Abstact
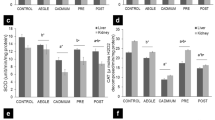
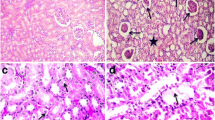
Cadmium is one of the most toxic pollutants in environment. Cadmium accumulation in blood affects the renal cortex and causes renal failure. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the effects of cadmium on rat liver tissue. Eighteen male albino rats aged ten weeks old were used in the study. 15 ppm of cadmium was administered to rats via consumption water daily. At the end of the 30th study day, the animals were killed under ether anesthesia. After the liver tissue samples were taken, histopathological and biochemical examinations were performed. Histopathologic changes have included vacuolar and granular degenerations in hepatocytes, heterochromatic nucleuses and sinusoidal and portal widenings. Central vein diameters were normal in cadmium exposed group. Whereas, there was statistically significant difference between two groups by means of sinusoidal (p< 0.001) and portal triad diameters (p< 0.01). Malondialdehyde (MDA) is an indicator of lipid peroxidation. In this study, MDA was used as a marker of oxidative stress-induced liver impairment in cadmium exposed rats. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) activities were also measured to evaluate the changes in antioxidative system in liver tissues. Current findings showed that MDA levels were increased and SOD and CAT activities were decreased in cadmium exposed group compared to control group. The difference between two groups was statistically significant (pvalues: MDA,p< 0.01; CAT,p< 0.01 and SOD,p< 0.05). In conclusion, these findings suggest the role of oxidative mechanisms in cadmium-induced liver tissue damage
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Friberg L, Elinder CG, Kjellström T: Enviroinmental health criteria: cadmium. World Health Organization (Geneva) 134: 36–43, 1992
Alfen T, Elinder CG, Jarup L: Cadmium: A public health problem. Nord Med 112: 331–333, 1997
Jonah MM, Bhattacharyya MH: Early changes in the tissue distribution of cadmium after oral but not intravenous cadmium exposure. Toxicology 58: 325–338, 1989
Oner G, Sentürk UK, Uysal N: Role of Cd – induced lipid peroxidation in kidney response to atrial natriuretic hormone. Nephron 72: 257–262, 1996
Oner G, Bilgen I, Edremitlioglu M, Aklan Z: The effect of cadmium and zinc ions on vascular tonus. Metal Ions Biol Med 6: 638–640, 2000
Kopp SK, Glonek T, Erlanger M, Perry E, Perry M, Barany M: Cadmium and lead effects on myocardial function and metabolism. J Environ Pathol Toxicol 4: 205–227, 1980
Voors AW, Johnson W, Shuman MS: Additive statistical effects of cadmium and lead on heart-related disease in a North Carolina autopsy series. Arch Environ Health 37(2): 98–102, 1982
Kayama F, Yoshida T, Elwell MR, Luster MI: Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in cadmium-induced hepatotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 131(2): 224–234, 1995
Stohs SJ, Bagchi D, Hassoun E, Bagchi M: Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of chromium and cadmium ions. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 19(3): 201–213, 2000
Shaikh ZA, Vu TT, Zaman K: Oxidative stress as a mechanism of chronic cadmium-induced hepatotoxicity and renal toxicity and protection by antioxidants. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 154(8): 256–263, 1999
Rikans LE, Yamano T: Mechanisms of cadmium-mediated acute hepatotoxicity. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 14(2): 110–117, 2000.
Yamano T, Shimizu M, Noda T: Age-related change in cadmium-induced hepatotoxicity in wistar rats: role of Kupffer cells and neutrophils. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 151(7): 9–15, 1998
Bilgen I, Oner G, Edremitlioglu M, Alkan Z, Cirrik S: Involvement of cholinoceptors in cadmium-induced endothelial dysfunction. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 14(1): 55–76, 2003
Draper HH, Hadley M: Malondialdehyde determination as index of lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 186: 421–431, 1990
Sun Y, Oberley LW, Li Y: A simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin Chem 34: 497–500, 1988
Aebi Y: Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105: 121–126, 1984
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ: Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Clin Chem 193: 265–269, 1951
Gokcimen A, Aydin G, Karaoz E, Malas M.A, Oncu M: Effect of diclofenac sodium administration during pregnancy in postnatal period. Fetal Diagnosis and Therapy 16: 417–422, 2001
Hoffmann EO, Cook JA, di Luzio NR, Coover JA: The effects of acute cadmium administration in the liver and kidney of the rat. Light and electron microscopic studies. Lab Invest 32(5): 655–664, 1975
Wlostowski T, Krasowska A, Laszkiewicz-Tiszczenko B: Dietary cadmium induces histopathological changes despite a sufficient metallothionein level in the liver and kidneys of the bank vole (Clethrionomys glareolus). Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 126(1): 21–28, 2000
Wada K, Fujii Y, Watanabe H, Satoh M, Furuichi Y: Cadmium directly acts on endothelin receptor and inhibits endothelin binding activity. FEBS 285(1): 71–74, 2000
Holecyova A, Torok J: The effect of cadmium on neuromuscular transmission in rabbit blood vessels. Bratisl Lek Listy 91(11): 839–943, 1990
Irmak MK, Fadillioglu E, Gulec M, Erdogan H, Yagmurca M, Akyol O: Effects of electromagnetic radiation from a cellular telephone on the oxidant and antioxidant levels in rabbits. Cell Biochem Funct 20: 279–283, 2002
Ilhan A, Gurel A, Armutcu F, Kamisli S, Iraz M, Akyol O, Ozen S: Ginkgo biloba prevents mobile phone-induced oxidative stress in rat brain. Clin Chim Acta 340: 153–162, 2004
Ozguner F, Oktem F, Ayata A, Koyu A, Yilmaz HR: A novel antioxidant agent caffeic acid phenethyl ester prevents long-term mobile phone exposure-induced renal impairment in rat: Prognostic value of malondialdehyde, N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase and nitric oxide determination. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry 277: 73–80, 2005.
Oury TD, Day BJ, Crapo JD: Extracellular superoxide dismutase in vessels and airways of humans and baboons. Free Rad Biol Med 20: 957–965, 1996
Nicholls DG, Budd SL: Mitochondria and neuronal survival. Physiol Rev 80: 315–360, 2000
Wu KK: Inducible cyclooxygenase and nitric oxide synthase. Adv Pharmacol 33: 179–207, 1995
Schmedtje JF, Ji YS, Liu WL, DuBois RN, Runge MS: Hypoxia induces cyclooxygenase-2 via the NF-kappaB p65 transcription factor in human vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 272: 601–608, 1997
Erdogan Z, Erdogan S, Celik S, Unlu A: Effects of ascorbic Acid on cadmium-induced oxidative stress and performance of broilers. Biol Trace Elem Res 104(1): 19–32, 2005
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koyu, A., Gokcimen, A., Ozguner, F. et al. Evaluation of the effects of cadmium on rat liver. Mol Cell Biochem 284, 81–85 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-005-9017-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-005-9017-2