Abstract
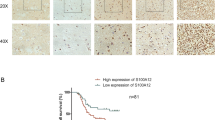
S100 proteins are Ca2+-binding polypeptides involved in the tumourigenesis of several human neoplasms. S100A13 is a key regulator of the stress-dependent release of FGF1, the prototype of the FGF protein family involved in angiogenesis. Indeed, S100A13 is a copper binding protein able to enhance the export of FGF1 in response to stress in vitro and to induce the formation of a multiprotein aggregate responsible for FGF1 release. We investigated the expression of S100A13 in human astrocytic gliomas in␣relation to tumour grading and vascularization. A series of 26 astrocytic gliomas was studied to evaluate microvessel density and to assess FGF1, S100A13 and VEGF-A expression. FGF1 was equally expressed in the vast majority of tumours, whereas S100A13 and VEGF-A were significantly up-regulated in high-grade vascularized gliomas. Moreover, both S100A13 and VEGF-A expression significantly correlated with microvessel density and tumour grading. These data suggest that the up-regulation of S100A13 and VEGF-A expression correlates with the activation of angiogenesis in high-grade human astrocytic gliomas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Folkman J (2002) Role of angiogenesis in tumor growth and metastasis. Semin Oncol 29:15–18
Dvorak HF (2002) Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor: a critical cytokine in tumor angiogenesis and a potential target for diagnosis and therapy. J Clin Oncol 20:4368–4380
Tonini T, Rossi F, Claudio PP (2003) Molecular basis of angiogenesis and cancer. Oncogene 22:6549–6556
Distler JH, Hirth A, Kurowska-Stolarska M, Gay RE, Gay S, Distler O (2003) Angiogenic and angiostatic factors in the molecular control of angiogenesis. Q J Nucl Med 47:149–161
Okunieff P, Fenton BM, Zhang L, Kern FG, Wu T, Greg JR, Ding I (2003) Fibroblast growth factors (FGFS) increase breast tumor growth rate, metastases, blood flow, and oxygenation without significant change in vascular density. Adv Exp Med Biol 530:593–601
Sugamoto T, Tanji N, Sato K, Fujita H, Nishio S, Sakanaka M, Yokoyama M (2001) The expression of basic fibroblast growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor in prostatic adenocarcinoma: correlation with neovascularization. Anticancer Res 21:77–88
Kornmann M, Beger HG, Korc M (1998) Role of fibroblast growth factors and their receptors in pancreatic cancer and chronic pancreatitis. Pancreas 17:169–175
Berger W, Setinek U, Mohr T, Kindas-Mugge I, Vetterlein M, Dekan G, Eckersberger F, Caldas C, Micksche M (1999) Evidence for a role of FGF-2 and FGF receptors in the proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer cells. Int J Cancer 83:415–423
Landriscina M, Cassano A, Ratto C, Longo R, Ippoliti M, Palazzotti B, Crucitti F, Barone C (1998) Quantitative analysis of basic fibroblast growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor in human colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 78:765–770
Friesel R, Maciag T (1999) Fibroblast growth factor prototype release and fibroblast growth factor receptor signalling. Thromb Haemost 82:748–754
Florkiewicz RZ, Majack RA, Buechler RD, Florkiewicz E (1995) Quantitative export of FGF-2 occurs through an␣alternative, energy-dependent, non-ER/Golgi pathway. J␣Cell Physiol 162:388–399
Prudovsky I, Bagalà C, Tarantini F, Mandinova A, Soldi R, Bellum S, Maciag T (2002) The intracellular translocation of the components of the fibroblast growth factor 1 release complex precedes their assembly to export. J Cell Biol 158:201–208
Jackson A, Tarantini F, Gamble S, Friedman S, Maciag T (1995) The release of fibroblast growth factor-1 from NIH 3T3 cells in response to temperature involves the function of cisteine residues. J Biol Chem 270:33–36
La Vallee TM, Tarantini F, Gamble S, Carreira CM, Jackson A, Maciag T (1998) Synaptotagmin-1 is required for fibroblast growth factor-1 release. J Biol Chem 273:22217–22223
Tarantini F, La Vallee TM, Jackson A, Gamble S, Carreira CM, Garfinkel S, Burgess WH, Maciag T (1998) The extravesicular domain of synaptotagmin-1 is released with the latent fibroblast growth factor-1 homodimer in response to heat shock. J Biol Chem 273:22209–22216
Carreira CM, La Vallee TM, Tarantini F, Jackson A, Lathrop T, Hampton B, Burgess WH, Maciag T (1998) S100A13 is involved in the regulation of fibroblast growth factor-1 and p40 Synaptotagmin-1 release in vitro. J Biol Chem 273:22224–22231
Landriscina M, Soldi R, Bagalà C, Micucci I, Bellum S, Tarantini F, Prudovsky I, Maciag T (2001) S100A13 participates in the release of FGF1 in response to heat shock in vitro. J Biol Chem 276:22544–22552
Landriscina M, Bagalà C, Mandinova A, Soldi R, Micucci I, Bellum S, Prudovsky I, Maciag T (2001) Copper induces the assembly of a multiprotein aggregate implicated in the release of FGF1 in response to stress. J Biol Chem 276:25549–25557
Plate KH, Mennel HD (1995) Vascular morphology and angiogenesis in glial tumors. Exp Toxicol Pathol 47:89–94
Puduvalli VK, Sawaya R (2000) Antiangiogenesis-therapeutic strategies and clinical implications for brain tumors. J␣Neurooncol 50:189–200
Folkerth RD (2000) Descriptive analysis and quantification of angiogenesis in human brain tumors. J Neurooncol 50:165–172
Abdulrauf SI, Edvardsen K, Ho KL, Yang XY, Rock JP, Rosenblum ML (1998) Vascular endothelial growth factor expression and vascular density as prognostic markers of survival in patients with low-grade astrocytoma. J Neurosurg 88:512–520
Lamszus K, Kunkel P, Westphal M (2003) Invasion as limitation to anti-angiogenic glioma therapy. Acta Neurochir Suppl 88:169–177
Brat DJ, Kaur B, Van Meir EG (2003) Genetic modulation of hypoxia induced gene expression and angiogenesis: relevance to brain tumors. Front Biosci 8:100–116
Ilg EC, Schafer BW, Heizmann CW (1996) Expression pattern of S100 calcium-binding proteins in human tumors. Int J Cancer 68:325–332
Sano H, Forough R, Maier JA, Case JP, Jackson A, Engleka K, Maciag T, Wilder RL (1990) Detection of high levels of heparin binding growth factor-1 (acidic fibroblast growth factor) in inflammatory arthritic joints. J Cell Biol 110:1417–1426
Cassano A, Bagalà C, Battelli C, Schinzari G, Quirino M, Ratto C, Landriscina M, Barone C (2002) Analysis of vascular endothelial growth factor, mitogen-activated protein kinase and p53 in human colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res 22:2179–2184
Hayrabedyan S, Kyurkchiev S, Kehayov1 I (2005) Endoglin (cd105) and S100A13 as markers of active angiogenesis in endometriosis. Reprod Biol 5(1):51–67
Mandinov L, Mandinova A, Kyurkchiev S, Kyurkchiev D, Kehayov I, Kolev V, Soldi R, Bagalà C, de Muinck ED, Lindner V, Post MJ, Simons M, Bellum S, Prudovsky I, Maciag T (2003) Copper chelation represses the vascular response to injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(11):6700–6705
Nakasaki T, Wada H, Sigemori C, Miki C, Gabazza EC, Nobori T, Nakamura S, Shiku H (2002) Expression of tissue factor and vascular endothelial growth factor is associated with angiogenesis in colorectal cancer. Am J Hematol 69:247–254
Burgess WH, Mehlman T, Friesel R, Johnson WV, Maciag T (1985) Multiple forms of endothelial cell growth factor. Rapid isolation and biological and chemical characterization. J Biol Chem 260:11389–11392
Godard S, Gerz G, Delorenzi M, Farmer P, Kobayashi H, Desbaillets I, Nozaki M, Diserens AC, Hamou MF, Dietrich PY, Regli L, Janzer RC, Bucher P, Stupp R, de Tribolet N, Domany E, Hegi ME (2003) Classification of human astrocytic gliomas on the basis of gene expression: a correlated group of genes with angiogenic activity emerges as a strong predictor of subtypes. Cancer Res 63:6613–6625
Bian XW, Du LL, Shi JO, Cheng YS, Liu FX (2000) Correlation of bFGF, FGFR-1 and VEGF expression with vascularity and malignancy of human astrocytomas. Anal Quant Cytol Histol 22:267–274
Donato R (2001) S100: a multigenic family of calcium-modulated proteins of EF-hand type with intracellular and extracellular functional roles. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 33:637–668
Banfalvi T, Udvarhelyi NM, Orosz Z, Gergye M, Gilde K, Timar J (2003) Heterogenous S-100B protein expression patterns in malignant melanoma and association with serum protein levels. Oncology 64:374–379
Kanner AA, Marchi N, Fazio V, Mayberg MR, Koltz MT, Siomin V, Stevens GH, Masaryk T, Ayumar B, Vogelbaum MA, Barnett GH, Janigro D (2003) Serum S100beta: a non-invasive marker of blood-brain barrier and brain lesions. Cancer 97:2806–2813
Vos MJ, Postma TJ, Martens F, Uitdehaag BM, Blankenstein MA, Vandertop WP, Slotman BJ, Heimans JJ (2004) Serum levels of S-100B protein and neuron-specific enolase in glioma patients: a pilot study. Anticancer Res 24:2511–2514
Rajenda A, Spinella PC, Drott HR, Dominguez TE, Sutton L, Helfaer M (2004) S-100beta protein-serum levels in children with brain neoplasms and its potential as a tumor marker. J Neurooncol 67:345–349
Camby I, Lefranc F, Titeca G, Neuci S, Fastrez M, Dedecken L, Schafer BW, Brotchi J, Heizmann CW, Pochet R, Salmon I, Kiss R, Decaestecker C (2000) Differential expression of S100 calcium-binding proteins characterizes distinct clinical entities in both WHO grade II and III astrocytic tumours. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 26:76–90
Ambartsumian N, Klingelhofer J, Grigorian M, Christensen C, Kriajevska M, Tulchinsky E, Georgiev G, Berezin V, Bock E, Rygaard J, Cao R, Cao Y, Lukanidin E (2001) The metastasis-associated Mts1 (S100A4) protein could act as an angiogenic factor. Oncogene 20:4685–4695
Belot N, Pochet R, Heizmann CW, Kiss R, Decaestecker C (2002) Extracellular S100A4 stimulates the migration of astrocytic tumor cells by modifying the organization of the actin cytoskeleton. Biochim Biophys Acta 1600:74–83
Rety S, Osterloh D, Arie JP, Tabaries S, Seeman J, Russo-Marie F, Gerke V, Lewit-Bentley A (2000) Structural basis of the Ca(2+)-dependent association between S100C (S100A11) and its target, the N-terminal part of annexin I. Structure Fold Des 8:175–184
Matsunaga H, Ueda H (2006) Evidence for serum-deprivation-induced co-release of FGF-1 and S100A13 from astrocytes. Neurochem Int (in press) [Epub ahead of print]
Birner P, Piribauer M, Fischer I, Gatterbauer B, Marosi C, Ambros PF, Ambros IM, Bredel M, Oberhuber G, Rossler K, Budka H, Harris AL, Hainfellner JA (2003) Vascular patterns in glioblastoma influence clinical outcome and associate with variable expression of angiogenic proteins: evidence for distinct angiogenic subtypes. Brain Pathol 13(2):133–143
Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W, Cartwright T, Hainsworth J, Heim W, Berlin J, Baron A, Griffing S, Holmgren E, Ferrara N, Fyfe G, Rogers B, Ross R, Kabbinavart F (2004) Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 50:2335–2342
Brewer GI, Merajver SD (2002) Cancer therapy with tetrathiomolybdate: antiangiogenesis by lowering body copper-a review. Integr Cancer Ther 1:327–337
Acknowledgement
The article is dedicated to the memory of Tom Maciag, friend, mentor and scientist. The authors are grateful to Tom, an outstanding researcher who inspired not only this work but the whole field of FGF1 biology. He recently died at the age of 57 years. This work was supported in part by FIRB grant 7013500 to CB, NIH grants HL32348, HL35627 and RR1555 (project 4) to IP and PRIN grant n. 2004054004_002 to␣ML.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Landriscina, M., Schinzari, G., Di Leonardo, G. et al. S100A13, a new marker of angiogenesis in human astrocytic gliomas. J Neurooncol 80, 251–259 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-006-9189-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-006-9189-y