Abstract
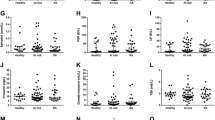
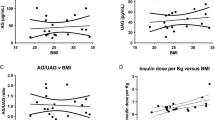
Background: Ghrelin is a powerful, endogenous orexigenic peptide. In addition, ghrelin has anti-inflammatory effects, and it has been reported that ghrelin down-regulates pro-inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin (IL)-1β and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α. Obestatin appears to decrease food intake and appetite, and its potential role in inflammation is not yet clear. The aims of this study were to assess total and acylated (active) ghrelin and obestatin serum levels and their relations with inflammatory status in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. Design: Fasting blood samples were obtained from 37 patients with RA, 29 patients with Behçet’s disease (BD) and 28 healthy controls (HC). Total ghrelin and obestatin levels were measured by radioimmunoassay and acylated ghrelin was quantified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Results: Patients with RA had lower total ghrelin, but higher obestatin levels than patients with BD (p < 0.05 for both), but when compared with HC group differences were not significant. There was no difference across groups in terms of acylated ghrelin. Total ghrelin level was not correlated with any study parameters in the all groups. Obestatin level correlated with erythrocyte sedimentation rate and DAS-28 in the RA group, the level of IL-6 in the BD group, and with the level of TNF-α in the HC group (r = 0.400, p < 0.05; r = 0.412, p < 0.05, r = 0.543, p < 0.01 and r = 0.528, p < 0.05, respectively). Conclusions: Our results did not show a significant correlation between circulating ghrelin and clinical or laboratory markers of disease activity in RA. Surprisingly, obestatin correlated with some inflammatory markers. So, obestatin seems to be more valuable than ghrelin in the pathogenesis of RA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kojima, M., H. Hosoda, Y. Date, M. Nakazato, H. Matsuo, and K. Kangawa. 1999. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 402:656–659 doi:10.1038/45230.
Hosoda, H., M. Kojima, and K. Kangawa. 2006. Biological, physiological, and pharmacological aspects of ghrelin. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 100:398–410 doi:10.1254/jphs.CRJ06002X.
Leite-Moreira, A. F., and J. B. Soares. 2007. Physiological, pathological and potential therapeutic roles of ghrelin. Drug Discov. Today 12:276–88 doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2007.02.009.
Zhang, J. V., P. G. Ren, O. Avsian-Kretchmer, C. W. Luo, R. Rauch, C. Klein et al. 2005. Obestatin, a peptide encoded by the ghrelin gene, opposes ghrelin’s effects on food intake. Science 310:996–999 doi:10.1126/science.1117255.
Sibilia, V., E. Bresciani, N. Lattuada, D. Rapetti, V. Locatelli, V. De Luca et al. 2006. Intracerebroventricular acute and chronic administration of obestatin minimally affect food intake but not weight gain in the rat. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 29:RC31–RC34.
Zizzari, P., R. Longchamps, J. Epelbaum, and M. T. Bluet-Pajot. 2007. Obestatin partially affects ghrelin stimulation of food intake and GH secretion in rodents. Endocrinology 148:1648–1653 doi:10.1210/en.2006–1231.
Dixit, V. D., and D. D. Taub. 2005. Ghrelin and immunity: a young player in an old field. Exp. Gerontol. 40:900–910 doi:10.1016/j.exger.2005.09.003.
Dixit, V. D., E. M. Schaffer, R. S. Pyle, S. K. Sakthivel, R. Palaniappan Jr., J. W. Lillard et al. 2004. Ghrelin inhibits leptin—and activation-induced proinflammatory cytokine expression by human monocytes and T cells. J Clin Invest. 114:57–66.
Granado, M., T. Priego, A. I. Martín, M. A. Villanúa, and A. López-Calderón. 2005. Anti-inflammatory effect of the ghrelin agonist growth hormone-releasing peptide-2 (GHRP-2) in arthritic rats. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 288:E486–92 doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00196.2004.
Peracchi, M., D. Conte, C. Terrani, S. Pizzinelli, C. Gebbia, V. Cappiello et al. 2003. Circulating ghrelin levels in celiac patients. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 98:2474–2478 doi:10.1111/j.1572–0241.2003.07709.x.
Otero, M., R. Nogueiras, F. Lago, C. Dieguez, J. J. Gomez-Reino, and O. Gualillo. 2004. Chronic inflammation modulates ghrelin levels in humans and rats. Rheumatology (Oxford) 43:306–310 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keh055.
Toussirot, E., G. Streit, N. U. Nguyen, G. Dumoulin, G. Le Huédé, P. Saas et al. 2007. Adipose tissue, serum adipokines, and ghrelin in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Metabolism 56:1383–1989 doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2007.05.009.
Jasin, H. E. 2005. Mechanisms of tissue damage in rheumatoid arthritis. In: Arthritis and allied conditions a textbook of rheumatology, Koopman, and Moreland eds. 15Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp. 1141–1164.
Sakane, T., M. Takeno, N. Suzuki, and G. Inaba. 1999. Behcet’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 341:1284–1291 doi:10.1056/NEJM199910213411707.
Roubenoff, R., R. A. Roubenoff, L. M. Ward, S. M. Holland, and D. B. Hellmann. 1992. Rheumatoid cachexia: depletion of lean body mass in rheumatoid arthritis. Possible association with tumor necrosis factor. J. Rheumatol. 19:1505–1510.
Walsmith, J., and R. A. Roubenoff. 2002. Cachexia in rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Cardiol. 85:89–99 doi:10.1016/S0167-5273(02)00237-1.
Arnett, F. C., S. M. Edworthy, D. A. Bloch, D. J. McShane, J. F. Fries, N. S. Cooper et al. 1988. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 31:315–24 doi:10.1002/art.1780310302.
The International Study Group for Behcet’s disease. 1992. Evaluation of diagnostic (‘classification’) criteria in Behcet’s disease—towards internationally agreed criteria. Br. J. Rheumatol. 31:299–308.
Leeb, B. F., I. Andel, J. Sautner, M. Bogdan, A. Maktari, T. Nothnagl et al. 2005. Disease activity measurement of rheumatoid arthritis: Comparison of the simplified disease activity index (SDAI) and the disease activity score including 28 joints (DAS28) in daily routine. Arthritis Rheum. 53:56–60 doi:10.1002/art.20923.
Yazici, C., K. Kose, M. Calis, M. DemIr, M. Kirnap, and F. Ates. 2004. Increased advanced oxidation protein products in Behcet’s disease: a new activity marker? Br. J. Dermatol. 151:105–11 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2004.06003.x.
Bekpinar, S., N. Kilic, Y. Unlucerci, A. Akdag-Kose, G. Azizlerli, and Z. Ozbek-Kir. 2005. Evaluation of nitrosative and oxidative stress in Behcet disease. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 19:167–71 doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2005.01075.x.
Hosoda, H., and K. Kangawa. 2004. Ghrelin measurement. Nippon Rinsho. 9:354–356.
Li, W. G., D. Gavrila, X. Liu, L. Wang, S. Gunnlaugsson, L. L. Stoll et al. 2004. Ghrelin inhibits proinflammatory responses and nuclear factor-kappaB activation in human endothelial cells. Circulation 109:2221–2216 doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000127956.43874.F2.
Işerim, S. O., G. Sener, B. Saglam, F. Ercan, N. Gedik, and B. C. Yeğen. 2008. Ghrelin alleviates biliary obstruction-induced chronic hepatic injury in rats. Regul Pept. 146:73–79 doi:10.1016/j.regpep.2007.08.014.
Wang, L., N. R. Basa, A. Shaikh, A. Luckey, D. Heber, D. H. St-Pierre et al. 2006. LPS inhibits fasted plasma ghrelin levels in rats: role of IL-1 and PGs and functional implications. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Live.r Physiol. 291:G611–G620 doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00533.2005.
Gayle, D. A., M. Desai, E. Casillas, R. Beloosesky, and M. G. Ross. 2006. Gender-specific orexigenic and anorexigenic mechanisms in rats. Life Sci. 79:1531–1536 doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2006.04.015.
Hataya, Y., T. Akamizu, H. Hosoda, N. Kanamoto, K. Moriyama, K. Kangawa et al. 2003. Alterations of plasma ghrelin levels in rats with lipopolysaccharide-induced wasting syndrome and effects of ghrelin treatment on the syndrome. Endocrinology 144:5365–5371 doi:10.1210/en.2003-0427.
Chang, L., J. Zhao, J. Yang, Z. Zhang, J. Du, and C. Tang. 2003. Therapeutic effects of ghrelin on endotoxic shock in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 473:171–176 doi:10.1016/S0014-2999(03)01972-1.
Kümpers, P., R. Horn, G. Brabant, A. Woywodt, M. Schiffer, H. Haller et al. 2008. Serum leptin and ghrelin correlate with disease activity in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 47:484–487 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/ken023.
Peracchi, M., M. T. Bardella, F. Caprioli, S. Massironi, D. Conte, L. Valenti et al. 2006. Circulating ghrelin levels in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 55:432–423 doi:10.1136/gut.2005.079483.
Otto, B., M. Tschöp, W. Heldwein, A. F. Pfeiffer, and S. Diederich. 2004. Endogenous and exogenous glucocorticoids decrease plasma ghrelin in humans. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 151:113–117 doi:10.1530/eje.0.1510113.
Madison, L. D., J. M. Scarlett, P. Levasseur, X. Zhu, K. Newcomb, A. Batra et al. 2008. Prostacyclin signaling regulates circulating ghrelin during acute inflammation. J. Endocrinol. 196:263–273 doi:10.1677/JOE-07-0478.
El Eter, E., A. Al Tuwaijiri, H. Hagar, and M. Arafa. 2007. In vivo and in vitro antioxidant activity of ghrelin: Attenuation of gastric ischemic injury in the rat. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 22:1791–1799 doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2006.04696.x.
Isik, A., S. S. Koca, B. Ustundag, H. Celik, and A. Yildirim. 2007. Paraoxonase and arylesterase levels in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 26:342–348 doi:10.1007/s10067-006-0300-8.
Hotta, M., R. Ohwada, H. Katakami, T. Shibasaki, N. Hizuka, and K. Takano. 2004. Plasma levels of intact and degraded ghrelin and their responses to glucose infusion in anorexia nervosa. J. Clin. Endocrino.l Metab. 89:5707–5712 doi:10.1210/jc.2004-0353.
Gourcerol, G., T. Coskun, L. S. Craft, J. P. Mayer, M. L. Heiman, L. Wang et al. 2007. Preproghrelin-derived peptide, obestatin, fails to influence food intake in lean or obese rodents. Obesity (Silver Spring) 15:2643–52.
Gourcerol, G., D. H. St-Pierre, and Y. Taché. 2007. Lack of obestatin effects on food intake: should obestatin be renamed ghrelin-associated peptide (GAP)? Regul Pept. 141:1–7 doi:10.1016/j.regpep.2006.12.023.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koca, S.S., Ozgen, M., Aydin, S. et al. Ghrelin and Obestatin Levels in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Inflammation 31, 329–335 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-008-9082-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-008-9082-2