Abstract
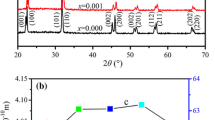
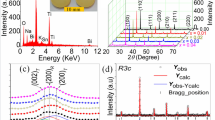
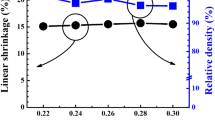
In this letter, MnO2-doped (Bi0.5Na0.5)0.94Ba0.06TiO3 (BNBT-6) lead-free piezoelectric ceramics were synthesized by solid state reaction, and the microstructure and electrical properties of the ceramics were investigated. X-ray diffraction (XRD) reveals that all specimens take on single perovskite type structure, and the diffraction peaks shift to a large angle as the MnO2 addition increases. Scanning electron microscopy shows that the grain sizes increases, and then decreases with increasing the MnO2 content. The experiment results indicate that the electrical properties of ceramics are significantly influenced by the MnO2 content, and the ceramics with homogeneous microstructure and excellent electrical properties are obtained with addition of 0.3 wt% MnO2 and sintered at 1160°C. The piezoelectric constant (d33), the electromechanical coupling factor (k p ), the dissipation factor (tan δ) and the dielectric constant (ɛ r ) reach 160 pC/N, 0.29, 0.026 and 879, respectively. These excellent properties indicate that the MnO2-doped BNBT-6 ceramics can be used for actuators.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Saito, H. Takao, T. Tani, T. Nonoyama, K. Takatori, T. Homma, T. Nagaya, M. Nakamura, Nature 432, 84–87 (2004)
T. Takenaka, H. Nagata, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 25, 2693–2700 (2005)
G.A. Smolenskii, V.A. Isupov, A.I. Agranovskaya, N.N. Kraink, Sov. Phys. Solid State 2, 2651–2653 (1961)
S.C. Zhao, G.R. Li, A.L. Ding, T.B. Wang, Q.R. Yin, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 39, 2277–2281 (2006)
T. Takenaka, K. Maruyama, K. Sakata, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 30(Part 1 No. 9B) 2236–2239 (1991)
D.L. West, D.A. Payne, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 86, 192–194 (2003)
X.X. Wang, X.G. Tang, H.L.W. Chan, Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 91–93 (2004)
W. Chen, Y.M. Li, Q. Xu, J. Zhou, J. Electroceram. 15, 229–235 (2005)
Y.M. Li, W. Chen, J. Zhou, Q. Xu, H.J. Sun, R.X. Xu, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 112, 5–9 (2004)
A. Herabut, A. Safari, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 80, 2954–2958 (1997)
J. Yoo, J. Hong, H. Lee, Y. Jeong, B. Lee, H. Song, J. Kwon, Sensors Actu. A 126, 41–47 (2006)
K. Pengpat, S. Hanphimol, S. Eitssayeam, U. Intatha, G. Rujijanagul, T. Tunkasiri, J Electroceram. 16, 301–305 (2006)
H.D. Li, C.D. Feng, W.L. Yao, Mater. Lett. 58, 1194–1198 (2004)
B.J. Chu, G.R. Li, Q.R. Yin, W.Z. Zhang, D.R. Chen, Acta Phys. Sin. 50, 2012–2016 (2001)
X.X. Wang, H.L.W. Chan, C.L. Choy, Solid State Commun. 125, 395–399 (2003)
S.J. Wu, Q. Xu, X.Z. Zhao, T. Liu, Y.M. Li, Mater. Lett. 60, 1453–1458 (2006)
H. Nagata, M. Yoshida, Y.Makiuchi, T. Takenaka, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 42, 7401–7404 (2003)
Y.M. Li, W. Chen, Q. Xu, J. Zhou, X.Y. Gu, Materials Letters 59, 1361–1364 (2005)
S.J. Zhang, T.R. Shrout, H. Nagata, et al. IEEE Trans. Ultrason Ferroelectr. Freq. Control, 54, 910 (2007)
T. Kamiya, T. Suzuki, T. Tsurami, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 31, 3058–3060 (1992)
IEEE Standard on Piezoelectricity. (American National Standards Institute, Washington, DC, 1976)
H.L. Du, Z.B. Pei, W.C. Zhou, F. Luo, S.B. Qu, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 421, 286–289 (2006)
H. Nagata, T. Takenka, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 21, 1299–1320 (2001)
L.S. He, C.E. Li, J. Mater. Sci. 35, 2477–2480 (2000)
S.J. Zhang, R. Xia, T. R. Shrout, Mater. Sci. Eng. B129, 131 (2006)
P. Roy-Chowdhury, S.B. Deshpande, J. Mater. Sci. 22, 2209–2211 (1987)
W. L. Zhong, Physics of Ferroelectrics. (Science Press, 1996), pp. 274–285
T. Kamiya, T. Suzuki, T. Tsurumi, M. Daimon, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 31, 3058–3061 (1992)
Y.D. Hou, P.X. Lu, M.K. Zhu, X.M. Song, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 116, 104–108 (2005)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 10374064) and Education Office Science Foundation of Shannxi province, China (Grant No.03JK061).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, XJ., Wang, Q. & Li, QL. Effects of MnO2 addition on microstructure and electrical properties of (Bi0.5Na0.5) 0.94Ba0.06TiO3 ceramics. J Electroceram 20, 89–94 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-007-9362-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-007-9362-5