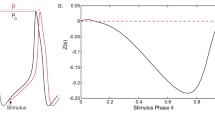
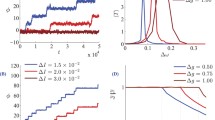
Abstract
A number of experimental groups have recently computed Phase Response Curves (PRCs) for neurons. There is a great deal of noise in the data. We apply methods from stochastic nonlinear dynamics to coupled noisy phase-resetting maps and obtain the invariant density of phase distributions. By exploiting the special structure of PRCs, we obtain some approximations for the invariant distributions. Comparisons to Monte-Carlo simulations are made. We show how phase-dependence of the noise can move the peak of the invariant density away from the peak expected from the analysis of the deterministic system and thus lead to noise-induced bifurcations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acebron JA, Bonilla LL, Prez Vicente, CJ, Ritort F, Spigler R (2005) The Kuramoto model: A simple paradigm for synchronization phenomena. Reviews of Modern Physics 77: 137–185.
Ariaratnam JT, Strogatz SH (2001) Phase diagram for the Winfree model of coupled nonlinear oscillators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86: 4278–4281.
Buzsaki G, Draguhn A (2004) Neuronal oscillations in cortical networks. Science 304: 1926–1929.
Chow CC, White JA, Ritt, J, Kopell N (1998) Frequency control in synchronized networks of inhibitory neurons. J. Comput. Neurosci. 5: 407–420.
Ermentrout B, Pascal M, Gutkin B (2001) The effects of spike frequency adaptation and negative feedback on the synchronization of neural oscillators. Neural Computation 13: 1285–1310.
Galan RF, Ermentrout GB, Urban NN (2005) Efficient estimation of phase-resetting curves in real neurons and its significance for neural-network modeling. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94: 158101.
Gardiner CW (1997) Handbook of Stochastic Methods (2nd edition). Springer, New York.
Goel P, Ermentrout B (2002) Synchrony, stability, and firing patterns in pulse-coupled oscillators Physica D 163: 191–216.
Izhikevich EM (2003) Simple model of spiking neurons. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 14: 1569–1572.
Jones SR, Pinto DJ, Kaper TJ, Kopell N (2000) Alpha-frequency rhythms desynchronize over long cortical distances: A modeling study. J. Comput. Neurosci. 9: 271–91.
Lasota A, Mackey MC (1986) Chaos, Fractals and Noise: Stochastic Aspects of Dynamics, Springer Applied Mathematical Science 97. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (Chapt. 10.5).
Lindner B, Garcia-Ojalvo J, Neiman A, Schimansky-Geier L (2004) Effects of noise in excitable systems, Phys. Rep. 392, 321.
Mirollo RM, Strogatz SH (1990) Synchronization of pulse-coupled biological oscillators. SIAM. J. Appl. Math. 50: 1645–1662.
Netoff TI, Banks MI, Dorval AD, Acker CD, Haas JS, Kopell N, White JA (2005) Synchronization in hybrid neuronal networks of the hippocampal formation. J. Neurophysiol. 93: 1197–208.
Oprisan SA, Canavier CC (2000) Phase response curve via multiple time scale analysis of limit cycle behavior of type I and type II excitability. Biophys. J. 78: 218–230.
Reyes AD, Fetz EE (1993) Effects of transient depolarizing potentials on the firing rate of cat neocortical neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 69: 1673–183.
Rodriguez R, Tuckwell HC (1996) Statistical properties of stochastic nonlinear dynamical models of single spiking neurons and neural networks. Physical Review E 54: 5585–5590.
Sompolinsky H, Golomb D, Kleinfeld D (1991) Phase coherence and computation in a neural network of coupled oscillators. In: Non-Linear Dynamics and Neural Networks, H.G. Schuster and W Singer Eds. (VCH, Weinheim, 1991), pp. 113–140.
Stoop R, Schindler K, Bunimovich LA (2000) Neocortical networks of pyramidal neurons: From local locking and chaos to macroscopic chaos and synchronization. Nonlinearity 13: 1515–1529.
Strogatz, S (2000) From Kuramoto to Crawford: Explaining the onset of synchronization in populations of globally coupled oscillators. Physica D 143: 1–20.
Tass PA (2003) Stochastic phase resetting of two coupled phase oscillators stimulated at different times. Phys. Rev. E 67:05 1902.
Van Vreeswijk C, Abbott LF, Ermentrout GB (1994) When inhibition not excitation synchronizes neural firing. J. Comput. Neurosci. 1: 313–321.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
B. Ermentrout supported in part by NIMH and NSF.
Action Editor: Wulfram Gerstner
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ermentrout, B., Saunders, D. Phase resetting and coupling of noisy neural oscillators. J Comput Neurosci 20, 179–190 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-005-5427-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-005-5427-0