Abstract
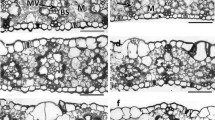
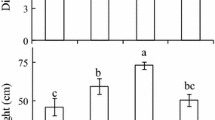
Five decades ago, a novel mode of CO2 assimilation that was later described as C4-photosynthesis was discovered on mature leaves of maize (Zea mays L.) plants. Here we show that 3- to 5-day-old developing maize leaves recapitulate the evolutionary advance from the ancient, inefficient C3 mode of photosynthesis to the C4 pathway, a mechanism for overcoming the wasteful process of photorespiration. Chlorophyll fluorescence measurements documented that photorespiration was high in 3-day-old juvenile primary leaves with non-specialized C3-like leaf anatomy and low in 5-day-old organs with the typical “Kranz-anatomy” of C4 leaves. Photosynthetic gas (CO2)-exchange measurements on 5-day-old leaves revealed the characteristic features of C4 photosynthesis, with a CO2 compensation point close to zero and little inhibition of photosynthesis by the normal oxygen concentration in the air. This indicates a very low photorespiratory activity in contrast to control experiments conducted with mature C3 sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) leaves, which display a high rate of photorespiration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Chl:
-
chlorophyll
- CO2-CP:
-
carbon dioxide compensation point
- ΔF/Fm′:
-
effective quantum yield of PSII of light-adapted leaves
- PSII:
-
photosystem II
References
Bassham, J.A., Calvin, M.: The Path of Carbon in Photosynthesis. — Prentice-Hall-Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey 1957.
Berry, J.A., Downton, W.J.S., Tregunna, E.B.: The photosynthetic carbon metabolism of Zea mays and Gomphrena globosa: the location of the CO2 fixation and the carboxyl transfer reactions. — Can. J. Bot. 48: 777–786, 1970.
Berry, J.A., Osmond, C.B., Lorimer, G.H.: Fixation of 18O2 during photorespiration. Kinetics and steady-state studies of the photorespiratory carbon oxidation cycle with intact leaves and isolated chloroplasts of C3 plants. — Plant Physiol. 62: 954–967, 1978.
Calvin, M.: Forty years of photosynthesis and related activities. — Photosynth. Res. 21: 2–16, 1989.
Dai, Z., Ku, M.S.B. Edwards, G. B.: C4 photosynthesis. The effects of leaf development on the CO2-concentrating mechanism and photorespiration in maize. — Plant Physiol. 107: 815–825, 1995.
De Veau, E.J., Burris, J.E.: Photorespiratory rates in wheat and maize as determined by 18O-labeling. — Plant Physiol. 90: 500–511, 1989.
El-Sharkawy, M.A.: Pioneering research on C4 leaf anatomical, physiological, and agronomic characteristics of tropical monocot and dicot plant species: Implications for crop water relations and productivity in comparison to C3 cropping systems. — Photosynthetica 47: 163–183, 2009.
Forrester, M.L., Krotkov, G., Nelson, C.D.: Effect of oxygen on photosynthesis, photorespiration and respiration in detached leaves. II. Corn and other monocotyledons. — Plant Physiol. 41: 428–431, 1966.
Ghannoum, O., Siebke, K., von Caemmerer, S., Conroy, J.P.: The photosynthesis of young Panicum C4 leaves is not C3-like. — Plant Cell Environ. 21: 1123–1131, 1998.
Hatch, M.D.: C4-photosynthesis: An unlikely process full of surprises. — Plant Cell Physiol. 33: 333–342, 1992.
Hatch, M.D.: C4 photosynthesis: discovery and resolution. — Photosynth. Res. 73: 251–256, 2002.
Hatch, M.D., Slack, C.R.: Photosynthesis in sugarcane leaves: a new carboxylation reaction and the pathway of sugar formation. — Biochem. J. 101: 103–111, 1966.
Jucknischke, A., Kutschera, U.: The role of the cotyledons and primary leaves during seedling etablishment in sunflower. — J. Plant Physiol. 153: 700–705, 1998.
Karpilow, Y.S.: The distribution of radioactive carbon14 amongst the products of photosynthesis in maize. — Trans. Kazan Agr. Inst. 41: 15–24, 1960.
Kutschera, U., Briggs, W.R.: From Charles Darwin’s botanical country-house studies to modern plant biology. — Plant Biol. 11: 785–795, 2009.
Kutschera, U., Niklas, K.J.: Photosynthesis research on yellowtops: macroevolution in progress. — Theory Biosci. 125: 81–92, 2006.
Kutschera, U., Niklas, J.K.: Evolutionary plant physiology: Charles Darwin’s forgotten synthesis. — Naturwissenschaften 96: 1339–1354, 2009.
Leakey, A.D.B., Uribelarrea, M., Ainsworth, E.A., Naidu, S.L., Rogers, A., Ort D.R., Long, S.P.: Photosynthesis, productivity, and yield of maize are not affected by open-air elevation of CO2 concentration in the absence of drought. — Plant Physiol. 140: 779–790, 2006.
Majeran, W., van Wijk, K.J.: Cell-type-specific differentiation of chloroplasts in C4 plants. — Trends Plant Sci. 14: 100–109, 2009.
Niklas, K.J., Kutschera, U.: The evolutionary development of plant body plans. — Funct. Plant Biol. 36: 682–695, 2009.
Niklas, K.J., Kutschera, U.: The evolution of the land plant life cycle. — New Phytol. 185: 27–41, 2010.
Sage, R.F.: The evolution of C4 photosynthesis. — New Phytol. 161: 341–370, 2004.
Scherp, P., Grotha, R., Kutschera, U.: Occurrence and phylogenetic significance of cytokinesis-related callose in green algae, bryophytes, ferns and seed plants. — Plant Cell Rep. 20: 143–149, 2001.
Stebbins, G.L.: Variation and Evolution in Plants. — Columbia Univ. Press, New York 1950.
Tregunna, E.B., Krotkov, G., Nelson, C.D.: Effect of oxygen on the rate of photorespiration in detached tobacco leaves. — Physiol. Plant. 19: 723–733, 1966.
Voznesenskaya, E.V., Franceschi, K.O., Kiirats, V.R., Freitag, H., Edwards, G.E.: Kranz anatomy is not essential for terrestrial C4 plant photosynthesis. Nature 414: 543–546, 2001.
Zelitch, I., Schultes, N.P., Peterson, R. B., Brown, P., Brutnell, T. P.: High glycolate oxidase activity is required for survival of maize in normal air. — Plant Physiol. 149: 195–204, 2009.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation (AvH-fellowships 2007/2008, Stanford/USA to U. K.). R.P. (Present address: ICG-3:Phytosphere Forschungszentrum Jülich, 52425 Jülich, Germany) was supported by the Marie Curie International Outgoing Fellowship Program (Nr: 041060 — LIFT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kutschera, U., Pieruschka, R. & Berry, J.A. Leaf development, gas exchange characteristics, and photorespiratory activity in maize seedlings. Photosynthetica 48, 617–622 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-010-0079-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-010-0079-3