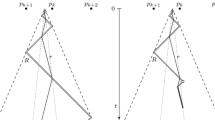
Abstract
In this paper, the problem of optimizing energy for communication and motion is investigated. We consider a single mobile robot with continuous high bandwidth wireless communication, e.g. caused by a multimedia application like video surveillance. This robot is connected to radio base station(s), and moves with constant speed from a given starting point on the plane to a target point. The task is to find the best path such that the energy consumption for mobility and the communication is optimized. This is motivated by the fact that the energy consumption of radio devices increases polynomially (at least to the power of two) with the transmission distance. We introduce efficient approximation algorithms to find the optimal path given the starting point, the target point and the position of the radio stations. We exemplify the influence of the communication cost by a starting scenario with one radio station. We study the performance of the proposed algorithm in simulation, compare it with the scenario without applying our approach, and present the results.










Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Position-critical Communications Model
References
Swarm-bots Project (2005) The European Commission (IST-2000-31010). http://www.swarm-bots.org. Accessed 16 Jan 2009
e-puck Education Robot Project (2009) Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne (EPFL). http://www.e-puck.org. Accessed 16 Jan 2009
Khepera Robots (2008) K-Team Corporation. http://www.k-team.com. Accessed 16 Jan 2009
Akyildiz IF, Melodia T, Chowdhury KR (2007) A survey on wireless multimedia sensor networks. Comput Networks 51(4):921–960. doi:10.1016/j.comnet.2006.10.002
Anh Tuan Hoang MM (2005) Exploiting wireless broadcast in spatially correlated sensor networks. In: IEEE ICC, pp 2807– 2811
Capkun S, Hubaux JP, Buttyán L (2003) Mobility helps security in ad hoc networks. In: Proceedings of the 4th ACM MobiHoc, pp 46–56
Das SM, Hu YC, Lee CG, Lu YH (2005) An efficient group communication protocol for mobile robots. In: IEEE ICRA
Goldenberg DK, Lin J, Morse AS, Rosen BE, Yang YR (2004) Towards mobility as a network control primitive. In: Proceedings of the 5th ACM MobiHoc. ACM Press, New York, NY, USA, pp 163–174. doi:10.1145/989459.989481
Grossglauser M, Tse DNC (2002) Mobility increases the capacity of ad hoc wireless networks. IEEE/ACM Trans Netw 10(4):477–486. doi:10.1109/TNET.2002.801403
Gruenewald M, Rueckert U, Schindelhauer C, Volbert K (2003) Directed power-variable infrared communication for the mini robot khepera. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International conference on autonomous minirobots for research and edutainment, pp 113–122
Koutsonikolas D, Das SM, Hu YC, Lu YH, Lee CSG (2006) Cocoa: coordinated cooperative localization for mobile multi-robot ad hoc networks. In: Proceedings of the 26th IEEE ICDCSW. IEEE computer society, Washington, DC, USA, p 9. doi:10.1109/ICDCSW.2006.30
Labella TH, Fuchs G, Dressler F (2006) A simulation model for self-organised management of sensor/actuator networks. In: GI/ITG KuVS Fachgespr”ach Selbstorganisierende, Adaptive, Kontextsensitive verteilte Systeme (SAKS)
Li XY, Wan PJ (2001) Constructing minimum energy mobile wireless networks. ACM Mobile Comp Commun Rev 5(4):55–67
Liu B, Brass P, Dousse O, Nain P, Towsley D (2005) Mobility improves coverage of sensor networks. In: Proceedings of the 6th ACM MobiHoc, pp 300–308
Lucent Technologies (2000) Orinoco PC card
Mei Y, Lu YH, Hu YC, Lee C (2005) A case study of mobile robot’s energy consumption and conservation techniques. In: 12th IEEE ICAR, pp 492–497
Meyer auf der Heide F, Schindelhauer C, Volbert K, Grünewald M (2004) Congestion, dilation, and energy in radio networks. TOCS 37(3):343–370
Powers M, Balch T, Lab B (2004) Value-based communication preservation for mobile robots. In: IEEE ICRA
Rodoplu V, Meng T (1998) Minimum energy mobile wireless networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE ICC, vol 3, pp 1633–1639
Schaubach K, Davis NJ, Rappaport T (1992) A ray tracing method for predicting path loss and delay spread in microcellular environment. In: Proceedings of IEEE 42nd vehicular technology conference. IEEE, pp 932–935
Tang C, McKinley PK (2006) Energy optimization under informed mobility. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 17(9):947–962. doi:10.1109/TPDS.2006.122
Tipler PA (1991) Physics for scientists and engineers. Worth, New York
Tseng YC, Wang YC, Cheng KY, Hsieh YY (2007) Imouse: an integrated mobile surveillance and wireless sensor system. Computer 40:60–66
Zeng QA, Agrawal DP (2002) Handoff in wireless mobile networks. In: Handbook of wireless networks and mobile computing, pp 1–25
Acknowledgements
This research is partially supported by DFG-Sonderforschungsbereich SPP 1183: Organic Computing. Smart Teams: Local, Distributed Strategies for Self-Organizing Robotic Exploration Teams.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ooi, C.C., Schindelhauer, C. Minimal Energy Path Planning for Wireless Robots. Mobile Netw Appl 14, 309–321 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-008-0150-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-008-0150-5