Abstract
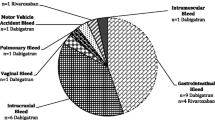
Although new oral anticoagulants (NOAs) have been marketed in many countries, concern exists about the management of bleedings related to these drugs due to the lack of specific antidotes. The aim of our study was to report on real life management of NOAs-related life-threatening or major bleedings. We report data from consecutive cases of NOAs related major bleedings admitted to 4 hospitals since NOAs became marketed in Italy. We treated 8 patients, 4 males, with mean age 84 ± 7 years, 7 of whom were on dabigatran and one on rivaroxaban. The indication for NOA was atrial fibrillation. All bleedings were spontaneous and involving the gastro-intestinal tract. At the time of bleeding all patients had a drop in hemoglobin levels over 20 g/L. Creatinine clearance was ≤30 mL/min in 4 patients. All patients received general supportive measures, 4 of 8 patients were transfused with packed red cells and one patient received platelet transfusion. Three patients were treated with tranexamic acid and one patient on dabigatran received 4-factor prothrombin complex concentrate (PCC) with bleeding cessation, although coagulation parameters were not corrected. The median time for normalization of coagulation parameters was 3 days (range 1–6 days). All patients were discharged alive and NOAs were discontinued. In NOAs related major gastro-intestinal bleeding general supportive measures seem to be effective for the majority of patients. Despite promoting bleeding cessation, 4-factor PCC does not reverse abnormal coagulation parameters.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miller CS, Grandi SM, Shimony A, Filion KB, Eisenberg MJ (2012) Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants (dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban) versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol 110:453–460
van der Hulle T, Kooiman J, den Exter PL, Dekkers OM, Klok FA, Huisman MV (2014) Effectiveness and safety of novel oral anticoagulants as compared with vitamin K antagonists in the treatment of acute symptomatic venous thromboembolism: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Thromb Haemost 12:320–328
Ruff CT, Giugliano RP, Braunwald E et al (2013) Comparison of the efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants with warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet. Ahead epub of print
Holster IL, Valkhoff VE, Kuipers EJ, Tjwa ET (2013) New oral anticoagulants increase risk for gastrointestinal bleeding: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 145(105–12):e15
Southworth MR, Reichman ME, Unger EF (2013) Dabigatran and post-marketing reports of bleeding. N Engl J Med 368:1272–1274
Larsen TB, Rasmussen LH, Skjøth F, Due KM, Callréus T, Rosenzweig M, Lip GY (2013) Efficacy and safety of dabigatran etexilate and warfarin in “real-world” patients with atrial fibrillation: a prospective nationwide cohort study. J Am Coll Cardiol 61:2264–2273
Miesbach W, Seifried E (2012) New direct oral anticoagulants—current therapeutic options and treatment recommendations for bleeding complications. Thromb Haemost 108:625–632
Pernod G, Albaladejo P, Godier A et al (2013) Working group on perioperative haemostasis. Management of major bleeding complications and emergency surgery in patients on long-term treatment with direct oral anticoagulants, thrombin or factor-Xa inhibitors: proposals of the working group on perioperative haemostasis (GIHP)—March 2013. Arch Cardiovasc Dis 106:382–393
Heidbuchel H, Verhamme P, Alings M et al (2013) European Heart Rhythm Association. European Heart Rhythm Association practical guide on the use of new oral anticoagulants in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Europace 15:625–651
Ward C, Conner G, Donnan G, Gallus A, McRae S (2013) Practical management of patients on apixaban: a consensus guide. Thromb J 11:27
Schulman S, Kearon C (2005) Definition of major bleeding in clinical investigations of antihemostatic medicinal products in non-surgical patients. J Thromb Haemost 3:692–694
Harper P, Young L, Merriman E (2012) Bleeding risk with dabigatran in the frail elderly. N Engl J Med 366:864–866
Harinstein LM, Morgan JW, Russo N (2013) Treatment of dabigatran-associated bleeding: case report and review of the literature. J Pharm Pract 26:264–269
Berger R, Salhanick SD, Chase M, Ganetsky M (2013) Hemorrhagic complications in emergency department patients who are receiving dabigatran compared with warfarin. Ann Emerg Med 61:475–479
Díaz MQ, Borobia AM, Núñez MA et al (2013) Use of prothrombin complex concentrates for urgent reversal of dabigatran in the Emergency Department. Haematologica 98:e143–e144
McDonald CJ, Kalish Ellett LM, Barratt JD, Caughey GE (2014) An international comparison of spontaneous adverse event reports and potentially inappropriate medicine use associated with dabigatran. Pharamacoepidemiol Drug Saf 2014; epub ahead of print
FDA Drug Safety Communication 2014 May 5. FDA study of Medicare patients finds risks lower for stroke and death but higher for gastrointestinal bleeding with Pradaxa (dabigatran) compared to warfarin
Beyer-Westendorf J, Forster K, Pannach S et al (2014) Rates, management and outcome of bleeding complications during rivaroxaban therapy in daily care-results from the Dresden NOAC registry. Blood; epub ahead of print
Desai J, Kolb JM, Weitz JI, Aisenberg J (2013) Gastrointestinal bleeding with the new oral anticoagulants-defining the issue and the management strategies. Thromb Haemost 110:205–212
Blech S, Ebner T, Ludwig-Schwellinger E, Stangier J, Roth W (2008) The metabolism and disposition of the oral direct thrombin inhibitor, dabigatran, in humans. Drug Metab Dispos 36:386–399
Lang D, Freudenberger C, Weinz C (2009) In vitro metabolism of rivaroxaban, an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor, in liver microsomes and hepatocytes of rats, dogs, and humans. Drug Metab Dispos 37:1046–1055
Heidbuchel H, Verhamme P, Alings M et al (2013) European Heart Rhythm Association. European Heart Rhythm Association Practical Guide on the use of new oral anticoagulants in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Europace 15:625–651
Lega JC, Bertoletti L, Gremillet C et al (2014) Meta-embol group. consistency of safety and efficacy of new oral anticoagulants across subgroups of patients with atrial fibrillation. PLoS ONE 9:e91398
Fontaine GV, Mathews K, Woller SC, Lloyd JF (2014) Major bleeding with dabigatran and rivaroxaban in patients with atrial fibrillation: a real-world setting. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost; epub ahead of print
Baglin T, Hillarp A, Tripodi A, Elalamy I, Buller H, Ageno W (2013) Measuring oral direct inhibitors (ODIs) of thrombin and factor Xa: a recommendation from the subcommittee on control of anticoagulation of the scientific and standardisation committee of the international society on thrombosis and haemostasis. J Thromb Haemost [Epub ahead of print]
Harenberg J, Marx S, Weiss C, Krämer R, Samama M, Schulman S (2012) Subcommittee on control of anticoagulation of the ISTH. Report of the subcommittee of control of anticoagulation on the determination of the anticoagulant effects of rivaroxaban. J Thromb Haemost 10:1433–1436
Douxfils J, Chatelain C, Chatelain B, Dogné JM, Mullier F (2013) Impact of apixaban on routine and specific coagulation assays: a practical laboratory guide. Thromb Haemost 110:283–294
Majeed A, Hwang HG, Connolly SJ et al (2013) Management and outcomes of major bleeding during treatment with dabigatran or warfarin. Circulation; epub ahead of print
Piccini JP, Garg J, Patel MR et al. Management of major bleedings events in patients treated with rivaroxaban vs warfarin: results from ROCKET AF trial. Eur Heart J; epub ahead of print
van Ryn J, Stangier J, Haertter S, Liesenfeld KH, Wienen W, Feuring M, Clemens A (2010) Dabigatran etexilate—a novel, reversible, oral direct thrombin inhibitor: interpretation of coagulation assays and reversal of anticoagulant activity. Thromb Haemost 103:1116–1127
Lillo-Le Louët A, Wolf M, Soufir L et al (2012) Life-threatening bleeding in four patients with an unusual excessive response to dabigatran: implications for emergency surgery and resuscitation. Thromb Haemost 108:583–585
Schulman S, Ritchie B, Goy JK, Nahirniak S, Almutawa M, Ghanny S (2014) Activated prothrombin complex concentrate for dabigatran-associated bleeding. Br J Haematol 164:308–310
Eerenberg ES, Kamphuisen PW, Sijpkens MK, Meijers JC, Buller HR, Levi M (2011) Reversal of rivaroxaban and dabigatran by prothrombin complex concentrate: a randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover study in healthy subjects. Circulation 124:1573–1579
Hoffman M, Dargaud Y (2012) Mechanisms and monitoring of bypassing agent therapy. J Thromb Haemost 10:1478–1485
Herrmann R, Thom J, Wood A, Phillips M, Muhammad S, Baker R (2013) Thrombin generation using the calibrated automated thrombinoscope to assess reversibility of dabigatran and rivaroxaban. Thromb Haemost 111(5). Epub ahead of print
Escolar G, Fernandez-Gallego V, Arellano-Rodrigo E et al (2013) Reversal of apixaban induced alterations in hemostasis by different coagulation factor concentrates: significance of studies in vitro with circulating human blood. PLoS ONE 8:e78696
Schiele F, van Ryn J, Canada K, Newsome C, Sepulveda E, Park J, Nar H, Litzenburger T (2013) A specific antidote for dabigatran: functional and structural characterization. Blood 121:3554–3562
Lu G, Deguzman FR, Hollenbach SJ, Karbarz MJ, Abe K, Lee G, Luan P, Hutchaleelaha A, Inagaki M, Conley PB, Phillips DR, Sinha U (2013) A specific antidote for reversal of anticoagulation by direct and indirect inhibitors of coagulation factor Xa. Nat Med 19:446–451
Grottke O, van Ryn J, Spronk HM, Rossaint R (2014) Prothrombin complex concentrates and a specific antidote to dabigatran are effective ex vivo in reversing the effects of dabigatran in an anticoagulation/liver trauma experimental model. Crit Care 18:R27
Acknowledgments
We are indebted with Lamberto Fattorini, Sandra Gori, Annamaria Bellizzi, Patrizia Fenu and Raffaella Bassu for the help in collecting patients data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masotti, L., Lorenzini, G., Seravalle, C. et al. Management of new oral anticoagulants related life threatening or major bleedings in real life: a brief report. J Thromb Thrombolysis 39, 427–433 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-014-1112-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-014-1112-3