Abstract
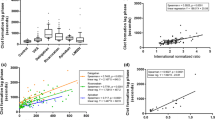
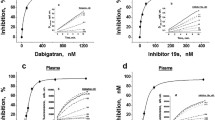
This study aimed to assess whether a global hemostatic assay we developed can measure the anticoagulant effects of the direct thrombin inhibitors (DTIs)—dabigatran and argatroban. A normal plasma pool (NPP) spiked with one of the DTIs and five plasma samples from patients with coronary heart disease spiked with dabigatran were examined. Fibrin formation and fibrin degradation were initiated by adding recombinant tissue factor (together with washed-frozen-thawed platelets and CaCl2) and recombinant tissue plasminogen activator. Fibrin optical density (OD) was recorded, based on which coagulation activation profile (Cp) and fibrinolysis activation profile (Fp) were determined. Moreover, the sum of OD values registered over time (fibrin OD-sum) was calculated to reflect the capacity of fibrin formation under the general effect by Cp and Fp. The endogenous thrombin potential (ETP) and the standard clotting markers i.e., activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) and prothrombin time expressed as International Normalized Ratio (INR) were also analyzed. Results demonstrated that APTT, INR and ETP could detect the effects of the DTIs except for INR in NPP containing dabigatran. In our global assay, the DTIs depressed the fibrin formation (shown as decreased fibrin OD-sum value) by leading to decrease of Cp and increase of Fp. Thus, our global assay which examines both fibrin formation and degradation seems more advantageous than the other methods mentioned above, as regards the possibility of being a laboratory tool to monitor the antithrombotic therapy with DTIs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boos CJ, Lip GYH (2006) Ximelagatran: an eulogy. Thromb Res 118:301–304
Hirsh J, Bauer KA, Donati MB, Gould M, Samama MM, Weitz JL (2008) Parenteral anticoagulants: American College of Chest physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest 133(6 suppl):141S–159S
Hursting MJ, Alford KL, Becker J-P et al (1997) Novastan R (brand of argatroban): a small molecule, direct thrombin inhibitor. Semin Thromb Haemost 23:403–515
Alatri A, Armstrong A-E, Greinacher A et al (2012) Results of a consensus meeting on the use of argatroban in patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia requiring antithrombotic therapy-an European Perspecive. Thromb Res 129:426–433
Engström M, Rundgren M, Schött U (2010) An evaluation of monitoring possibilities of argatroban using rotational thromboelastography and activated partial thromboplastin time. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 54:86–91
Schulman S, Kearon C, Kakkar AK, For the RE-COVER Study Group et al (2009) Dabigatran versus warfarin in the treatment of acute venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med 361:2342–2352
Eriksson BI, Dahl OE, Rosencher N, For the RE- Novate study group et al (2007) Dabigatran etexilate versus enoxaparin for prevention of venous thromboembolism after total hip replacement: a randomized, double-blind, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 370:949–956
Connolly SJ, Ezekowitz MD, Yusuf S et al, RE-LY Steering Committee and Investigators (2009) Dabigatran versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 361:1139–1151
Eikelboom JW, Weitz JI (2011) New oral anticoagulants for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation. Clin Invest 1:3–7
van Ryn J, Stangier J, Haertter S et al (2010) Dabigatran etexilate—a novel reversible, oral direct thrombin inhibitor: interpretation of coagulation assays and reversal of anticoagulant activity. Thromb Haemost 103:1116–1127
Lindahl TL, Baghaei F, Blixter IF et al (2011) Effects of the oral, direct thrombin inhibitor dabigatran on five common coagulation assays. Thromb Haemost 105:371–378
He S, Antovic A, Blombäck M (2001) A simple and rapid laboratory method for determination of haemostasis potential in plasma. II. Modifications for use in routine laboratories and research work. Thromb Res 103:355–361
He S, Zhu K, Skeppholm M, Vedin J et al (2007) A global assay of haemostasis which uses recombinant tissue factor and tissue-type plasminogen activator to measure the rate of fibrin formation and fibrin degradation in plasma. Thromb Haemost 98:871–882
Hemker HC, Al Dieri R, De Smedt E, Bèguin S (2006) Thrombin generation, a function test of haemostatic-thrombotic system. Thromb Haemost 96:553–561
He S, Ekman GJ, Hedner U (2005) The effect of platelets on fibrin gel structure formed in the presence of recombinant factor VIIa in hemophilia plasma and in plasma from a patient with Glanzmann thrombasthenia. J Thromb Haemost 3:272–279
He S, Blombäck M, Bark N, Johnsson H, Wallèn NH (2010) The direct thrombin inhibitors (argatroban, bivalirudin and lepirudin) and the indirect Xa-inhibitor (danaparoid) increase fibrin network porosity and thus facilitate fibrinolysis. Thromb Haemost 103:1076–1084
Collet JP, Park D, Lesty C, Soria J, Soria C, Montalescot G, Weisel JW (2000) Influence of fibrin network conformation and fibrin fiber diameter on fibrinolysis speed: dynamic and structural approaches by confocal microscopy. Arterioscler ThrombVasc Biol 20:1354–1361
Samama MM, Le Flem L, Guinet C, Gerotziafas G, Depasse F (2007) Three different patterns of calibrated automated thrombogram obtained with six different anticoagulants. J Thromb Haemost 5:2554–2556
Wienen W, Stassen JM, Priepke H, Ries UJ, Hauel N (2007) In-vitro profile and ex-vivo anticoagulant activity of the direct thrombin inhibitor dabigatran and its orally active prodrug, dabigatran etexilate. Thromb Haemost 98:155–162
Wiman B, Andersson T, Hallqvist J, Reuterwall C, Ahlbom A, deFaire U (2000) Plasma levels of tissue plasminogen activator/plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 complex and von Willebrand factor are significant risk markers for recurrent myocardial infarction in the Stockholm Heart Epidemiology Program (SHEEP) study. Arterioscler Thromb VascBiol 20:2019–2023
Gorog DA (2010) Prognostic value of plasma fibrinolysis activation markers in cardiovascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 55:2701–2709
Fatah K, Beving H, Albåge A, Ivert T, Blombäck M (1996) Acetylsalicylic acid may protect the patient by increasing fibrin gel porosity. Is withdrawing of treatment harmful to the patient ? Eur Heart J 17:1362–1366
He S, Bark N, Wang H, Svensson J, Blombäck M (2009) Effects of acetylsalicylic acid on increase of fibrin network porosity and the consequent upregulation of fibrinolysis. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 53:24–29
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Ingrid Jacobsson, Airi Åsen, Nida Soutani, Fariborz Mobarrez and Dr. Graciela Elgue for their excellent assistance in the laboratory work. The study was supported by Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH, Biberach, Germany, and by funds from Karolinska Institutet and Magnus Bergvall Foundation.
Conflict of interest
The work was supported by Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH, Biberach, Germany
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, S., Wallèn, H., Bark, N. et al. In vitro studies using a global hemostasis assay to examine the anticoagulation effects in plasma by the direct thrombin inhibitors: dabigatran and argatroban. J Thromb Thrombolysis 35, 131–139 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-012-0791-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-012-0791-x