Abstract
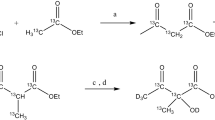
Adding the 13C labelled 2-keto-isovalerate and 2-oxobutanoate precursors to a minimal medium composed of 12C labelled glucose instead of the commonly used (2D, 13C) glucose leads not only to the 13C labelling of (I, L, V) methyls but also to the selective 13C labelling of the backbone Cα and CO carbons of the Ile and Val residues. As a result, the backbone (1H, 15N) correlations of the Ile and Val residues and their next neighbours in the (i + 1) position can be selectively identified in HN(CA) and HN(CO) planes. The availability of a selective HSQC spectrum corresponding to the sole amide resonances of the Ile and Val residues allows connecting them to their corresponding methyls by the intra-residue NOE effect, and should therefore be applicable to larger systems.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TauF1:
-
Residues 163-441 of the Tau protein
- HMQC:
-
Heteronuclear multiple quantum coherence
- HSQC:
-
Heteronuclear single quantum coherence
- NMR:
-
Nuclear magnetic resonance
- NOESY:
-
Nuclear Overhauser Effect spectroscopy
- TOCSY:
-
Total correlation spectroscopy
References
Brutscher B (2002) Intraresidue HNCA and COHNCA experiments for protein backbone resonance assignment. J Magn Reson 156:155–159
Butner KA, Kirschner MW (1991) Tau protein binds to microtubules through a flexible array of distributed weak sites. J Cell Biol 115:717–730
Chau MF, Radeke MJ, de Ines C, Barasoain I, Kohlstaedt LA, Feinstein SC (1998) The microtubule-associated protein tau cross-links to two distinct sites on each alpha and beta tubulin monomer via separate domains. Biochemistry 37:17692–17703
Cornilescu G, Delaglio F, Bax A (1999) Protein backbone angle restraints from searching a database for chemical shift and sequence homology. J Biomol NMR 13:289–302
Diercks T, Coles M, Kessler H (1999) An efficient strategy for assignment of cross-peaks in 3D heteronuclear NOESY experiments. J Biomol NMR 15:177
Gardner KH, Kay LE (1998) The use of 2H, 13C, 15N multidimensional NMR to study the structure and dynamics of proteins. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 27:357–406
Gelis I, Bonvin AM, Keramisanou D, Koukaki M, Gouridis G, Karamanou S, Economou A, Kalodimos CG (2007) Structural basis for signal-sequence recognition by the translocase motor SecA as determined by NMR. Cell 131:756–769
Goode BL, Denis PE, Panda D, Radeke MJ, Miller HP, Wilson L, Feinstein SC (1997) Functional interactions between the proline-rich and repeat regions of tau enhance microtubule binding and assembly. Mol Biol Cell 8:353–365
Goto NK, Kay LE (2000) New developments in isotope labeling strategies for protein solution NMR spectroscopy. Curr Opin Struct Biol 10:585–592
Goto NK, Gardner KH, Mueller GA, Willis RC, Kay LE (1999) A robust and cost-effective method for the production of Val, Leu, Ile (delta 1) methyl-protonated 15N-, 13C-, 2H-labeled proteins. J Biomol NMR 13:369–374
Grzesiek S, Bax A (1992) Improved 3D triple-resonance NMR techniques applied to a 31-Kda protein. J Magn Reson 96:432–440
Hanoulle X, Melchior A, Sibille N, Parent B, Denys A, Wieruszeski JM, Horvath D, Allain F, Lippens G, Landrieu I (2007) Structural and functional characterization of the interaction between cyclophilin B and a heparin-derived oligosaccharide. J Biol Chem 282:34148–34158
LeMaster DM (1988) Protein NMR resonance assignment by isotropic mixing experiments on random fractionally deuterated samples. FEBS Lett 233:326–330
Lippens G, Wieruszeski JM, Leroy A, Smet C, Sillen A, Buee L, Landrieu I (2004) Proline-directed random-coil chemical shift values as a tool for the NMR assignment of the tau phosphorylation sites. Chembiochem 5:73–78
Mandelkow EM, Biernat J, Drewes G, Gustke N, Trinczek B, Mandelkow E (1995) Tau domains, phosphorylation, and interactions with microtubules. Neurobiol Aging 16:355–362; discussion 362–353
Mikol V, Kallen J, Walkinshaw MD (1994) X-ray structure of a cyclophilin B/cyclosporin complex: comparison with cyclophilin A and delineation of its calcineurin-binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:5183–5186
Mueller GA, Kirby TW, DeRose EF, London RE (2003) NMR assignment of protein side chains using residue-correlated labeling and NOE spectra. J Magn Reson 165:237–247
Neidhardt FC, Curtiss III R, Ingraham JL, Lin ECC, Low Jr KB, Magasanik B, Reznikoff WS, Riley M, Schaechter M, Umbarger HE (1996) Escherichia coli and Salmonella. Cellular and Molecular Biology, 2nd edn. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC
Palmer AG, Cavanagh J, Wright PE, Rance M (1991) Sensitivity improvement in proton-detected two-dimensional heteronuclear correlation NMR spectroscopy. J Magn Reson 93:151–170
Pervushin K, Riek R, Wider G, Wuthrich K (1997) Attenuated T2 relaxation by mutual cancellation of dipole-dipole coupling and chemical shift anisotropy indicates an avenue to NMR structures of very large biological macromolecules in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:12366–12371
Piotto M, Bourdonneau M, Elbayed K, Wieruszeski JM, Lippens G (2006) New DEFT sequences for the acquisition of one-dimensional carbon NMR spectra of small unlabelled molecules. Magn Reson Chem 44:943–947
Rosen MK, Gardner KH, Willis RC, Parris WE, Pawson T, Kay LE (1996) Selective methyl group protonation of perdeuterated proteins. J Mol Biol 263:627–636
Sibille N, Bersch B, Coves J, Blackledge M, Brutscher B (2002) Side chain orientation from methyl 1H–1H residual dipolar couplings measured in highly deuterated proteins. J Am Chem Soc 124:14616–14625
Sibille N, Sillen A, Leroy A, Wieruszeski JM, Mulloy B, Landrieu I, Lippens G (2006) Structural impact of heparin binding to full-length Tau as studied by NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry 45:12560–12572
Sillen A, Barbier P, Landrieu I, Lefebvre S, Wieruszeski JM, Leroy A, Peyrot V, Lippens G (2007) NMR investigation of the interaction between the neuronal protein tau and the microtubules. Biochemistry 46:3055–3064
Sprangers R, Kay LE (2007) Quantitative dynamics and binding studies of the 20S proteasome by NMR. Nature 445:618–622
Sprangers R, Velyvis A, Kay LE (2007) Solution NMR of supramolecular complexes: providing new insights into function. Nat Methods 4:697–703
Tugarinov V, Kay LE (2003) Ile, Leu, and Val methyl assignments of the 723-residue malate synthase G using a new labeling strategy and novel NMR methods. J Am Chem Soc 125:13868–13878
Tugarinov V, Hwang PM, Ollerenshaw JE, Kay LE (2003) Cross-correlated relaxation enhanced 1H[bond]13C NMR spectroscopy of methyl groups in very high molecular weight proteins and protein complexes. J Am Chem Soc 125:10420–10428
Tugarinov V, Choy WY, Orekhov VY, Kay LE (2005) Solution NMR-derived global fold of a monomeric 82-kDa enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:622–627
Van Melckebeke H, Simorre JP, Brutscher B (2004) Amino acid-type edited NMR experiments for methyl-methyl distance measurement in 13C-labeled proteins. J Am Chem Soc 126:9584–9591
Verdegem D, Dijkstra K, Hanoulle X, Lippens G (2008) Graphical interpretation of Boolean operators for protein NMR assignments. J Biomol NMR 42:11–21
Yang D, Zheng Y, Liu D, Wyss DF (2004) Sequence-specific assignments of methyl groups in high-molecular weight proteins. J Am Chem Soc 126:3710–3711
Acknowledgements
The NMR facilities used in this study were funded by the Région Nord-Pas de Calais (France), FEDER, Ministère de la Recherche, the CNRS, the University of Lille 1 and the Institut Pasteur de Lille. Financial support from the TGIR-TGE RMN for conducting the research is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sibille, N., Hanoulle, X., Bonachera, F. et al. Selective backbone labelling of ILV methyl labelled proteins. J Biomol NMR 43, 219–227 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-009-9307-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-009-9307-1