Abstract
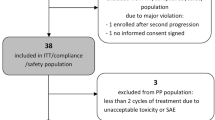
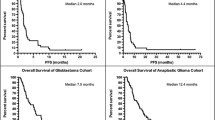
Gimatecan is a lipophilic oral camptothecin analogue with preclinical activity in glioma models. We conducted a multicenter phase II trial to evaluate the efficacy of gimatecan in adults with recurrent glioblastoma. Eligibility criteria included ≤1 prior treatment for recurrent disease, age ≥18, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status 0–1, and normal organ function. Patients taking enzyme-inducing anti-seizure medications were excluded. Gimatecan 1.22 mg/m2 was given orally once daily for 5 consecutive days during each 28-day cycle. The primary endpoint was progression-free survival at 6 months. A Simon 2-stage optimal design was used in which 19 patients were evaluated in the 1st stage, with an additional 36 patients accrued if >4 patients in stage 1 achieved PFS at 6 months. 29 patients were enrolled in the study, with median age of 58 years (range, 25–77 years); 58.6 % female. All patients received prior surgery, radiation therapy, and at least one chemotherapy regimen. The daily dose was reduced to 1.0 mg/m2 after four of the first 10 patients experienced grade 4 hematologic toxicity. Treatment-related grade 3/4 toxicities included thrombocytopenia (17.2 %), leukopenia (17.2 %) and neutropenia (10.3 %). None of the 19 patients treated at 1.0 mg/m2/day experienced grade 4 hematologic toxicity. One patient had a partial radiographic response by modified Macdonald criteria. Only 3 patients (12 %) were progression-free at 6 months. Median time to progression was 12.0 weeks (7.0, 17.0).Treatment with gimatecan 1.0 mg/m2/day for 5 days, repeated every 28-days showed minimal efficacy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, Cairncross JG, Eisenhauer E, Mirimanoff RO (2005) Groups EOfRaToCBTaR, Group NCIoCCT. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:987–996
Wick W, Puduvalli VK, Chamberlain MC, van den Bent MJ, Carpentier AF, Cher LM, Mason W, Weller M, Hong S, Musib L, Liepa AM, Thornton DE, Fine HA (2010) Phase III study of enzastaurin compared with lomustine in the treatment of recurrent intracranial glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol 28:1168–1174
Friedman HS, Prados MD, Wen PY, Mikkelsen T, Schiff D, Abrey LE, Yung WK, Paleologos N, Nicholas MK, Jensen R, Vredenburgh J, Huang J, Zheng M, Cloughesy T (2009) Bevacizumab alone and in combination with irinotecan in recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol 27:4733–4740
Garcia-Carbonero R, Supko JG (2002) Current perspectives on the clinical experience, pharmacology, and continued development of the camptothecins. Clin Cancer Res 8:641–661
Friedman HS, Petros WP, Friedman AH, Schaaf LJ, Kerby T, Lawyer J, Parry M, Houghton PJ, Lovell S, Rasheed K, Cloughsey T, Stewart ES, Colvin OM, Provenzale JM, McLendon RE, Bigner DD, Cokgor I, Haglund M, Rich J, Ashley D, Malczyn J, Elfring GL, Miller LL (1999) Irinotecan therapy in adults with recurrent or progressive malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol 17:1516–1525
Prados MD, Lamborn K, Yung WK, Jaeckle K, Robins HI, Mehta M, Fine HA, Wen PY, Cloughesy T, Chang S, Nicholas MK, Schiff D, Greenberg H, Junck L, Fink K, Hess K, Kuhn J, Consortium NABT (2006) A phase II trial of irinotecan (cpt-11) in patients with recurrent malignant glioma: a north american brain tumor consortium study. Neuro–Oncol 8:189–193
Batchelor TT, Gilbert MR, Supko JG, Carson KA, Nabors LB, Grossman SA, Lesser GJ, Mikkelsen T, Phuphanich S, Consortium NC (2004) Phase II study of weekly irinotecan in adults with recurrent malignant glioma: final report of nabtt 97–11. Neuro–Oncol 6:21–27
Lopez KA, Tannenbaum AM, Assanah MC, Linskey K, Yun J, Kangarlu A, Gil OD, Canoll P, Bruce JN (2011) Convection-enhanced delivery of topotecan into a pdgf-driven model of glioblastoma prolongs survival and ablates both tumor-initiating cells and recruited glial progenitors. Cancer Res 71:3963–3971
De Cesare M, Pratesi G, Perego P, Carenini N, Tinelli S, Merlini L, Penco S, Pisano C, Bucci F, Vesci L, Pace S, Capocasa F, Carminati P, Zunino F (2001) Potent antitumor activity and improved pharmacological profile of st1481, a novel 7-substituted camptothecin. Cancer Res 61:7189–7195
Hsiang YH, Lihou MG, Liu LF (1989) Arrest of replication forks by drug-stabilized topoisomerase i-dna cleavable complexes as a mechanism of cell killing by camptothecin. Cancer Res 49:5077–5082
De Cesare M, Pratesi G, Veneroni S, Bergottini R, Zunino F (2004) Efficacy of the novel camptothecin gimatecan against orthotopic and metastatic human tumor xenograft models. Clin Cancer Res 10:7357–7364
Zhu AX, Ready N, Clark JW, Safran H, Amato A, Salem N, Pace S, He X, Zvereva N, Lynch TJ, Ryan DP, Supko JG (2009) Phase i and pharmacokinetic study of gimatecan given orally once a week for 3 of 4 weeks in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 15:374–381
Sessa C, Cresta S, Cerny T, Baselga J, Rota Caremoli E, Malossi A, Hess D, Trigo J, Zucchetti M, D’Incalci M, Zaniboni A, Capri G, Gatti B, Carminati P, Zanna C, Marsoni S, Gianni L (2007) Concerted escalation of dose and dosing duration in a phase I study of the oral camptothecin gimatecan (st1481) in patients with advanced solid tumors. Ann Oncol 18:561–568
Boni C, Gamucci T, Bonetti A, Bisagni G, Dall’o’ E, Zanna C, Marsoni S, Sessa C, Azienda Ospedaliera S, Nuova M, Emilia R (2004) A phase II study of the novel oral camptothecin st1481 in pretreated metastatic colorectal cancer (crc). J Clin Onco 3684
Mariani P, Moliterni A, Da Prada G, Hess D, Gamucci T, Zaniboni A, Malossi A, Barbieri P, Marsoni S, Gianni L (2006) A phase II trial of the novel oral camptothecin gimatecan (g) in women with anthracycline (a) and taxane (t) pre-treated advanced breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 662
Pecorelli S, Ray-Coquard I, Tredan O, Colombo N, Parma G, Tisi G, Katsaròs D, Lhommé C, Lissoni AA, Vermorken JB, du Bois A, Poveda A, Frigerio L, Barbieri P, Carminati P, Brienza S, Guastalla JP (2010) Phase II of oral gimatecan in patients with recurrent epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube or peritoneal cancer, previously treated with platinum and taxanes. Ann Oncol 21:759–765
Grossman SA, Carson KA, Phuphanich S, Batchelor T, Peereboom D, Nabors LB, Lesser G, Hausheer F, Supko JG (2008) Consortium NAtBTTC. Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of karenitecin in patients with recurrent malignant gliomas. Neuro–Oncol 10:608–616
Zamboni WC, Gajjar AJ, Heideman RL, Beijnen JH, Rosing H, Houghton PJ, Stewart CF (1998) Phenytoin alters the disposition of topotecan and n-desmethyl topotecan in a patient with medulloblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 4:783–789
Gilbert MR, Supko JG, Batchelor T, Lesser G, Fisher JD, Piantadosi S, Grossman S (2003) Phase i clinical and pharmacokinetic study of irinotecan in adults with recurrent malignant glioma. Clin Cancer Res 9:2940–2949
Macdonald DR, Cascino TL, Schold SC, Cairncross JG (1990) Response criteria for phase ii studies of supratentorial malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol 8:1277–1280
Simon R (1989) Optimal two-stage designs for phase II clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 10:1–10
Wong ET, Hess KR, Gleason MJ, Jaeckle KA, Kyritsis AP, Prados MD, Levin VA, Yung WK (1999) Outcomes and prognostic factors in recurrent glioma patients enrolled onto phase ii clinical trials. J Clin Oncol 17:2572–2578
Lamborn KR, Yung WK, Chang SM, Wen PY, Cloughesy TF, DeAngelis LM, Robins HI, Lieberman FS, Fine HA, Fink KL, Junck L, Abrey L, Gilbert MR, Mehta M, Kuhn JG, Aldape KD, Hibberts J, Peterson PM, Prados MD, Consortium NABT (2008) Progression-free survival: an important end point in evaluating therapy for recurrent high-grade gliomas. Neuro–Oncol 10:162–170
Gerrits CJ, de Jonge MJ, Schellens JH, Stoter G, Verweij J (1997) Topoisomerase I inhibitors: the relevance of prolonged exposure for present clinical development. Br J Cancer 76:952–962
Petrangolini G, Pratesi G, De Cesare M, Supino R, Pisano C, Marcellini M, Giordano V, Laccabue D, Lanzi C, Zunino F (2003) Antiangiogenic effects of the novel camptothecin st1481 (gimatecan) in human tumor xenografts. Mol Cancer Res 1:863–870
Smith LM, Willmore E, Austin CA, Curtin NJ (2005) The novel poly(adp-ribose) polymerase inhibitor, ag14361, sensitizes cells to topoisomerase I poisons by increasing the persistence of DNA strand breaks. Clin Cancer Res 11:8449–8457
Eng WK, McCabe FL, Tan KB, Mattern MR, Hofmann GA, Woessner RD, Hertzberg RP, Johnson RK (1990) Development of a stable camptothecin-resistant subline of p388 leukemia with reduced topoisomerase I content. Mol Pharmacol 38:471–480
Vassal G, Hamelin N, Opolon P, Versace R, Geoerger B (2008) The topoisomerase I inhibitor gimatecan exhibits synergistic antitumor activity in combination with imatinib mesylate and everolimus against malignant glioma xenografts. 2073
Braun MS, Richman SD, Quirke P, Daly C, Adlard JW, Elliott F, Barrett JH, Selby P, Meade AM, Stephens RJ, Parmar MK, Seymour MT (2008) Predictive biomarkers of chemotherapy efficacy in colorectal cancer: results from the uk mrc focus trial. J Clin Oncol 26:2690–2698
Naniwa J, Kigawa J, Kanamori Y, Itamochi H, Oishi T, Shimada M, Shimogai R, Kawaguchi W, Sato S, Terakawa N (2007) Genetic diagnosis for chemosensitivity with drug-resistance genes in epithelial ovarian cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer 17:76–82
Furuta T, Takemura H, Liao ZY, Aune GJ, Redon C, Sedelnikova OA, Pilch DR, Rogakou EP, Celeste A, Chen HT, Nussenzweig A, Aladjem MI, Bonner WM, Pommier Y (2003) Phosphorylation of histone h2ax and activation of mre11, rad50, and nbs1 in response to replication-dependent DNA double-strand breaks induced by mammalian DNA-topoisomerase I cleavage complexes. J Biol Chem 278:20303–20312
Acknowledgments
Grant support from Sigma-Tau Research.
Conflict of interest
N. Salem is employed by Sigma-Tau.
Ethical standards
This study complies with the current laws of the United States of America.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, J., Wen, P.Y., Abrey, L.E. et al. A phase II trial of oral gimatecan for recurrent glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 111, 347–353 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-012-1023-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-012-1023-0