Abstract
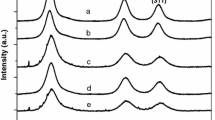
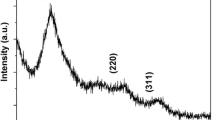
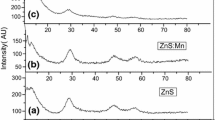
Mn-doped ZnS nanoparticles, having average diameter 3–5 nm, have been synthesized using chemical precipitation technique without using any external capping agent. Zinc blende crystal structure has been confirmed using the X-ray diffraction studies. The effect of various concentrations of Mn doping on the photoluminescent properties of ZnS nanoparticles has been studied. The time-resolved photoluminescence spectra of the ZnS:Mn quantum dots have been recorded and various parameters like lifetimes, trap depths, and decay constant have been calculated from the decay curves at room temperature. The band gap was calculated using UV–Visible absorption spectra.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhargava RN (1997) J Lumin 72–74:46. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2313(96)00162-7
Bhargava RN (1996) J Lumin 70:85. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2313(96)00046-4
Zhao Y, Zhang Y, Zhu H, Hadjipanayis GC, Xiao JQ (2004) J Am Chem Soc 126:6874. doi:https://doi.org/10.1021/ja048650g
Lu SW, Lee BI, Wang ZL, Tong W, Wagner BK, Park W et al (2001) J Lumin 92:73. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2313(00)00238-6
Hu JT, Li LS, Yang WD, Manna L, Wang LW, Alivisatos AP (2001) Science 292:2060. doi:https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1060810
Cruz AB, Shen Q, Toyoda T (2005) Mater Sci Eng C 25:761. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2005.06.022
Denzler D, Olschewski M, Sattler K (1998) J Appl Phys 84:2841. doi:https://doi.org/10.1063/1.368425
Chen W, Sammynaiken R, Huang Y, Malm JO, Wallenberg R, Bovin JO et al (2001) J Appl Phys 89:1120. doi:https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1332795
Kubo T, Isobe T, Sena M (2002) J Lumin 99:39. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2313(02)00296-X
Lacomi F (2003) Surf Sci 532:816. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0039-6028(03)00446-1
Yuan H, Xie S, Liu D, Yan X, Zhou Z, Ci L (2003) J Cryst Growth 258:225. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0248(03)01502-1
Kim D, Min K, Lee J, Park JH, Chun JH (2006) Mater Sci Eng B 131:13. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2005.11.005
Cullity BD (1956) Element of X-ray diffraction, 2nd edn. Addison-Wesley, New York, p 99
Yao JH, Elder KR, Guo H, Grant M (1993) Phys Rev B 47:14110. doi:https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.47.14110
Warad HC, Gosh SC, Hemtanon B, Thanochayonont C, Dutta J (2005) Sci Technol Adv Mater 6:296
Zou X, Ying E, Dong S (2006) Nanotechnology 17:4758. doi:https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/17/18/038
Silverstein RM, Clayton Bassler G, Morrill TC (1991) Spectrometric identification of organic compounds, 5th edn. Wiley, New York, pp 91–164
Bol AA, Meijerink A (1998) Phys Rev B 58:R15997. doi:https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.58.R15997
Kar S, Chaudhari S (2005) J Phys Chem B 109:3298. doi:https://doi.org/10.1021/jp045817j
Falcony C, Garcia M, Ortiz A, Zlonso JC (1992) J Appl Phys 72:1525. doi:https://doi.org/10.1063/1.351720
Samelson H, Lempicki A (1962) Phys Rev 125:901. doi:https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.125.901
Bhatti HS, Sharma R, Verma NK (2005) Parmana 65:541. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02704213
Cruz AB, Shen Q, Toyoda T (2005) Jpn J Appl Phys 44:4354. doi:https://doi.org/10.1143/JJAP.44.4354
Bhattacharyya D, Chaudhari S, Pal AK (1992) Vacuum 43:313. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/0042-207X(92)90163-Q
Vlasenko NA, Zynio SA, Kopytiko Y (1975) Phys Stat Solidi a 29:671
Bube RH (1950) Phys Rev 80:655. doi:https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.80.655
Acknowledgement
We acknowledge Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), Government of India, for their generous funding for the research work vide their letter No. ERIP/ER/0504321/M/01/855 dated 16th December 2005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jindal, Z., Verma, N.K. Photoluminescent properties of ZnS:Mn nanoparticles with in-built surfactant. J Mater Sci 43, 6539–6545 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2818-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2818-4