means with few potential side effects to prevent atherogenesis or halt its progression and combat arterial hypertension. Adjustment of vitamin D dosing regimens is required in patients with chronic kidney disease; however, prospective clinical trials are urgently needed to guide these recommendations with evidence.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Holick MF (2007) Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J Med 357:266
Bouillon R, Bischoff-Ferrari H, Willett W (2008) Vitamin D and health: perspectives from mice and man. J Bone Miner Res 23:974
Rammos G, Tseke P, Ziakka S (2008) Vitamin D, the renin-angiotensin system, and insulin resistance. Int Urol Nephrol 40:419
Tan X, Wen X, Liu Y (2008) Paricalcitol inhibits renal inflammation by promoting vitamin D receptor-mediated sequestration of NF-kappaB signaling. J Am Soc Nephrol 19:1741
Tian S, Li J, Wang L et al (2007) Urinary levels of RANTES and M-CSF are predictors of lupus nephritis flare. Inflamm Res 56:304
Raffetseder U, Rauen T, Djudjaj S et al (2009) Differential regulation of chemokine CCL5 expression in monocytes/macrophages and renal cells by Y-box protein-1. Kidney Int 75:185
Krohn R, Raffetseder U, Bot I et al (2007) Y-box binding protein-1 controls CC chemokine ligand-5 (CCL5) expression in smooth muscle cells and contributes to neointima formation in atherosclerosis-prone mice. Circulation 116:1812
Eleftheriadis T, Antoniadi G, Liakopoulos V et al. (2009) Paricalcitol reduces basal and lipopolysaccharide-induced (LPS) TNF-alpha and IL-8 production by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Int Urol Nephrol
Hass GM, Landerholm W, Hemmens A (1966) Production of calcific athero-arteriosclerosis and thromboarteritis with nicotine, vitamin D and dietary cholesterol. Am J Pathol 49:739
Inoue T, Kawashima H (1988) 1, 25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 stimulates 45Ca2 + -uptake by cultured vascular smooth muscle cells derived from rat aorta. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 152:1388
Micheletti RG, Fishbein GA, Currier JS et al (2008) Monckeberg sclerosis revisited: a clarification of the histologic definition of Monckeberg sclerosis. Arch Pathol Lab Med 132:43
Moe SM, O’Neill KD, Duan D et al (2002) Medial artery calcification in ESRD patients is associated with deposition of bone matrix proteins. Kidney Int 61:638
Gottfried E, Rehli M, Hahn J et al (2006) Monocyte-derived cells express CYP27A1 and convert vitamin D3 into its active metabolite. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 349:209
Rostand SG (1997) Ultraviolet light may contribute to geographic and racial blood pressure differences. Hypertension 30:150
Melamed ML, Michos ED, Post W et al (2008) 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and the risk of mortality in the general population. Arch Intern Med 168:1629
Krause R, Buhring M, Hopfenmuller W et al (1998) Ultraviolet B and blood pressure. Lancet 352:709
Sugden JA, Davies JI, Witham MD et al (2008) Vitamin D improves endothelial function in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and low vitamin D levels. Diabet Med 25:320
Pfeifer M, Begerow B, Minne HW et al (2001) Effects of a short-term vitamin D(3) and calcium supplementation on blood pressure and parathyroid hormone levels in elderly women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:1633
Zhou C, Lu F, Cao K et al (2008) Calcium-independent and 1, 25(OH)2D3-dependent regulation of the renin-angiotensin system in 1alpha-hydroxylase knockout mice. Kidney Int 74:170
Yuan W, Pan W, Kong J et al (2007) 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 suppresses renin gene transcription by blocking the activity of the cyclic AMP response element in the renin gene promoter. J Biol Chem 282:29821
Fitzpatrick LA, Bilezikian JP, Silverberg SJ (2008) Parathyroid hormone and the cardiovascular system. Curr Osteoporos Rep 6:77
Peterlik M, Cross HS (2005) Vitamin D and calcium deficits predispose for multiple chronic diseases. Eur J Clin Invest 35:290
Scragg R, Sowers M, Bell C (2007) Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D, ethnicity, and blood pressure in the third national health and nutrition examination survey. Am J Hypertens 20:713
Wang TJ, Pencina MJ, Booth SL et al (2008) Vitamin D deficiency and risk of cardiovascular disease. Circulation 117:503
Pilz S, Dobnig H, Fischer JE et al (2008) Low vitamin D levels predict stroke in patients referred to coronary angiography. Stroke 39:2611
Michos ED, Melamed ML (2008) Vitamin D and cardiovascular disease risk. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 11:7
Dobnig H, Pilz S, Scharnagl H et al (2008) Independent association of low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D levels with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. Arch Intern Med 168:1340
Melamed ML, Muntner P, Michos ED et al (2008) Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and the prevalence of peripheral arterial disease: results from NHANES 2001 to 2004. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28:1179
Pilz S, Marz W, Wellnitz B et al (2008) Association of vitamin D deficiency with heart failure and sudden cardiac death in a large cross-sectional study of patients referred for coronary angiography. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:3927
Reis J P, von Muhlen D, Michos E D et al. (2009) Serum vitamin D, parathyroid hormone levels, and carotid atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis, (in press)
Kovesdy CP, Kalantar-Zadeh K (2008) Bone and mineral disorders in pre-dialysis CKD. Int Urol Nephrol 40:427
Wang AY, Lam CW, Sanderson JE et al (2008) Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D status and cardiovascular outcomes in chronic peritoneal dialysis patients: a 3-year prospective cohort study. Am J Clin Nutr 87:1631
Wolf M, Shah A, Gutierrez O et al (2007) Vitamin D levels and early mortality among incident hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int 72:1004
Teng M, Wolf M, Lowrie E et al (2003) Survival of patients undergoing hemodialysis with pricalcitol or calcitriol therapy. N Engl J Med 349:446
Teng M, Wolf M, Ofsthun MN et al (2005) Activated injectable vitamin D and hemodialysis survival: a historical cohort study. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:1115
Mosekilde L (2005) Vitamin D and the elderly. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 62:265
Daher EF, Silva Junior GB, Queiroz AL et al (2009) Acute kidney injury due to anabolic steroid and vitamin supplement abuse: report of two cases and a literature review. Int Urol Nephrol 41:717
Taskapan H, Vieth R, Oreopoulos DG (2008) Unusually prolonged vitamin D intoxication after discontinuation of vitamin D: possible role of primary hyperparathyroidism. Int Urol Nephrol 40:801
Acknowledgement
Work of PRM is supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB542, TRR57, SFB854).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mertens, P.R., Müller, R. Vitamin D and cardiovascular risk. Int Urol Nephrol 42, 165–171 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-009-9685-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-009-9685-z