Abstract
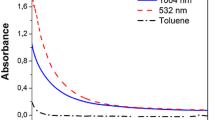
The effects of liquid environment on nucleation, growth and aggregation of gold nanoparticles were studied. Gold nanoparticles were prepared by pulsed laser ablation in deionised water with various concentrations of ethanol and also in pure ethanol. UV/visible extinction and TEM observations were employed for characterization of optical properties and particle sizes respectively. Preparation in water results in smaller size, shorter wavelength of maximum extinction and stable solution with an average size of 6 nm. Nanoparticles in solution with low concentration ethanol up to 20 vol% are very similar to those prepared in water. In the mixture of deionised water and 40 up to 80 vol% ethanol, wavelength of maximum extinction shows a red shift and mean size of nanoparticles was increased to 8.2 nm. Meanwhile, in this case, nanoparticles cross-linked each other and formed string type structures. In ethanol, TEM experiments show a mean size of 18 nm and strong aggregation of nanoparticles. The data were discussed qualitatively by considering effects of polarity of surrounding molecules on growth mechanism and aggregation. This study provided a technique to control size, cross-linking and aggregation of gold nanoparticles via changing the nature of liquid carrier medium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bohren C.F., Huffman D.R. (1983) Absorption and Scattering of Light by Small Particles. Wiley, New York
Chen G.X., Hong M.H., Lan B., Wang Z.B., Lu Y.F., Chong T.C. (2004) A Convenient way to prepare magnetic colloids by direct Nd:YAG laser ablation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 228: 169–175
Dolgave S.I., Simakin A.V., Voronov V.V., Shafeev G.A., Verduraz F.B. (2002) Nanoparticles produced by laser ablation of solids in liquid environment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 186: 546–551
Fu G., Cai W., Gan Y., Jia J. (2004) An ambience-induced optical absorption peak for Au/SiO2 mesoporous assembly. Chem. Phys. Lett. 385: 15–19
Hayens C.L., McFarland A.D., Zhao L., Duyne R.P.V., Schatz G.C., Gunnarsson L., Prikulis J., Kasemo B., Kall M. (2003) Nanoparticle optics: the importance of radiative dipole coupling in two-dimensional nanoparticle arrays. J. Phys. Chem. B 107: 7337–7342
Hodak J.H., Henglein A., Giersig M., Hartland G.V. (2000) Photophysics of nanometer sized metal particles: electron–phonon coupling and coherent excitation of breathing vibrational modes. J. Phys. Chem. B 104: 11708–11718
Huang Y., Li D., Li J. (2004) β-Cyclodextrin controlled assembling nanostructures from gold nanoparticles to gold nanowires. Chem. Phys. Lett. 389: 14–18
Inasawa S., Sugiyama M., Koda S. (2003) Size controlled formation of gold nanoparticles using photochemical grwoth and photothermal size reduction by 308 nm laser pulse. Jpn. Appl. Phys. 42: 6705–6712
Liao J., Zhang Y., Xu W.Y.L., Ge C., Liu J. (2003a) Linear aggregation of gold nanoparticles in ethanol. Coll. Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 223: 177–183
Liao J.H., Chen K.J., Xu L.N., Ge C.W., Wang J., Huang L., Gu N. (2003b) Self-assembly of length-tunable gold nanoparticle chains in organic solvents. Appl. Phys. A. 76: 541–543
Link S., Mohamed M.B., El-sayed M.A. (1999) Simulation of the optical absorption spectra of gold nanorods as a function of their aspect ratio and the effect of the medium dielectric constant. J. Phys. Chem. B 103: 3073–3077
Mafune F., Kohno J., Takeda Y., Kondow T. (2001) Dissociation and aggregation of gold nanoparticles under laser irradiation. J. Phys. Chem. B 105: 9050–9056
Mafune F. (2004) Structural diagram of gold nanoparticles in solution under irradiation of UV pulse laser. Chem. Phys. Lett. 394: 133–137
Mafune F., Kohno J., Takeda Y., Kondow T. (2003) Formation of stable platinum nanoparticles by laser ablation in water. J. Phys. Chem. B. 107: 4218–4223
Norman T.J., Grant C.D., Schwartzberg A.M., Zhang J.Z. (2005) Structural correlations with shift in the extended plasma resonance of gold nanoparticle aggregates. Optical Mater. 27: 1197–1203
Mafune F., Kohno J., Takeda Y., Kondow T., Sawabe H. (2000) Structure and stability of silver nanoparticles in aqueous solution produced by laser ablation. J. Phys. Chem. B 104: 9111–9117
Pileni M.P., 1998. Optical properties of nanosized particles dispersed in colloidal solution or arranged in 2D or 3D superlattices. New J. Chem. 22, 693–702
Quintana M., Haro-Poniatowski E., Morales J., Batina N. (2002) Synthesis of selenium nanoparticles by pulsed laser ablation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 195: 175–186
Rao C.N.R., A. Muller & A.K. Cheetham, 2004. The Chemistry of Nanomaterials., Vol. 1., Wiley-VCH
Sasaki T., Liang C., Nichols W.T., Shimizu Y., Koshizaki N. (2004) Fabrication of oxide base nanostructures using pulsed laser ablation in aqueous solutions. Appl. Phys. A. 79: 1489–1492
Seto T., Orii T., Hirasawa M., Aya N. (2003) Fabrication of silicon nanostructured films by deposition of size-selected nanoparticles generated by pulsed laser ablation. Thin Solid Films 437: 230–234
Shim J.H., Lee B., Cho Y.W. (2002) Thermal stability of unsupported nanoparticle: a molecular dynamics study. Surf. Sci. 512: 262–268
Simakin A.V., Voronov V.V., Kirichenko N.A., Shafeev G.A. (2004) Nanoparticles produced by laser ablation of solids in liquid environment. Appl. Phys. A 79: 1127–1132
Sun X., Dong S., Wang E. (2003) One-step synthesis and characterization of polyelectrolyte-protected gold nanoparticles through a thermal process. Polymer 45: 2181–2184
Tarasenko N.V., Butsen A.V., Nevar E.A. (2005) Laser-induced modification of metal nanoparticles formed by laser ablation technique in liquids. Appl. Surf. Sci. 247: 418–422
Tilaki R.M., Iraji zad A., Mahdavi S.M. (2006) Stability, size and optical properties of silver nanoparticles prepared by laser ablation in different carrier media. Appl. Phys. A 84: 215–219
Tsuji T., Iryo K., Watanabe N., Tsuji M. (2002) Preparation of silver nanoparticles by laser ablation in solution: influence of laser wavelength on particle size. Appl. Surf. Sci. 202: 80–85
Tsuji T., Hamagami T., Kawamura T., Yamaki J., Tsuji M. (2005) Laser ablation of cobalt and cobalt oxides in liquids: influence of solvent on composition of prepared nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 243: 214–219
Ullmann M., Friedlander S.K., Schmidt-Ott A. (2002) Nanoparticle formation by laser ablation. J. Nanoparticles Res. 4: 499–509
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank N. Taghavinia for valuable comments, F. Hessari and F. S. Torknic from Materials and Energy Research Center for TEM data. This work was financially supported by the Ministry of Science, Research and Technology, and High Tech. Center of the Ministry of Industries and Mines.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tilaki, R.M., zad, A.I. & Mahdavi, S.M. The effect of liquid environment on size and aggregation of gold nanoparticles prepared by pulsed laser ablation. J Nanopart Res 9, 853–860 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-006-9143-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-006-9143-0