Abstract
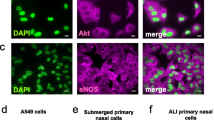
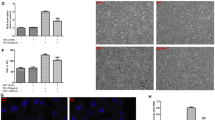
RSV infection is characterized by airway edema. Stabilization of hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) is important in both inflammation and edema formation. In this study we evaluated whether RSV induced release of nitric oxide (NO) by bronchial airway epithelial cells leading to the stabilization of HIF-1α and subsequent transcription of VEGF165. Primary human bronchial epithelial cells (HBEpC) were used; cell supernatants were analyzed. Western blot analysis was used for the detection of HIF-1α. Bronchial airway epithelial monolayer permeability was assessed using electric cell-substrate impedance sensing (ECIS) in real time. There was increased stabilization of HIF-1α in RSV infected cells. Addition of an NO inhibitor blocked RSV mediated HIF-1α expression. Antagonism of NO also inhibited VEGF production and HBEpC monolayer permeability. Our results demonstrate that in HBEpC, RSV induced NO causes stabilization of HIF-1α in vitro.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RSV:
-
Respiratory Syncytial Virus; NO, Nitric Oxide; HIF-1α, Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1α; VEGF, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor; Carboxy PTIO, Carboxy 2-(4-Carbixyphenyl)-4, 4, 5, 5-tetramethylimidazoline-1oxyl-3-oxide sodium salt.
References
Dodge, R., F. D. Martinez, M. G. Cline, M. D. Lebowitz, and B. Burrows. 1996. Early childhood respiratory symptoms and the subsequent diagnosis of asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 98:48–54.
Shay, D. K., R. C. Holman, R. D. Newman, L. L. Liu, J. W. Stout, and L. J. Anderson. 1999. Bronchiolitis-associated hospitalizations among US children, 1980–1996. JAMA 282:1440–1446.
Dowell, S. F., L. J. Anderson, H. E. Gary, Jr., D. D. Erdman, J. F. Plouffe, T. M. File, Jr., B. J. Marston, and R. F. Breiman. 1996. Respiratory syncytial virus is an important cause of community-acquired lower respiratory infection among hospitalized adults.J. Infect. Dis. 174:456–462.
Falsey, A. R., C. K. Cunningham, W. H. Barker, R. W. Kouides, J. B. Yuen, M. Menegus, L. B. Weiner, C. A. Bonville, and R. F. Betts. 1995. Respiratory syncytial virus and influenza A infections in the hospitalized elderly. J. Infect. Dis. 172:389–394.
Bar-on, M. E., and J. R. Zanga. 1996. Bronchiolitis. Prim. Care 23:805–819.
Hayden, F. G., D. D. Richman, and R. J. Whitley, eds. 1997. Clinical Virology. Churchill Livingstone, New York.
Roberts, W. G. and G. E. Palade. 1997. Neovasculature induced by vascular endothelial growth factor is fenestrated. Cancer Res. 57:765–772.
Antony, A. B., R. S. Tepper, and K. A. Mohammed. 2002. Cockroach extract antigen increases bronchial airway epithelial permeability. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 110:589–595.
Sriram, P. S., K. A. Mohammed, N. Nasreen, J. Hardwick, R. Van Horn, K. Sanders, and V. B. Antony. 2002. Adherence of ovarian cancer cells induces pleural mesothelial cell (PMC) permeability. Oncol. Res. 13:79–85.
Lee, C. G., H. J. Yoon, Z. Zhu, H. Link, Z. Wang, J. M. Gwaltney, M. Landry, and J. A. Elias. 2000. Respiratory syncytial virus stimulation of vascular endothelial cell growth Factor/Vascular permeability factor. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 23:662–669.
Semenza, G. L. 2001. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1: control of oxygen homeostasis in health and disease. Pediatr. Res. 49:614–617.
Jaakkola, P., D. R. Mole, Y. M. Tian, M. I. Wilson, J. Gielbert, S. J. Gaskell, A. Kriegsheim, H. F. Hebestreit, M. Mukherji, C. J. Schofield, et al. 2001. Targeting of HIF-alpha to the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitylation complex by O2-regulated prolyl hydroxylation. Science 292:468–472.
Ivan, M., K. Kondo, H. Yang, W. Kim, J. Valiando, M. Ohh, A. Salic, J. M. Asara, W. S. Lane, and W. G. Kaelin, Jr. 2001. HIFalpha targeted for VHL-mediated destruction by proline hydroxylation: Implications for O2 sensing. Science 292:464–468.
Sandau, K. B., J. Fandrey, and B. Brune. 2001. Accumulation of HIF-1alpha under the influence of nitric oxide. Blood 97:1009–1015.
Maxwell, P. H., M. S. Wiesener, G. W. Chang, S.C. Clifford, E. C. Vaux, M. E. Cockman, C. C. Wykoff, C. W. Pugh, E. R. Maher, and P. J. Ratcliffe. 1999. The tumour suppressor protein VHL targets hypoxia-inducible factors for oxygen-dependent proteolysis. Nature 399:271–275.
Cramer, T., Y. Yamanishi, B. E. Clausen, I. Forster, R. Pawlinski, N. Mackman, V. H. Haase, R. Jaenisch, M. Corr, V. Nizet, et al. 2003. HIF-1alpha is essential for myeloid cell-mediated inflammation. Cell 112:645–657.
Wang, G. L., B. H. Jiang, and G. L. Semenza. 1995. Effect of altered redox states on expression and DNA-binding activity of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 212:550–556.
Kao, Y. J., P. A. Piedra, G. L. Larsen, and G. N. Colasurdo. 2001. Induction and regulation of nitric oxide synthase in airway epithelial cells by respiratory syncytial virus. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 163:532–539.
Mohammed, K. A., N. Nasreen, J. Hardwick, C. S. Logie, C. E. Patterson, and V. B. Antony. 2001. Bacterial induction of pleural mesothelial monolayer barrier dysfunction. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 281:L119–125.
Lundien, M. C., K. A. Mohammed, N. Nasreen, R. S. Tepper, J. A. Hardwick, K. L. Sanders, R. D. Van Horn, and V. B. Antony. 2002. Induction of MCP-1 expression in airway epithelial cells: Role of CCR2 receptor in airway epithelial injury. J. Clin. Immunol. 22:144–152.
Goldie, R. G., and K. E. Pedersen. 1995. Mechanisms of increased airway microvascular permeability: Role in airway inflammation and obstruction. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 22:387–396.
Deguchi, M., H. Sakuta, K. Uno, K. Inaba, and S. Muramatsu. 1995. Exogenous and endogenous type I interferons inhibit interferon-gamma-induced nitric oxide production and nitric oxide synthase expression in murine peritoneal macrophages. J. Interferon. Cytokine Res. 15:977–984.
Faure, V., Y. Courtois, and O. Goureau. 1997. Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase expression by interferons alpha and beta in bovine retinal pigmented epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 272:32169–32175.
Sandau, K. B., H. G. Faus, and B. Brune. 2000. Induction of hypoxia-inducible-factor 1 by nitric oxide is mediated via the PI 3K pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 278:263–267.
Kimura, H., A. Weisz, Y. Kurashima, K. Hashimoto, T. Ogura, F. D’Acquisto, R. Addeo, M. Makuuchi, and H. Esumi. 2000. Hypoxia response element of the human vascular endothelial growth factor gene mediates transcriptional regulation by nitric oxide: Control of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 activity by nitric oxide. Blood 95:189–197.
Palmer, L. A., B. Gaston, and R. A. Johns. 2000. Normoxic stabilization of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 expression and activity: Redox-dependent effect of nitrogen oxides. Mol. Pharmacol. 58:1197–1203.
Kimura, H., A. Weisz, T. Ogura, Y. Hitomi, Y. Kurashima, K. Hashimoto, F. D’Acquisto, M. Makuuchi, and H. Esumi. 2001. Identification of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 ancillary sequence and its function in vascular endothelial growth factor gene induction by hypoxia and nitric oxide. J. Biol. Chem. 276:2292–2298.
Semenza, G. L. 1999. Regulation of mammalian O2 homeostasis by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Annu. Rev. Cell. Dev. Biol. 15:551–578.
Wenger, R. H. 2002. Cellular adaptation to hypoxia: O2-sensing protein hydroxylases, hypoxia-inducible transcription factors, and O2-regulated gene expression. Faseb. J. 16:1151–1162.
Semenza, G. L. 2000. HIF-1 and human disease: One highly involved factor. Genes Dev. 14:1983–1991.
Brune, B., and J. Zhou. 2003. The role of nitric oxide (NO) in stability regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha). Curr. Med. Chem. 10:845–855.
Dvorak, H. F., J. A. Nagy, D. Feng, L. F. Brown, and A. M. Dvorak. 1999. Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor and the significance of microvascular hyperpermeability in angiogenesis. Curr. Top Microbiol. Immunol. 237:97–132.
Dvorak, H. F. 2003. Rous-Whipple Award Lecture. How tumors make bad blood vessels and stroma. Am. J. Pathol. 162:1747–1757.
Veikkola, T., and K. Alitalo. 1999. VEGFs, receptors and angiogenesis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 9:211–220.
Miao, H. Q., P. Lee, H. Lin, S. Soker, and M. Klagsbrun. 2000. Neuropilin-1 expression by tumor cells promotes tumor angiogenesis and progression. Faseb. J. 14:2532–2539.
Pettersson, A., J. A. Nagy, L. F. Brown, C. Sundberg, E. Morgan, S. Jungles, R. Carter, J. E. Krieger, E. J. Manseau, V. S. Harvey, et al. 2000. Heterogeneity of the angiogenic response induced in different normal adult tissues by vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor. Lab. Invest. 80:99–115.
Dvorak, H. F., V. S. Harvey, P. Estrella, L. F. Brown, J. McDonagh, and A. M. Dvorak. 1987. Fibrin containing gels induce angiogenesis. Implications for tumor stroma generation and wound healing. Lab. Invest. 57:673–686.
Barnes, P. J. 1995. Nitric oxide and airway disease. Ann. Med. 27:389–393.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kilani, M.M., Mohammed, K.A., Nasreen, N. et al. RSV Causes HIF-1α Stabilization via NO Release in Primary Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Inflammation 28, 245–251 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-004-6047-y
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-004-6047-y