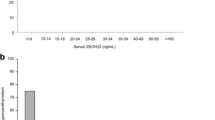
We examined the effects of fluoride intoxication on certain blood plasma biochemical indices in rats. Fortyeight adult female Wistar rats weighing 123-142 g were divided into eight groups: two control groups (0 and 28 days) and six experimental groups, namely sham-injected animals (vehicle), injected with pineal proteins (PP) and melatonin (Mel), intoxicated with fluoride (F), and also F+PP and F+Mel groups. Fluoride (150 ppm, per os administration with drinking water), melatonin (10 mg/kg, i.p.), and PP (100 μg/kg, i.p.) were administered daily for 28 days. Blood samples were collected at the end of experiments to estimate plasma [Na+] and [K+], alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity, and levels of glucose and proteins in different animal groups. The plasma [K+] and [Na+], and ALP activity were significantly (P < 0.05) elevated in F-treated animals, as compared with others. Administration of PP and Mel in F-treated rats caused significant (P < < 0.05) reduction of [Na+], [K+], and ALP levels. Interestingly, PP and Mel administrations resulted in noticeable (P < 0.05) increases in the plasma glucose level in F-intoxicated animals, as compared to other groups. These findings convincingly indicate that PP and Mel exert ameliorative effects on fluoride-induced adverse changes in certain biochemical parameters in rats.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. J. Collier, D. K. Beede, W. W. Thatcher, et al., “Influences of environment and its modification on dairy animal health and production,” J. Dairy Sci., 65, 2213–2227 (1982).
J. W. West, “Effects of heat stress on production of dairy cattle,” J. Dairy Sci., 86, 2131–2144 (2003).
R. K. Ringer, “Effects on domestic animals,” in: Ecotoxicology and Climate, J. A. Bourdeau, W. K. Haines, and C. R. K. Murti (eds.), John Wiley and Sons Ltd. (1989), pp. 225–232.
V. K. Bharti, “Fluorosis: A serious health problem of domestic animals,” Livestock Int., 10, No. 12, 17–20 (2006).
R. Rzeuski, D. Chlubek, and Z. Machoy, “Interactions between fluoride and biological free-radical reactions,” Fluoride, 31, 43–45 (1998).
X. Y. Guo, G. F. Sun, and Y. C. Sun, “Oxidative stress from fluoride induced hepatotoxicity in rats,” Fluoride, 36, No. 1, 25–29 (2003).
S. L. Chawla, R. Yadav, D. Shah, and M. V. Rao, “Protective action of melatonin against fluoride-induced hepatotoxicity in adult female mice,” Fluoride, 41, No. 1, 44–51 (2008).
V. K. Bharti and R. S. Srivastava, “Fluoride-induced oxidative stress in rat’s brain and its amelioration by buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) pineal proteins and melatonin,” Biol. Trace Elem. Res., 130, No. 2, 131–140 (2009).
P. Celi, A. D. Trana, and A. Quaranta, “Metabolic profile and oxidative status in goats during the peripartum period,” Aust. J. Exp. Agric., 48, No. 7, 1004–1008 (2008).
W.H.O. Environmental Health Criteria, 36: Fluorine and Fluoride. WHO. Geneva. (1984).
C. Rodriguez, J. C. Mayo, R. M. Sainz, et al., “Regulation of antioxidant enzymes: a significant role for melatonin,” J. Pineal Res., 36, No. 1, 1–9 (2004).
M. Diaz-Munoz, R. Hernandez-Munoz, J. Suarez, et al., “Day-night cycle of lipid peroxidation in rat cerebral cortex and their relationship to the glutathione cycle and superoxide dismutase activity,” Neuroscience, 16, 859–863 (1985).
P. J. Mullenix, P. K. Denbesten, A. Schunior, and W. J. Kernan, “Neurotoxicity of sodium fluoride in rats,” Neurotoxicol. Teratol., 17, 169–177 (1995).
M. L. Vani and K. P. Reddy, “Effects of fluoride accumulation on some enzymes of brain and gastrocnemius muscle of mice,” Fluoride, 33, 17–26 (2000).
H. J. Romijn, “The pineal: a tranquillizing organ,” Life Sci., 23, 2257–2274 (1978).
P. Voisin, M. G. Harrington, J. L. Weller, et al., “Noradrenergic control of the synthesis of two rat pineal proteins,” Brain Res., 517, Nos. 1/2, 25–34 (1990).
R. J. Reiter, D. Melchiorri, E. Sewerynek, and B. Poeggler, “A review of the evidence supporting melatonin’s role as an antioxidant,” J. Pineal Res., 23, 43–50 (1995).
R. J. Reiter, “Pineal melatonin: cell biology of its synthesis and of its physiological interactions,” Endocrinol. Rev., 12, 151–180 (1991).
D. E. Blask, M. K. Vaughan, and R. J. Reiter, in: The Pineal Gland, R. Relkin (ed.), Elsevier, Amsterdam (1983), pp. 201–224.
M. Tandon, R. S. Srivastava, S. K. Meur, and M. Saini, “Proteins and peptides present in pineal gland and other brain structures of buffaloes,” Indian J. Animal Sci., 76 (5), 383–394 (2006).
V. Sejian, Studies on Pineal-Adrenal Relationship in Goats (Capra hircus) Under Thermal Stress, Ph.D. Thesis, Indian Veterinary Research Institute, Izatnagar, India (2006).
V. K. Bharti and R. S. Srivastava “Pineal proteins up-regulate specific antioxidant defense systems in the brain,” Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev., 2, No. 2, 88–92 (2009).
V. K. Bharti and R. S. Srivastava, “Protective role of pineal proteins at different dose level on fluoride-induced changes in plasma biochemicals and blood antioxidants enzymes in rats,” Biol. Trace Elem. Res., DOI: 10.1007/s12011-010-8733-y (2010).
B. L. Oser, Hawk’s Physiological Chemistry, McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York (1965).
J. A. Varner, K. F. Jenson, W. Horvath, and R. L. Isaacson, “Chronic administration of aluminum fluoride or sodium fluoride to rats in drinking water: alteration in neuronal and cerebrovascular integrity,” Brain Res., 784, 284–298 (1998).
V. K. Bharti, M. Gupta, and D. Lall, “Ameliorative effects of boron on serum profile in buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) fed a high fluoride ration,” Trop. Anim. Health Prod., 40, No. 2, 111–116 (2008).
R. J. Verma and D. M. Guna Sherlin, “Sodium fluorideinduced hypoproteinemia and hypoglycemia in parental and F (1)-generation rats and amelioration by vitamins,” Food Chem. Toxicol., 40, No. 12, 1781–1788 (2002).
L. I. Ding, “The nervous systemic complications of chronic fluorosis,” Chin. J. Endemiol., 2, 97–98 (1983).
J. A. Luke, The Effect of Fluoride on the Physiology of the Pineal Gland, Ph.D. Thesis, School of Biological Sciences, University of Surrey, England (1997).
D. Shanthakumari, S. Srinivasalu, and S. Subramanian, “Effects of fluoride intoxication on lipid peroxidation and antioxidant status in experimental rats,” Toxicology, 204, 219–228 (2004).
S. M. Farley, J. E. Wrgedal, L. Smith, et al., “Fluoride therapy for osteoporosis: Characterization of the skeletal response by serial measurement of serum alkaline phosphatase activity,” Metabolism, 36, 211–218 (1987).
S. P. S. Teotia and M. Teotia, “Endemic fluoride: bone and teeth-update,” Indian J. Environ. Toxicol., 1, 1 (1991).
V. Menon, M. Ram, J. Dorn, et al., “Oxidative stress and glucose levels in a population-based sample,” Diabetic Med., 21, 1346–1352 (2004).
B. Benson and I. Ebels, “Pineal peptides,” J. Neural Transm., Suppl., 13, 157–173 (1978).
B. Bojková, M. Marková, E. Ahlersová, et al., “Metabolic effects of prolonged melatonin administration and shortterm fasting in laboratory rats,” Acta Vet. Brno, 75, 21–32 (2006).
M. Ogeturk, I. Kus, A. Kavakli, et al., “Effects of melatonin on carbon tetrachloride-induced changes in rat serum,” J. Physiol. Biochem., 60, 205–210 (2004).
V. Sejian and R. S. Srivastava, “Effects of melatonin on adrenal cortical functions of Indian goats under thermal stress,” Vet. Med. Int., 2010, 1–6. DOI:10.4061/2010/348919 (2010).
M. Ramasamy, Studies on Bubaline Pineal Proteins/Peptides below 20 kDa and Their Immunopotentiation in Guinea Pigs, Ph.D. Thesis, Indian Veterinary Research Institute, Izatnagar, India (2006).
D. Swarup, S. Dey, S. R. C. Patra, et al., “Clinicoepidemiological observations of industrial bovine fluorosis in India,” Indian J. Anim. Sci., 71, 1111–1115 (2001).
D. Chlubek, H. E. Grucka, R. Polaniak, et al., “Activity of pancreatic antioxidant enzymes and malondialdehyde concentrations in rats with hyperglycemia caused by fluoride intoxication,” J. Trace Element Med. Biol., 17, No. 1, 57–60 (2003).
V. K. Bharti, M. Gupta, D. Lall, and V. Kapoor, “Effect of boron on haemogram and biochemical profile of urine in buffalo calves fed a high fluoride ration,” Fluoride, 40, No. 4, 238–243 (2007).
A. K. Susheela, “Fluorosis management programme in India,” Curr. Sci., 77, No. 10, 1050–1056 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Neirofiziologiya/Neurophysiology, Vol. 42, No. 4, pp. 309-315, July-August, 2010.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bharti, V.K., Srivastava, R.S. Effects of Epiphyseal Proteins and Melatonin on Blood Biochemical Parameters of Fluoride-Intoxicated Rats. Neurophysiology 42, 258–264 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-011-9158-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-011-9158-8