Abstract
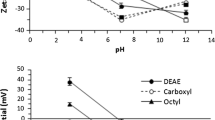
Although adhesion of bacteria and yeast have been extensively studied by a wide range of experimental and theoretical approaches, significantly less attention has been focused on microalgae adhesion to solid materials. This work is focused on physicochemical aspects of microalgae adhesion. The results are based on experimental characterization of surface properties of both microalgae and solids by contact angle and zeta potential measurements. These data are used in modeling the surface interactions (thermodynamic and colloidal models) resulting in quantitative prediction of the interaction intensities. Finally, the model predictions are compared with experimental adhesion tests of microalgae onto model solids in order to identify the physicochemical forces governing the microalgae–solid interaction. The model solids were prepared in order to cover a wide range of properties (hydrophobicity and surface charge). The results revealed that, in low ionic strength environment, the adhesion was influenced mostly by electrostatic attraction/repulsion between surfaces, while with increasing ionic strength grew the importance of apolar (hydrophobic) interactions. The impact of solid surface properties on the degree of colonization by microlagae was statistically more significant than the influence of medium composition on cell surface of Chlorella vulgaris.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barberousse H, Brayner R, Do Rego AMB, Castaing JC, Beurdeley-Saudou P, Colombert JF (2007) Adhesion of façade coating colonizers, as mediated by physic–chemical properties. Biofouling 23:15–24
Boonaert CJ-P, Dupont-Gillain CC, Dengis PB, Dufrene YF, Rouxhet PG (1999) Cell separation, flocculation. In: Flickinger MC, Drew SW (eds) Encyclopedia of bioprocess technology: fermentation, biocatalysis and bioseparation. Wiley, New York, pp 531–548
Borowitzka MA (1999) Commercial production of microalgae: ponds, tanks, tubes and fermenters. J Biotechnol 70:313–321
Bos R, van der Mei HC, Busscher HJ (1999) Physicochemistry of initial microbial adhesive interactions—its mechanisms and methods for study. FEMS Microbiol Rev 23:179–230
Brányiková I, Maršálková B, Doucha J, Brányik T, Bišová K, Zachleder V, Vítová M (2011) Microalgae—novel highly efficient starch producers. Biotechnol Bioeng 108:766–776
Callow ME (2000) Algal biofilms. In: Evans LV (ed) Biofilms: recent advances in their study and control. Hardwood, Amsterdam, pp 189–209
Carvalho AP, Meireles LA, Malcata XF (2006) Microalgal reactors: a review of enclosed system designs and performances. Biotechnol Prog 22:1490–1506
Carvalho AP, Silva SO, Baptista JM, Malcata Xavier F (2011) Light requirements in microalgal photobioreactors: an overview of biophotonic aspects. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89:1275–1288
Chen CY, Yeh KL, Aisyah R, Lee DJ, Chang JS (2011) Cultivation, photobioreactor design and harvesting of microalgae for biodiesel production: a critical review. Bioresour Technol 102:71–81
Dengis PB, Nélissen LR, Rouxhet PG (1995) Mechanism of yeast flocculation: comparison of top and bottom-fermenting strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:718–728
Doucha J, Lívanský K (2006) Productivity, CO2/O2 exchange and hydraulics in outdoor open high density microalgal (Chlorella sp.) photobioreactors operated in a Middle and Southern European climate. J Appl Phycol 18:811–826
Doušková I, Doucha J, Livansky K, Machat J, Novak P, Umysova D, Zachleder V, Vitova M (2009) Simultaneous flue gas bioremediation and reduction of microalgal biomass production costs. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82:179–185
Goers S, Schumann R, Haeubner N, Karsten U (2007) Fungal and algal biomass in biofilms on artificial surfaces quantified by ergosterol and chlorophyll a as biomarkers. Int Biodeter Biodegr 60:50–59
Hadjoudja S, Deluchat V, Baudu M (2010) Cell surface characterisation of Microcystis aeruginosa and Chlorella vulgaris. J Colloid Interf Sci 342:293–299
Irving TE, Allen GD (2011) Species and material considerations in the formation and development of microalgal biofilms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 92:283–294
Johnson MB, Wen Z (2010) Development of an attached microalgal growth system for biofuel production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:525–534
Kolská Z, Řezníčková A, Švorčík V (2012) Surface characterization of polymer foils. E-Polymers 083:1–13
Korenevsky A, Beveridge TJ (2007) The surface physicochemistry and adhesiveness of Shewanella are affected by their surface polysaccharides. Microbiology 153:1872–1883
Kuřec M, Brányik T (2011) The role of physicochemical interactions and FLO genes expression in the immobilization of industrially important yeasts by adhesion. Colloid Surf B-Biointerfaces 84:491–497
Lorite GS, Rodrigues CM, de Souza AA, Kranz C, Mizaikoff B, Cotta MA (2011) The role of conditioning film formation and surface chemical changes on Xylella fastidiosa adhesion and biofilm evolution. J Colloid Interf Sci 359:289–295
Ludyansky ML (1991) Algal fouling in the cooling system. Biofouling 3:13–21
Mei L, van der Mei HC, Ren Y, Norde W, Busscher HJ (2009) Poisson analysis of streptococcal bond strengthening on stainless steel with and without a salivary conditioning film. Langmuir 25:6227–6231
Pulz O, Gross W (2004) Valuable products from biotechnology of microalgae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 65:635–648
Raja R, Hemaiswarya S, Kumar NA, Sridhar S, Rengasamy R (2008) A perspective on the biotechnological potential of microalgae. Crit Rev Microbiol 34:77–88
Redman JA, Walker SL, Elimelech M (2004) Bacterial adhesion and transport in porous media: role of the secondary energy minimum. Environ Sci Technol 38:1777–1785
Sekar R, Venugopalan VP, Satpathy KK, Nair KVK, Rao VNR (2004) Laboratory studies on adhesion of microalgae to hard substrates. Hydrobiologia 512:109–116
Sharma PK, Hanumantha Rao K (2002) Analysis of different approaches for evaluation of surface energy of microbial cells by contact angle goniometry. Adv Colloid Interfac 98:341–463
Smole MS, Stakne K, Kleinschek KS, Kurecic M, Bele M, Svetec DG, Ribitsch V (2009) Electrokinetic properties of polypropylene-layered silicate nanocomposite fibers. J Appl Polym Sci 113:1276–1281
Tang HY, Chen M, Garcia MED, Abunasser N, Ng KYS, Salley SO (2011) Culture of microalgae Chlorella minutissima for biodiesel feedstock production. Biotechnol Bioeng 108:2280–2287
van der Mei HC, Bos R, Busscher HJ (1998) A reference guide to microbial cell surface hydrophobicity based on contact angles. Colloid Surf B-Biointerfaces 11:213–221
van Oss CJ (1995) Hydrophobicity of biosurfaces—origin, quantitative determination and interaction energies. Colloid Surf B-Biointerfaces 5:91–110
van Oss CJ (2003) Long-range and short-range mechanisms of hydrophobic attraction and hydrophilic repulsion in specific and aspecific interactions. Mol Recognit 16:177–190
van Oss CJ (2006) Interfacial forces in aqueous media. Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton, pp 22–24
Xu L, Guo C, Wang F, Zheng S, Liu Ch Z (2011) A simple and rapid harvesting method for microalgae by in situ magnetic separation. Bioresour Technol 102:10047–10051
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Grant Agency of the Czech Republic (project GAČR P503/10/1270) for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sirmerova, M., Prochazkova, G., Siristova, L. et al. Adhesion of Chlorella vulgaris to solid surfaces, as mediated by physicochemical interactions. J Appl Phycol 25, 1687–1695 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-013-0015-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-013-0015-6