Abstract
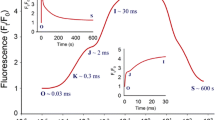
The effect of temperature, O2 and Mg++ on the kinetic characteristics of the slow inactivation (fallover) of Rubisco isolated from spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) was determined. Comparing 25 and 45 °C, the rate of activity decline of Rubisco increased by 20-fold, but the final ratio of steady state to initial activity increased from 0.38 to 0.62, respectively. Low CO2 increased the extent of fallover but only caused a marginal increase in fallover rate in agreement with results reported previously. In contrast, increased O2 during catalysis significantly increased only the fallover rate. Low Mg++ greatly increased the fallover of Rubisco both in rate and extent. Rubisco carbamylation was assayed using a new separation technique and it revealed that a loss of carbamylation largely accounted for the increased fallover observed with low Mg++. In conclusion, Rubisco fallover is facilitated by high temperature, low concentration of CO2 or Mg++, and high O2. The physiological importance of these factors in affecting Rubisco fallover and contributing to photosynthetic inhibition at high temperatures in planta are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Fallover:
-
slow inactivation of Rubisco during catalysis
- Rubisco:
-
ribulose-1,5-bisphosph ate carboxylase/oxygenase
- ribulose-P2 :
-
ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate
- pentodiulose-P2 :
-
glycero-2,3-diulose-1,5-bisphosphate
- xylulose-P2 :
-
xylulose-1,5-bisphosphate
- carboxytetritol-P2 :
-
2′-carboxytetritol-1,4-bisph osphate
- carboxyarabinitol-P2 :
-
2-carboxyarabinitol-1,5-bisphosphate
References
NG Bukhov, C Wiese, S Neimanis and U Heber, Heat sensitivity of chloroplasts and leaves: leakage of protons from thylakoids and reversible activation of cyclic electron transport. Photosynth Res 59 (1999) 81-93
YR Chen and FC Harman, A signature of the oxygenase intermediate in cataylsis by ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase as provided by a site-directed mutant. J Biol Chem 270 (1995) 11741-11744
SJ Crafts-Brandner and ME Salvucci, Rubisco activase constrains the photosynthetic potential of leaves at high temperature and CO2. Proc Natl Aca Sci USA 97 (2000) 13430-13435
DL Edmondson, MR Badger and TJ Andrews, A kinetic characterization of slow inactivation of Ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase during catalysis. Plant Physiol 93 (1990a) 1376-1382
DL Edmondson, MR Badger and TJ Andrews, Slow inactivation of Ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase during catalysis is caused by accumulation of a slow tight-binding inhibitor at the catalytic site. Plant Physiol 93 (1990b) 1390-1397
DL Edmondson, MR Badger and TJ Andrews, Slow inactivation of Ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase during catalysis is not due to decarbamylation of the catalytic site. Plant Physiol 93 (1990c) 1383-1389
DL Edmondson, HJ Kane and TJ Andrews, Substrate isomerization inhibits ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase– oxygenase during catalysis. FEBS Lett 260 (1990d) 62-66
MR Harpel, EH Serpersu, JA Lamerdin, ZH Huang, DA Gage and FC Hartman, Oxygenation mechanism of Ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. Structure and origin of 2-carboxytetritol 1,4-bisphosphate, a novel O2-dependent side product generated by a site-directed mutant. Biochemistry 34 (1995) 11296-11306
NP Hall and NE Tolbert, A rapid procedure for the isolation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from spinach leaves. FEBS Lett 96 (1978) 167-169
S Ishijima, A Uchibori, H Takagi, R Maki and M Ohnishi, Light-induced increase in free Mg2+ concentration in spinach chloroplasts: measurement of free Mg2+ by using a fluorescent probe and necessity of stromal alkalinization. Arch Biochem Biophys 412 (2003) 126-132
DB Jordan, R Chollet and WL Ogren, Binding of phosphorylated effectors by active and inactive forms of Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. Biochemistry 22 (1983) 3410-3418
DB Jordan and WL Ogren, The CO2/O2 specificity of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. Dependence on ribulosebisphosphate concentration, pH and temperature. Planta 161 (1984) 308-313
HJ Kane, JM Wilkin, AR Portis and TJ Andrews, Potent inhibition of ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase by an oxidized impurity in ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate. Plant Physiol 117 (1998) 1059-1069
K Kim and AR Portis Jr, Oxygen-dependent H2O2 production by Rubisco. FEBS Lett 571 (2004) 124-128
K Kim and AR Portis Jr, Temperature dependence of photosynthesis in Arabidopsis plants with modifications in Rubisco activase and membrane fluidity. Plant Cell Physiol 46 (2005) 522-530
WA Laing and JT Christeller, A model for the kinetics of activation and catalysis of Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. Biochem J 159 (1976) 563-570
EM Larson, CM O’Brien, G Zhu, RJ Spreitzer and AR Portis Jr, Specificity of activase is changed by a Pro-89 to Arg substitution in the large subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. J Biol Chem 272 (1997) 17033-17037
GH Lorimer, MR Badger and TJ Andrews, The activation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase by carbon dioxide and magnesium ions. Equilibria, kinetics, a suggested mechanism, and physiological implications. Biochemistry 15 (1976) 529-536
SD McCurry and NE Tolbert, Inhibition of Ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase by Xylulose 1,5-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem 252 (1977) 8344-8346
D Paech, J Pierce, SD McCurry and NE Tobert, Inhibition of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase by ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate epimerization and degradation products. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 83 (1978) 1084-1092
MA Parry, PJ Andralojc, RAC Mitchell, PJ Madgwick and AJ Keys, Manipulation of Rubisco: the amount, activity, function and regulation. J Exp Bot 54 (2003) 1321-1333
FG Pearce and TJ Andrews, The relationship between side reactions and slow inhibition of Ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase revealed by a loop 6 mutant of the tobacco enzyme. J Biol Chem 278 (2003) 32526-32536
AR Portis, RM Lilley and TJ Andrews, Subsaturating ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate concentration promotes inactivation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco). Plant Physiol 109 (1995) 1441-1451
AR Portis Jr, Regulation of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activity. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Mol Biol 43 (1992) 415-437
AR Portis Jr, Evidence of a low stromal Mg2+ concentration in intact chloroplasts in the dark. Plant Physiol 67 (1981) 985-989
AR Portis Jr and HW Heldt, Light-dependent changes of the Mg2+ concentration in the stroma in relation to the Mg2+ dependency of CO2 fixation in intact chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta 449 (1976) 434-436
SP Robinson and AR Portis, Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activase protein prevents the in vitro decline in activity of Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. Plant Physiol 90 (1989) 968-971
ME Salvucci and SJ Crafts-Brandner, Inhibition of photosynthesis by heat stress: the activation state of Rubisco as a limiting factor in photosynthesis. Physiol Plant 120 (2004a) 179-186
ME Salvucci and SJ Crafts-Brandner, Mechanism for deactivation of Rubisco under moderate heat stress. Physiol Plant 122 (2004b) 513-519
SM Schrader, RR Wise, WF Wacholtz, DR Ort and TD Sharkey, Thylakoid membrane responses to moderately high leaf temperature in Pima cotton. Plant Cell Environ 27 (2004) 725-735
ZY Wang and AR Portis Jr, Dissociation of ribulose 1, 5-bisphosphate bound to ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase and its enhancement by ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase activase-mediated hydrolysis of ATP. Plant Physiol 99 (1992) 1348-1353
RR Wise, AJ Olson, SM Schrader and TD Sharkey, Electron transport is the functional limitation of photosynthesis in field-grown Pima cotton plants at high temperature. Plant Cell Environ 27 (2004) 717-724
G Zhu, HJ Bohnert, RG Jensen and GF Wildner, Formation of the tight-binding inhibitor, 3-ketoarabinitol-1,5-bisphosphate by ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase is O2-dependent. Photosynth Res 55 (1998) 67-74
G Zhu and RG Jensen, Fallover of ribulose 1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activity. Decarbamylation of catalytic sites depends on pH. Plant Physiol 97 (1991a) 1354-1358
G Zhu and RG Jensen, Xylulose 1,5-bisphophate synthesized by ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase during catalysis binds to decarbamylated enzyme. Plant Physiol 97 (1991b) 1348-1353
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
*Mention of a trademark, proprietary product or vendor does not constitute a guarantee or warranty of the product by the U.S. Department of Agriculture and does not imply its approval to the exclusion of other products or vendors that may also be suitable.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, ., Portis, A.R. Kinetic Analysis of the Slow Inactivation of Rubisco During Catalysis: Effects of Temperature, O2 and Mg++ . Photosynth Res 87, 195–204 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-005-8386-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-005-8386-4