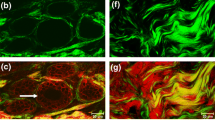
Abstract
Advances in optical imaging technologies that allow the subcellular resolution of undissected tissue have begun to offer new clues into the biology of development and disease. For cancer, such advances mean that the primary tumor is no longer a black box and that the disease can be studied throughout the metastatic cascade and not just as an endpoint. In this review we examine the advances in multiphoton imaging technology that have been used to define the microenvironment and its role in delineating the invasion and intravasation steps of metastasis inside living mammary tumors. Results show that the tumor microenvironment is a dynamic place where interactions between tumor cells, macrophages, blood vessels, and extracellular matrix fibers define the metastatic phenotype.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ECM:
-
extracellular matrix
- MPIVI:
-
multiphoton-based intravital imaging
- SHG:
-
second harmonic generation
- MMPs:
-
matrix metallo-proteases
- GFP:
-
green fluorescent protein
- CFP:
-
cyan fluorescent protein
References
Weigelt B, Peterse JL, van ’t Veer LJ. Breast cancer metastasis: markers and models. Nat Rev Cancer 2005;5(8):591–602.
Callahan R, Smith GH. MMTV-induced mammary tumorigenesis: gene discovery, progression to malignancy and cellular pathways. Oncogene 2000;19(8):992–1001.
Varghese HJ, Mackenzie LT, Groom AC, Ellis CG, Ryan A, MacDonald IC, et al. In vivo videomicroscopy reveals differential effects of the vascular-targeting agent ZD6126 and the anti-angiogenic agent ZD6474 on vascular function in a liver metastasis model. Angiogenesis 2004;7(2):157–64.
Graham KC, Wirtzfeld LA, MacKenzie LT, Postenka CO, Groom AC, MacDonald IC, et al. Three-dimensional high-frequency ultrasound imaging for longitudinal evaluation of liver metastases in preclinical models. Cancer Res 2005;65(12):5231–7.
Al-Mehdi AB, Tozawa K, Fisher AB, Shientag L, Lee A, Muschel RJ. Intravascular origin of metastasis from the proliferation of endothelium-attached tumor cells: a new model for metastasis. Nat Med 2000;6(1):100–102.
Im JH, Fu W, Wang H, Bhatia SK, Hammer DA, Kowalska MA, et al. Coagulation facilitates tumor cell spreading in the pulmonary vasculature during early metastatic colony formation. Cancer Res 2004;64(23):8613–9.
Hoffman RM. The multiple uses of fluorescent proteins to visualize cancer in vivo. Nat Rev Cancer 2005;5(10):796–806.
Brown EB, Boucher Y, Nasser S, Jain RK. Measurement of macromolecular diffusion coefficients in human tumors. Microvasc Res 2004;67(3):231–6.
Jain RK. Normalization of tumor vasculature: an emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy. Science 2005;307(5706):58–62.
Tyrrell JA, Mahadevan V, Tong RT, Brown EB, Jain RK, Roysam B. A 2-D/3-D model-based method to quantify the complexity of microvasculature imaged by in vivo multiphoton microscopy. Microvasc Res 2005;70(3):165–78.
Farina KL, Wyckoff JB, Rivera J, Lee H, Segall JE, Condeelis JS, et al. Cell motility of tumor cells visualized in living intact primary tumors using green fluorescent protein. Cancer Res 1998;58(12):2528–32.
Wang W, Wyckoff JB, Frohlich VC, Oleynikov Y, Huttelmaier S, Zavadil J, et al. Single cell behavior in metastatic primary mammary tumors correlated with gene expression patterns revealed by molecular profiling. Cancer Res 2002;62(21):6278–88.
Condeelis J, Segall JE. Intravital imaging of cell movement in tumours. Nat Rev Cancer 2003;3(12):921–30.
Wyckoff J, Wang W, Lin EY, Wang Y, Pixley F, Stanley ER, et al. A paracrine loop between tumor cells and macrophages is required for tumor cell migration in mammary tumors. Cancer Res 2004;64(19):7022–9.
Emptage NJ. Fluorescent imaging in living systems. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2001;1(5):521–5.
Centonze VE, White JG. Multiphoton excitation provides optical sections from deeper within scattering specimens than confocal imaging. Biophys J 1998;75(4):2015–24.
Williams RM, Zipfel WR, Webb WW. Interpreting second-harmonic generation images of collagen I fibrils. Biophys J 2005;88(2):1377–86.
Agarwal AR, Mih J, George SC. Expression of matrix proteins in an in vitro model of airway remodeling in asthma. Allergy Asthma Proc 2003;24(1):35–42.
Sahai E, Wyckoff J, Philippar U, Segall JE, Gertler F, Condeelis J. Simultaneous imaging of GFP, CFP and collagen in tumors in vivo using multiphoton microscopy. BMC Biotechnol 2005;5:14.
Brown E, McKee T, diTomaso E, Pluen A, Seed B, Boucher Y, et al. Dynamic imaging of collagen and its modulation in tumors in vivo using second-harmonic generation. Nat Med 2003;9(6):796–800.
Campagnola PJ, Millard AC, Terasaki M, Hoppe PE, Malone CJ, Mohler WA. Three-dimensional high-resolution second-harmonic generation imaging of endogenous structural proteins in biological tissues. Biophys J 2002;82(1 Pt 1):493–508.
Agarwal A, Coleno ML, Wallace VP, Wu WY, Sun CH, Tromberg BJ, et al. Two-photon laser scanning microscopy of epithelial cell-modulated collagen density in engineered human lung tissue. Tissue Eng 2001;7(2):191–202.
Cahalan MD, Parker I, Wei SH, Miller MJ. Two-photon tissue imaging: seeing the immune system in a fresh light. Nat Rev Immunol 2002;2(11):872–80.
Jain RK, Brown EB, Munn LL, Fukumura D. Intravital Microscopy of Normal and Diseased Tissue in the Mouse. In: Live Cell Imaging: a Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor, New York: CSHL; 2004.
Lin EY, Jones JG, Li P, Zhu L, Whitney KD, Muller WJ, et al. Progression to malignancy in the polyoma middle T oncoprotein mouse breast cancer model provides a reliable model for human diseases. Am J Pathol 2003;163(5):2113–26.
Wyckoff JB, Segall JE, Condeelis JS. The collection of the motile population of cells from a living tumor. Cancer Res 2000;60(19):5401–4.
Motoike T, Loughna S, Perens E, Roman BL, Liao W, Chau TC, et al. Universal GFP reporter for the study of vascular development. Genesis 2000;28(2):75–81.
Faust N, Varas F, Kelly LM, Heck S, Graf T. Insertion of enhanced green fluorescent protein into the lysozyme gene creates mice with green fluorescent granulocytes and macrophages. Blood 2000;96(2):719–26.
Sasmono RT, Oceandy D, Pollard JW, Tong W, Pavli P, Wainwright BJ, et al. A macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor-green fluorescent protein transgene is expressed throughout the mononuclear phagocyte system of the mouse. Blood 2003;101(3):1155–63.
Stalder AK, Ermini F, Bondolfi L, Krenger W, Burbach GJ, Deller T, et al. Invasion of hematopoietic cells into the brain of amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice. J Neurosci 2005;25(48):11125–32.
Wyckoff JB, Jones JG, Condeelis JS, Segall JE. A critical step in metastasis: in vivo analysis of intravasation at the primary tumor. Cancer Res 2000;60(9):2504–11.
Wang W, Goswami S, Lapidus K, Wells AL, Wyckoff JB, Sahai E, et al. Identification and testing of a gene expression signature of invasive carcinoma cells within primary mammary tumors. Cancer Res 2004;64(23):8585–94.
Condeelis J, Pollard JW. Macrophages: obligate partners for tumor cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. Cell 2006;124(2):263–6.
Quaranta V. Motility cues in the tumor microenvironment. Differentiation 2002;70(9–10):590–8.
Friedl P, Wolf K. Tumour-cell invasion and migration: diversity and escape mechanisms. Nat Rev Cancer 2003;3(5):362–74.
Ingman W, Wyckoff J, Xue C, Lin EY, Wang W, Goswami S, et al. Imaging invasion and metastasis in vivo. In: Wells A, editor. Cell motility in cancer invasion and metastasis. Massachusetts: Kluwer; 2005 (chapter 3). Kluwer; 2005.
Bailly M, Condeelis J. Cell motility: insights from the backstage. Nat Cell Biol 2002;4(12):E292–4.
Buccione R, Orth JD, McNiven MA. Foot and mouth: podosomes, invadopodia and circular dorsal ruffles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2004;5(8):647–57.
Yamaguchi H, Lorenz M, Kempiak S, Sarmiento C, Coniglio S, Symons M, et al. Molecular mechanisms of invadopodium formation: the role of the N-WASP-Arp2/3 complex pathway and cofilin. J Cell Biol 2005;168(3):441–52.
Yamaguchi H, Wyckoff J, Condeelis J. Cell migration in tumors. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2005;17(5):559–64.
Hynes NE, Lane HA. ERBB receptors and cancer: the complexity of targeted inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer 2005;5(5):341–54.
Barnes CJ, Kumar R. Epidermal growth factor receptor family tyrosine kinases as signal integrators and therapeutic targets. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2003;22(4):301–7.
Klijn JG, Look MP, Portengen H, Alexieva-Figusch J, van Putten WL, Foekens JA. The prognostic value of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGF-R) in primary breast cancer: results of a 10 year follow-up study. Breast Cancer Res Treat 1994;29(1):73–83.
Siegel PM, Hardy WR, Muller WJ. Mammary gland neoplasia: insights from transgenic mouse models. Bioessays 2000;22(6):554–63.
Xue C, Wyckoff J, Liang F, Sidani M, Violini S, Tsai KL, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor overexpression results in increased tumor cell motility in vivo coordinately with enhanced intravasation and metastasis. Cancer Res 2006;66(1):192–7.
Pal SK, Pegram M. Epidermal growth factor receptor and signal transduction: potential targets for anti-cancer therapy. Anticancer Drugs 2005;16(5):483–94.
Bailly M, Wyckoff J, Bouzahzah B, Hammerman R, Sylvestre V, Cammer M, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor distribution during chemotactic responses. Mol Biol Cell 2000;11(11):3873–83.
Lichtner RB, Kaufmann AM, Kittmann A, Rohde-Schulz B, Walter J, Williams L, et al. Ligand mediated activation of ectopic EGF receptor promotes matrix protein adhesion and lung colonization of rat mammary adenocarcinoma cells. Oncogene 1995;10(9):1823–32.
Wyckoff JB, Insel L, Khazaie K, Lichtner RB, Condeelis JS, Segall JE. Suppression of ruffling by the EGF receptor in chemotactic cells. Exp Cell Res 1998;242(1):100–9.
Lewis CE, Pollard JW. Distinct role of macrophages in different tumor microenvironments. Cancer Res 2006;66(2):605–12.
Leek RD, Harris AL. Tumor-associated macrophages in breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 2002;7(2):177–89.
Henderson IC, Patek AJ. The relationship between prognostic and predictive factors in the management of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 1998;52(1-3):261–88.
Goswami S, Sahai E, Wyckoff JB, Cammer M, Cox D, Pixley FJ, et al. Macrophages promote the invasion of breast carcinoma cells via a colony-stimulating factor-1/epidermal growth factor paracrine loop. Cancer Res 2005;65(12):5278–83.
Shestakova EA, Wyckoff J, Jones J, Singer RH, Condeelis J. Correlation of beta-actin messenger RNA localization with metastatic potential in rat adenocarcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res 1999;59(6):1202–5.
Shaner NC, Campbell RE, Steinbach PA, Giepmans BN, Palmer AE, Tsien RY. Improved monomeric red, orange and yellow fluorescent proteins derived from Discosoma sp. red fluorescent protein. Nat Biotechnol 2004;22(12):1567–72.
Levene MJ, Dombeck DA, Kasischke KA, Molloy RP, Webb WW. In vivo multiphoton microscopy of deep brain tissue. J Neurophysiol 2004;91(4):1908–12.
Wang W, Mouneimne G, Sidani M, Wyckoff J, Chen X, Makris A, et al. The activity status of cofilin is directly related to invasion, intravasation, and metastasis of mammary tumors. J Cell Biol 2006;173(3):395–404.
Goswami S, Wang W, Wyckoff JB, Condeelis JS. Breast cancer cells isolated by chemotaxis from primary tumors show increased survival and resistance to chemotherapy. Cancer Res 2004;64(21):7664–7.
Wang W, Goswami S, Sahai E, Wyckoff JB, Segall JE, Condeelis JS. Tumor cells caught in the act of invading: their strategy for enhanced cell motility. Trends Cell Biol 2005;15(3):138–45.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank current and former laboratory members for their contributions to the work discussed in this review. The research summarized here was supported by CA100324.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Figures are available in color format in the online version of the article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sidani, M., Wyckoff, J., Xue, C. et al. Probing the Microenvironment of Mammary Tumors Using Multiphoton Microscopy. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 11, 151–163 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10911-006-9021-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10911-006-9021-5