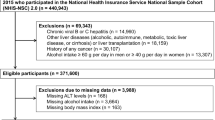
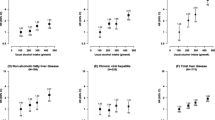
Abstract
The aim of this cross-sectional study was to present nationally representative findings on the co-occurrence of obesity and specific patterns of alcohol use associated with elevated serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT) among adults in the United States. We analyzed data from 8,373 adults aged ≥ 20 years who participated in the 2005–2008 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. We produced prevalence ratios by using the co-occurrence of obesity (i.e., body mass index ≥ 30.0 kg/m2 or waist circumference ≥ 102 cm in men and ≥ 88 cm in women) and specific patterns of alcohol use (i.e., non-drinkers, non-excessive drinkers, and excessive drinkers) as a predictor; elevations in serum ALT, AST, and GGT were used as an outcome variable while adjusting for covariates in multivariate regression models. Approximately 34.7% of adult men and 38.6% of adult women in the United States had co-occurrence of obesity and any alcohol use, including 16.4% of men and 9.8% of women who had co-occurrence of obesity and excessive drinking during 2005–2008. When compared to male non-drinkers without obesity after multivariate adjustment, male excessive drinkers with obesity were 3.08 (95% CI: 1.80–5.28), 2.42 (95% CI: 1.80–3.26), and 3.15 (95% CI: 1.82–5.46) times more likely to exhibit elevated serum ALT, AST, and GGT, respectively. Similarly, when compared to female non-drinkers without obesity, female excessive drinkers with obesity were 2.36 (95% CI: 1.38–4.04), 3.27 (95% CI: 1.85–5.78), and 3.43 (95% CI: 2.19–5.40) times more likely to have elevated serum ALT, AST, and GGT, respectively. The co-occurrence of obesity and excessive drinking may place adults at an increased risk for potential liver injury. Our study findings provide support for evidence-based clinical and population-based interventions that integrate health behavior change among adults who have these co-occurring risk factors.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, L. A., Knuiman, M. W., Divitini, M. L., & Olynyk, J. K. (2008). Body mass index is a stronger predictor of alanine aminotransaminase levels than alcohol consumption. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 23, 1089–1093.
Alatalo, P., Koivisto, H., Hietala, J., Puukka, K., Bloigu, R., & Niemela, O. (2008). Effect of moderate alcohol consumption on liver enzymes increases with increasing body mass index. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 88, 1097–1103.
Alatalo, P., Koivisto, H., Puukka, K., Hietala, J., Anttila, P., Bloigu, R., et al. (2009). Biomarkers of liver status in heavy drinkers, moderate drinkers and abstainers. Alcohol and Alcoholism, 44, 199–203.
APHA. (2008). Alcohol screening and brief intervention: A guide for public health practitioners. Washington DC: National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, US Department of Transportation. American Public Health Association (APHA) and Education Development Center, Inc.
Barros, A. J., & Hirakata, V. N. (2003). Alternatives for logistic regression in cross-sectional studies: An empirical comparison of models that directly estimate the prevalence ratio. BMC Medical Research Methodology, 3, 21.
Breslow, R. A., & Smothers, B. A. (2005). Drinking patterns and body mass index in never smokers: National Health Interview Survey, 1997–2001. American Journal of Epidemiology, 161, 368–376.
Calle, E. E., Rodriguez, C., Walker-Thurmond, K., & Thun, M. J. (2003). Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of US adults. The New England Journal of Medicine, 348, 1625–1638.
CDC. (2007). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Surveillance for acute viral hepatitis—United States, 2007. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 58, 1–27.
CDC. (2009a). The guide to community preventive services. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Atlanta, Georgia. URL: http://www.thecommunityguide.org/pa/index.html.
CDC. (2009b). Recommended community strategies and measurements to prevent obesity in the United States. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 58, 1–26.
CDC. (2010). National health and nutrition examination survey. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Atlanta, Georgia. URL: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes.htm.
Chang, Y., Ryu, S., Sung, E., & Jang, Y. (2007). Higher concentrations of alanine aminotransferase within the reference interval predict nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clinical Chemistry, 53, 686–692.
Chen, P. H., Chen, J. D., & Lin, Y. C. (2009). A better parameter in predicting insulin resistance: Obesity plus elevated alanine aminotransferase. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 15, 5598–5603.
Conigrave, K. M., Davies, P., Haber, P., & Whitfield, J. B. (2003). Traditional markers of excessive alcohol use. Addiction, 98, 31–43.
Conway, B., & Rene, A. (2004). Obesity as a disease: No lightweight matter. Obesity Reviews, 5, 145–151.
Day, C. P. (1997). Alcoholic liver disease: Dose and threshold–new thoughts on an old topic. Gut, 41, 857–858.
Diehl, A. M. (2010). Hepatic complications of obesity. Gastroenterology Clinics of North America, 39, 57–68.
Dolman, J. M., & Hawkes, N. D. (2005). Combining the audit questionnaire and biochemical markers to assess alcohol use and risk of alcohol withdrawal in medical inpatients. Alcohol and Alcoholism, 40, 515–519.
Ely, M., Hardy, R., Longford, N. T., & Wadsworth, M. E. J. (1999). Gender differences in the relationship between alcohol consumption and drink problems are largely accounted for body water. Alcohol and Alcoholism, 34, 894–902.
Fabricatore, A. N. (2007). Behavior therapy and cognitive-behavioral therapy of obesity: Is there a difference? Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 107, 92–99.
Flegal, K. M., Carroll, M. D., Ogden, C. L., & Curtin, L. R. (2010). Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2008. The Journal of the American Medical Association, 303, 235–241.
Ford, E. S., Li, C., Zhao, G., & Tsai, J. (2010). Trends in obesity and abdominal obesity among adults in the United States from 1999–2008. International Journal of Obesity (Online First). doi:10.1038/ijo.2010.186.
Ford, E. S., Schulze, M. B., Bergmann, M. M., Thamer, C., Joost, H. G., & Boeing, H. (2008). Liver enzymes and incident diabetes: Findings from the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition (EPIC)-potsdam study. Diabetes Care, 31, 1138–1143.
Foster, G. D., Makris, A. P., & Bailer, B. A. (2005). Behavioral treatment of obesity. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 82, 230S–235S.
Giboney, P. T. (2005). Mildly elevated liver transaminase levels in the asymptomatic patient. American Family Physician, 71, 1105–1110.
Gramenzi, A., Caputo, F., Biselli, M., Kuria, F., Loggi, E., Andreone, P., et al. (2006). Review article: Alcoholic liver disease–pathophysiological aspects and risk factors. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 24, 1151–1161.
Gregg, E. W., Cheng, Y. J., Cadwell, B. L., Imperatore, G., Williams, D. E., Flegal, K. M., et al. (2005). Secular trends in cardiovascular disease risk factors according to body mass index in US adults. The Journal of the American Medical Association, 293, 1868–1874.
Grundy, S. M., Cleeman, J. I., Daniels, S. R., Donato, K. A., Eckel, R. H., Franklin, B. A., et al. (2005). Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: An American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation, 112, 2735–2752.
Guh, D., Zhang, W., Bansback, N., Amarsi, Z., Birmingham, C. L., & Anis, A. (2009). The incidence of co-morbidities related to obesity and overweight: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health, 9, 88.
Hammond, R. A., & Levine, R. (2010). The economic impact of obesity in the United States. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy, 3, 285–295.
Hart, C. L., Morrison, D. S., Batty, G. D., Mitchell, R. J., & Davey Smith, G. (2010). Effect of body mass index and alcohol consumption on liver disease: Analysis of data from two prospective cohort studies. BMJ, 340, c1240.
Huang, T. T., & Glass, T. A. (2008). Transforming research strategies for understanding and preventing obesity. The Journal of the American Medical Association, 300, 1811–1813.
Hughes, S. C., Chambers, C. D., Kassem, N., Wahlgren, D. R., Larson, S., Riley, E. P., et al. (2009). Inconsistent report of pre-pregnancy-recognition alcohol use by Latinas. Maternal and Child Health Journal, 13, 857–864.
Johnson, S. S., Paiva, A. L., Cummins, C. O., Johnson, J. L., Dyment, S. J., Wright, J. A., et al. (2008). Transtheoretical model-based multiple behavior intervention for weight management: Effectiveness on a population basis. Preventive Medicine, 46, 238–246.
Kim, H. C., Nam, C. M., Jee, S. H., Han, K. H., Oh, D. K., & Suh, I. (2004). Normal serum aminotransferase concentration and risk of mortality from liver diseases: Prospective cohort study. BMJ, 328, 983.
Korn, E., & Graubard, B. (1999). Analysis of health surveys. New York: John Wiley and Sons, Inc.
Lee, T. H., Kim, W. R., Benson, J. T., Therneau, T. M., & Melton, L. J., 3rd. (2008). Serum aminotransferase activity and mortality risk in a United States community. Hepatology, 47, 880–887.
Li, C., Ford, E. S., Zhao, G., Balluz, L. S., & Giles, W. H. (2009). Estimates of body composition with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry in adults. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 90, 1457–1465.
Mason, J., Starke, R., & Van Kirk, J. (2010). Gamma-glutamyl transferase: A novel cardiovascular risk biomarker. Preventive Cardiology, 13, 36–41.
McIntosh, J. (2008). Is alcohol consumption good for you? Results from the 2005 Canadian community health survey. Addiction Research and Theory, 16, 553–563.
Morris, M. J. (2008). Cardiovascular and metabolic effects of obesity. Clin Exp Physiology and Pharmacology, 35, 416–419.
NACB. (2000). Laboratory medicine practice guidelines: Laboratory guidelines for screening, diagnosis and monitoring of hepatic injury. The National Academy of Clinical Biochemistry (NACB). Washington, DC.
NIAAA. (1997). Alcohol alert: Alcohol metabolism. No. 35. National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA). Rockville, MD.
NIAAA. (1999). Alcohol alert: Are women more vulnerable to alcohol’s effects? National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA). No. 46. Rockville, MD.
NIAAA. (2004). Binge drinking defined. Newsletter, Winter 2004, Number 3. National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, National Institute of Health, US Department of Health and Human Services. Rockville, Maryland.
NIAAA. (2005). National Institute on alcohol abuse and alcoholism. Helping patients who drink too much: A Clinician’s Guide. NIH Pub No. 05-3769. Bethesda, MD.
Nijem, K., Kristensen, P., Al-Khatib, A., & Bjertness, E. (2005). Application of different statistical methods to estimate relative risk for self-reported health complaints among shoe factory workers exposed to organic solvents and plastic compounds. Norwegian Journal of Epidemiology, 15, 111–116.
Nyblom, H., Berggren, U., Balldin, J., & Olsson, R. (2004). High AST/ALT ratio may indicate advanced alcoholic liver disease rather than heavy drinking. Alcohol and Alcoholism, 39, 336–339.
Ogden, C., Yanovski, S., Carroll, M., & Flegal, K. (2007). The epidemiology of obesity. Gastroenterology, 132, 2087–2102.
Okosun, I. S., Seale, J. P., Daniel, J. B., & Eriksen, M. P. (2005). Poor health is associated with episodic heavy alcohol use: Evidence from a National Survey. Public Health, 119, 509–517.
Orzano, A. J., & Scott, J. G. (2004). Diagnosis and treatment of obesity in adults: An applied evidence-based review. The Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine, 17, 359–369.
Peterson, K. (2004). Biomarkers for alcohol use and abuse: A summary. Alcohol Research & Health, 28, 30–37.
Pratt, D. S., & Kaplan, M. M. (2000). Evaluation of abnormal liver-enzyme results in asymptomatic patients. The New England Journal of Medicine, 342, 1266–1271.
Puukka, K., Hietala, J., Koivisto, H., Anttila, P., Bloigu, R., & Niemela, O. (2006). Additive effects of moderate drinking and obesity on serum gamma-glutamyl transferase activity. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 83, 1351–1354; quiz 1448–1359.
Rehm, J., Room, R., Graham, K., Monteiro, M., Gmel, G., & Sempos, C. T. (2003). The relationship of average volume of alcohol consumption and patterns of drinking to burden of disease: An overview. Addiction, 98, 1209–1228.
Ruhl, C. E., & Everhart, J. E. (2009). Elevated serum alanine aminotransferase and gamma-glutamyltransferase and mortality in the United States population. Gastroenterology, 136, 477–485.
Ruhl, C. E., & Everhart, J. E. (2010). Trunk fat is associated with increased serum levels of alanine aminotransferase in the United States. Gastroenterology, 138, 1346–1356, 1356 e1341–1343.
SAMHSA. (2006). The role of biomarkers in the treatment of alcohol use disorders. Substance abuse and mental health services administration (SAMHSA). Substance Abuse Treatment Advisory, 5.
Sato, K. K., Hayashi, T., Nakamura, Y., Harita, N., Yoneda, T., Endo, G., et al. (2008). Liver enzymes compared with alcohol consumption in predicting the risk of type 2 diabetes: The Kansai Healthcare Study. Diabetes Care, 31, 1230–1236.
Sharpe, P. C. (2001). Biochemical detection and monitoring of alcohol abuse and abstinence. Annals of Clinical Biochemistry, 38, 652–664.
St George, A., Bauman, A., Johnston, A., Farrell, G., Chey, T., & George, J. (2009). Effect of a lifestyle intervention in patients with abnormal liver enzymes and metabolic risk factors. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 24, 399–407.
Stockwell, T., Donath, S., Cooper-Stanbury, M., Chikritzhs, T., Catalano, P., & Mateo, C. (2004). Under-reporting of alcohol consumption in household surveys: A comparison of quantity-frequency, graduated-frequency and recent recall. Addiction, 99, 1024–1033.
Stranges, S., Dorn, J. M., Muti, P., Freudenheim, J. L., Farinaro, E., Russell, M., et al. (2004a). Body fat distribution, relative weight, and liver enzyme levels: A population-based study. Hepatology, 39, 754–763.
Stranges, S., Freudenheim, J. L., Muti, P., Farinaro, E., Russell, M., Nochajski, T. H., et al. (2004b). Differential effects of alcohol drinking pattern on liver enzymes in men and women. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 28, 949–956.
Stranges, S., Notaro, J., Freudenheim, J. L., Calogero, R. M., Muti, P., Farinaro, E., et al. (2006). Alcohol drinking pattern and subjective health in a population-based study. Addiction, 101, 1265–1276.
Sullivan, P. W., Ghushchyan, V., & Ben-Joseph, R. H. (2008). The effect of obesity and cardiometabolic risk factors on expenditures and productivity in the United States. Obesity (Silver Spring), 16, 2155–2162.
Targher, G. (2010). Elevated serum gamma-glutamyltransferase activity is associated with increased risk of mortality, incident type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular events, chronic kidney disease and cancer—a narrative review. Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine, 48, 147–157.
Tsai, J., Floyd, R. L., & O’ Connor, M. J. (2008). Paradigms for alcohol use and co-occurring behavioral health risk factors among women of childbearing age. In K. I. DiGuarde (Ed.), Binge drinking research progress (pp. 87–100). Hauppauge, NY: Nova Science Publishers, Inc.
Tsai, J., Ford, E. S., Li, C., Pearson, W. S., & Zhao, G. (2010a). Binge drinking and suboptimal self-rated health among adult drinkers. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 34, 1–7.
Tsai, J., Ford, E. S., Li, C., Zhao, G., Pearson, W. S., & Balluz, L. S. (2010b). Multiple healthy behaviors and optimal self-rated health: Findings from the 2007 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System Survey. Preventive Medicine, 51, 268–274.
USPSTF. (2004). Screening for obesity in adults: Recommendations and rationale. American Journal of Nursing, 104, 94–95, 97–98, 100.
Valencia-Martin, J. L., Galan, I., & Rodriguez-Artalejo, F. (2009). Alcohol and self-rated health in a Mediterranean country: The role of average volume, drinking pattern, and alcohol dependence. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 33, 240–246.
Vanbuskirk, K., & Potenza, M. (2010). The treatment of obesity and its co-occurrence with substance use disorders. Journal of Addiction Medicine, 4, 1–10.
Visscher, T. L., & Seidell, J. C. (2001). The public health impact of obesity. Annual Review of Public Health, 22, 355–375.
Vozarova, B., Stefan, N., Lindsay, R. S., Saremi, A., Pratley, R. E., Bogardus, C., et al. (2002). High alanine aminotransferase is associated with decreased hepatic insulin sensitivity and predicts the development of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes, 51, 1889–1895.
WHO. (2000). Obesity: Preventing and managing the global epidemic. The World Health Organization (WHO) Technical Report. Series 894.
Zhao, G., Ford, E. S., Li, C., & Mokdad, A. H. (2009a). Weight control behaviors in overweight/obese US adults with diagnosed hypertension and diabetes. Cardiovascular Diabetology, 8, 13.
Zhao, G., Ford, E. S., Li, C., Strine, T. W., Dhingra, S., Berry, J. T., & Mokdad, A. H. (2009b). Serious psychological distress and its associations with body mass index: Findings from the 2007 behavioral risk factor surveillance system. International Journal of Public Health, 54, 30–36.
Acknowledgments
The authors of this study sincerely thank the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS), Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), for data collection and for making the NHANES datasets available.
Conflicts of interest
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsai, J., Ford, E.S., Zhao, G. et al. Co-occurrence of obesity and patterns of alcohol use associated with elevated serum hepatic enzymes in US adults. J Behav Med 35, 200–210 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10865-011-9353-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10865-011-9353-5