Abstract
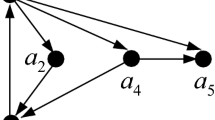
We propose an optical computational device which uses light rays for solving the subset-sum problem. The device has a graph-like representation and the light is traversing it by following the routes given by the connections between nodes. The nodes are connected by arcs in a special way which lets us to generate all possible subsets of the given set. To each arc we assign either a number from the given set or a predefined constant. When the light is passing through an arc it is delayed by the amount of time indicated by the number placed in that arc. At the destination node we will check if there is a ray whose total delay is equal to the target value of the subset sum problem (plus some constants). The proposed optical solution solves a NP-complete problem in time proportional with the target sum, but requires an exponential amount of energy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaronson S (2005) NP-complete problems and physical reality, ACM SIGACT News Complexity Theory Column, March. ECCC TR05-026, quant-ph/0502072
Adleman L (1994) Molecular computation of solutions to combinatorial problems. Science 266:1021–1024
Agrawal GP (2002) Fiber-optic communication systems, 3rd edn. Wiley-Interscience
Bajcsy M, Zibrov AS, Lukin MD (2003) Stationary pulses of light in an atomic medium. Nature 426:638–641
Bringsjord S, Taylor J (2004) P = NP, cs.CC/0406056
Cormen TH, Leiserson CE, Rivest RR (1990) Introduction to algorithms. MIT Press
Faist J (2005) Optoelectronics: silicon shines on. Nature 433:691–692
Feitelson DG (1988) Optical computing: a survey for computer scientists, MIT Press
Flyckt SO, Marmonier C (2002) Photomultiplier tubes: principles and applications. Photonis, Brive, France
Garey MR, Johnson DS (1979) Computers and intractability: a guide to NP-completeness. Freeman & Co, San Francisco, CA
Gilmore PC, Gomory RE (1965) Multistage cutting stock problems of two and more dimensions. Oper Res 13(1):94–120
Goodman JW (1982) Architectural development of optical data processing systems. Aust J Electr Electron Eng 2:139–149
Haist T and Osten W (2007) An optical solution for the traveling salesman problem. Opt Express 15:10473–10482
Hartmanis J (1995) On the weight of computations. B EATCS 55:136–138
Hau LV, Harris SE, Dutton Z, Behroozi CH (1999) Light speed reduction to 17 m per second in an ultracold atomic gas. Nature 397:594–598
Kieu TD (2003) Quantum algorithm for Hilbert’s tenth problem. Int J Theor Phys 42:1461–1478
Lenslet website (2005) http://www.lenslet.com
Liu C, Dutton Z, Behroozi CH, Hau LV (2001) Observation of coherent optical information storage in an atomic medium using halted light pulses. Nature 409:490–493
Murphy N, Naughton TJ, Woods D, Henley B, McDermott K, Duffy E, van der Burgt PJM, Woods N (2006) Implementations of a model of physical sorting. In: Adamatzky A, Teuscher C (eds) From Utopian to genuine unconventional computers workshop, Luniver Press, pp 79–100
Naughton TJ (2000) A model of computation for Fourier optical processors. In: Lessard RA, Galstian T (eds) Optics in computing, Proceedings SPIE 4089:24–34
Oltean M (2006) A light-based device for solving the Hamiltonian path problem. In: Calude C et al (eds) Unconventional computing LNCS 4135, Springer-Verlag, pp 217–227
Oltean M (2007) Solving the Hamiltonian path problem with a light-based computer. Nat Comput doi:10.1007/s11047-007-9042-z
Paniccia M, Koehl S (2005) The silicon solution. IEEE Spectrum, IEEE Press, October
Reif JH, Tyagi A (1997) Efficient parallel algorithms for optical computing with the discrete Fourier transform primitive. Appl Optics 36(29):7327–7340
Rong H, Jones R, Liu A, Cohen O, Hak D, Fang A, Paniccia M (2005a) A continuous-wave Raman silicon laser. Nature 433:725–728
Rong H, Liu A, Jones R, Cohen O, Hak D, Nicolaescu R, Fang A, Paniccia M (2005b) An all-silicon Raman laser. Nature 433:292–294
Schultes D (2005) Rainbow Sort: sorting at the speed of light. Nat Comput, Springer-Verlag 5(1):67–82
Shaked NT, Messika S, Dolev S and Rosen J (2007) Optical solution for bounded NP-complete problems. Appl Optics 46:711–724
Shor P (1997) Polynomial-time algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer. SIAM J Comput 26(5):1484–1509
Thoughts on the subset sum problem (P vs. NP) (accessed 2006) http://idrone.net/2006/06/11/thoughts-on-the-subset-sum-problem-p-vs-np
Vergis A, Steiglitz K, Dickinson B (1986) The complexity of analog computation. Math Comput Simulat 28:91–113
Woods D, Naughton TJ (2005) An optical model of computation. Theor Comput Sci 334 (1–3):227–258
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oltean, M., Muntean, O. Solving the subset-sum problem with a light-based device. Nat Comput 8, 321–331 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11047-007-9059-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11047-007-9059-3