Abstract
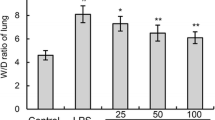
The object of our study is to investigate the protective effects of Borneol on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury (ALI) in mice. To determine the effects of Borneol on the histopathological changes in mice with ALI, inflammatory cell count in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and lung wet/dry weight ratio were measured in LPS-challenged mice, and lung histopathologic changes observed via paraffin section were assessed. Next, cytokine production induced by LPS in BALF and RAW 264.7 cells was measured by enzyme-linked imunosorbent assay (ELISA). To further study the mechanism of Borneol-protective effects on ALI, nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) pathways were investigated. In the present study, Borneol obviously alleviated pulmonary inflammation by reducing inflammatory infiltration, histopathological changes, descended cytokine production, and pulmonary edema initiated by LPS. Furthermore, Borneol significantly suppressed phosphorylation of NF-κB/P65, IκBa, p38, JNK, and ERK. Taken together, our results suggest that Borneol suppressed inflammatory responses in LPS-induced acute lung injury through inhibition of the NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathways. Borneol may be a promising potential preventive agent for acute lung injury treatment.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yen, Y.T., H.R. Yang, H.C. Lo, Y.C. Hsieh, S.C. Tsai, C.W. Hong, and C.H. Hsieh. 2013. Enhancing autophagy with activated protein C and rapamycin protects against sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Surgery 153(5): 689–698.
Liu, Z., Z. Yang, Y. Fu, F. Li, D. Liang, E. Zhou, X. Song, W. Zhang, X. Zhang, Y. Cao, and N. Zhang. 2013. Protective effect of gossypol on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. Inflammation Research 62(5): 499–506.
Atabai, K., and M.A. Matthay. 2002. The pulmonary physician in critical care. 5: acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome: definitions and epidemiology. Thorax 57(5): 452–458.
Rubenfeld, G.D., E. Caldwell, E. Peabody, J. Weaver, D.P. Martin, M. Neff, E.J. Stern, and L.D. Hudson. 2005. Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury. New England Journal of Medicine 353: 1685–1693.
Suda, K., M. Tsuruta, J. Eom, C. Or, T. Mui, J.E. Jaw, et al. 2011. Acute lung injury induces cardiovascular dysfunction: effects of IL-6 and budesonide/formoterol. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology 45: 510–516.
Ware, L.B., and M.A. Matthay. 2000. The acute respiratory distress syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 342: 1334–1349.
Hemmila, M.R., and L.M. Napolitano. 2006. Severe respiratory failure: advanced treatment options. Critical Care Medicine 34(9 Suppl): S 278–S 290.
Steinberg, K.P., L.D. Hudson, R.B. Goodman, et al. 2006. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) Clinical Trials Network. Efficacy and safety of corticosteroids for persistent acute respiratory distress syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 354: 1671–1684.
Kawabata, K., T. Hagio, S. Matsumoto, S. Nakao, S. Orita, Y. Aze, and H. Ohno. 2000. Delayed neutrophil elastase inhibition prevents subsequent progression of acute lung injury induced by endotoxin inhalation in hamsters. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 161(6): 2013–2018.
Wiedemann, H.P., A.P. Wheeler, Berna rd. GR, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) Clinical Trials Network, et al. 2006. Comparison of two fluid-management strategies in acute lung injury. New England Journal of Medicine 354(2564): 2575.
Yang R, Yang L, Shen X, Cheng W, Zhao B, Ali KH, Qian Z, and Ji H (2012) Suppression of NF-κB pathway by crocetin contributes to attenuation of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 15;674(2–3):391–6.
Silva-Filho, J.C., N.N. Oliveira, D.D. Arcanjo, L.J. Quintans-Júnior, S.C. Cavalcanti, M.R. Santos, R.D. Oliveira, and A.P. Oliveira. 2011. Investigation of mechanisms involved in (−)-Borneol-induced vasorelaxant response on rat thoracic aorta. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology 22: 171–177.
Liu, R., L. Zhang, X. Lan, L. Li, T.T. Zhang, J.H. Sun, and G.H. Du. 2011. Protection by borneol on cortical neurons against oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion: Involvement of anti-oxidation and anti-inflammation through nuclear transcription factor kappaB signaling pathway. Neuroscience 10(176): 408–419.
Chen, Y.M., and N.S. Wang. 2004. [Effect of borneol on the intercellular tight junction and pinocytosis vesicles in vitro blood–brain barrier model]. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 24(7): 632–634.
Takaishi, M., K. Uchida, F. Fujita, and M. Tominaga. 2004. Inhibitory effects of monoterpenes on human TRPA1 and the structural basis of their activity. J Physiol Sci 64(1): 47–57.
Xiao, X., M. Yang, D. Sun, and S. Sun. 2012. Curcumin protects against sepsis-induced acute lung injury in rats. Journal of Surgical Research 176(1): e31–e39.
Hudson, L.D., J.A. Milberg, D. Anardi, and R.J. Maunder. 1995. Clinical risks for development of the acute respiratory distress syndrome. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 151: 293–301.
Zhu, T., W. Zhang, and D.X. Wang. 2012. Insulin up-regulates epithelial sodium channel in LPS-induced acute lung injury model in rats by SGK1 activation. Injury 43: 1277–1283.
Deng, J., D.X. Wang, W. Deng, C.Y. Li, J. Tong, and H. Ma. 2012. Regulation of alveolar fluid clearance and ENaC expression in lung by exogenous angiotensin II. Respiratory Physiology & Neurobiology 181(1): 53–61.
Deng, W., C.Y. Li, J. Tong, W. Zhang, and D.X. Wang. 2012. Regulation of ENaC-mediated alveolar fluid clearance by insulin via PI3K/Akt pathway in LPS-induced acute lung injury. Respiratory Research 30(13): 29.
Hidalgo, M.A., A. Romero, J. Figueroa, P. Cortés, I.I. Concha, J.L. Hancke, and R.A. Burgos. 2005. Andrographolide interferes with binding of nuclear factor-k B to DNA in HL-60-derived neutrophilic cells. British Journal of Pharmacology 144(5): 680–686.
Jeon, Y.J., S.H. Han, Y.W. Lee, M. Lee, K.H. Yang, and H.M. Kim. 2000. Dexamethasone inhibits IL-1 beta gene expression in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells by blocking NF-kappa B/Rel and AP-1 activation. Immunopharmacology 48(2): 173–183.
Abraham, S.M., T. Lawrence, A. Kleiman, P. Warden, M. Medghalchi, J. Tuckermann, J. Saklatvala, and A.R. Clark. 2006. Antiinflammatory effects of dexamethasone are partly dependent on induction of dual specificity phosphatase 1. Journal of Experimental Medicine 203(8): 1883–1889.
Tumurkhuu, G., N. Koide, J. Dagvadorj, A. Morikawa, F. Hassan, S. Islam, Y. Naiki, I. Mori, T. Yoshida, and T. Yokochi. 2008. The mechanism of development of acute lung injury in lethal endotoxic shock using alp ha-galactosylceramide sensitization. Clinical and Experimental Immunology 152(1): 182–191.
Mirzapoiazova, T., I.A. Kolosova, L. Moreno, S. Sammani, J.G. Garcia, and A.D. Verin. 2007. Suppression of endotoxin-induced inflammation by taxol. European Respiratory Journal 30(3): 429–435.
Windsor, A.C., P.G. Mullen, A.A. Fowler, and H.J. Sugerman. 1993. Role of the neutrophil in adult respiratory distress syndrome. British Journal of Surgery 80(1): 10–17.
Martin, T.R. 1997. Cytokines and the acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS): a question of balance. Nature Medicine 3(3): 272–273.
Whitley, M.Z., D. Thanos, M.A. Read, T. Maniatis, and T. Collins. 1994. A striking similarity in the organization of the E-selectin and beta interferon gene promoters. Molecular and Cellular Biology 14(10): 6464–6475.
Shu, H.B., A.B. Agranoff, E.G. Nabel, K. Leung, C.S. Duckett, A.S. Neish, T. Collins, and G.J. Nabel. 1993. Differential regulation of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 gene expression by specific NF-kappa B subunits in endothelial and epithelial cells. Molecular and Cellular Biology 13(10): 6283–6289.
Akira, S., S. Uematsu, and O. Takeuchi. 2006. Pathogen recognition and innate Immunity. Cell 124(4): 783–801.
Chow, C.W., M.T. Herrera, T. Suzuki, and G.P. Downey. 2003. Oxidative stress and acute lung injury. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology 29: 427–431.
van Furth, R. 1992. Development and distribution of mononuclear phagocytes. In Inflammation basic principles and clinical correlates, 2nd ed, ed. J.I. Gallin, I.M. Goldstein, and R. Snyderman, 325–351. New York: Raven.
Tosi, M.F., J.M. Stark, C.W. Smith, A. Hamedani, D.C. Gruenert, and M.D. Infeld. 1992. Induction of ICAM-1 expression on human airway epithelial cells by inflammatory cytokines: effects on neutrophil–epithelial cell adhesion. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology 7(2): 214–221.
Bradley, P.P., D.A. Priebat, R.D. Christensen, and G. Rothstein. 1982. Measurement of cutaneous inflammation: estimation of neutrophil content with an enzyme marker. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 78(3): 206–209.
Waage, A., P. Brandtzaeg, A. Halstensen, P. Kierulf, and T. Espevik. 1989. The complex pattern of cytokines in serum from patients with meningococcal septic shock. Journal of Experimental Medicine 169(1): 333–338.
Casey, L.C., R.A. Balk, and R.C. Bone. 1993. Plasma cytokine and endo-toxin levels correlate with survival in patients with sepsis syndrome. Annals of Internal Medicine 119(8): 771–778.
Tomashefski Jr., J.F. 2000. Pulmonary pathology of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Clinics in Chest Medicine 21(3): 435–466.
Everhart, M.B., W. Han, T.P. Sherrill, M. Arutiunov, V.V. Polosukhin, J.R. Burke, R.T. Sadikot, J.W. Christman, F.E. Yull, and T.S. Blackwell. 2006. Duration and Intensity of NF-k B activity determine the severity of endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. Journal of Immunology 176(8): 4995–5005.
Moine, P., R. McIntyre, M.D. Schwartz, D. Kaneko, R. Shenkar, Y. Le Tulzo, E.E. Moore, and E. Abraham. 2000. NF-kappaB regulatory mechanisms in alveolar macrophages from patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Shock 13(2): 85–91.
Liu, S., G. Feng, G.L. Wang, and G.J. Liu. 2008. p38MAPK inhibition attenuates LPS-induced acute lung injury involvement of NF-kappaB pathway. European Journal of Pharmacology 584(1): 159–165.
Jiang, Y., A. Liu, and L. Zhang. 1999. The role of activation of p38 MAPK induced by LPS in TNF-alpha gene expression. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 79(5): 360–364.
Cheng, C., Y. Qin, X. Shao, H. Wang, Y. Gao, M. Cheng, and A. Shen. 2007. Induction of TNF-alpha by LPS in Schwann cell is regulated by MAPK activation signals. Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology 27(7): 909–921.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Nature Science Foundation of Jilin province (no. 20101579) and the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (no. 2011AA10A214) for their great support in financing these researches.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Weiting Zhong and Yiwen Cui contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, W., Cui, Y., Yu, Q. et al. Modulation of LPS-Stimulated Pulmonary Inflammation by Borneol in Murine Acute Lung Injury Model. Inflammation 37, 1148–1157 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9839-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9839-8