Abstract
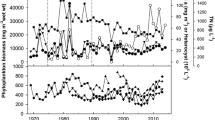
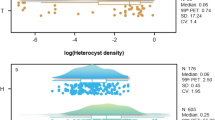
In the 1990s a sharp decrease in nitrogen loading occurred in Estonian rivers, bringing about a reduction of the nitrogen-to-phosphorus ratio (N:P ratio) in the large shallow lakes, Peipsi (3,555 km2, mean depth 7.1 m) and Võrtsjärv (270 km2, 2.8 m). The average mass ratio of total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP) in Võrtsjärv (45) was about twice as high as that in Peipsi (22). In Peipsi, the N2-fixing Gloeotrichia echinulata, Aphanizomenon flos-aquae and Anabaena species prevailed in the summer phytoplankton, while in Võrtsjärv the dominant cyanobacteria were Limnothrix planktonica, L. redekei and Planktolyngbya limnetica, which cannot fix N2; the main N2-fixing taxa Aphanizomenon skujae and Anabaena sp. seldom gained dominance. In May–October the critical TN:TP mass ratio, below which N2-fixing cyanobacteria (Nfix) achieved high biomasses, was ∼40 in Võrtsjärv and ∼30 in Peipsi. The percentages of both total cyanobacteria (CY) and Nfix (CY% and Nfix%) in Peipsi achieved their maximum values at an N:P mass ratio at or below 20 for both TN:TP and Nmin:SRP. In Võrtsjärv, the TN:TP supporting a high Nfix% was between 30 and 40 and the Nmin:SRP supporting this high percentage was in the same range as that in Peipsi (<20), though the maximum Nfix% values in Võrtsjärv (69%) were much lower than in Peipsi (96%). The Nmin:SRP ratio explained 77% of the variability in Nfix% in May–October. The temperature dependence of Nfix% approximated to the maximum function type, with an upper limiting value at a certain water temperature, and this was most distinct in May–October. The critical TN:TP ratios obtained from our study (roughly 30 for Peipsi and 40 for Võrtsjärv) are much higher than the Redfield N:P mass ratio routinely considered (7). Our results represent valuable guidelines for creating effective management strategies for large shallow lakes. They provide a basis for stressing the urgent need to decrease phosphorus loading and to keep the in-lake P concentration low, and not to implement nitrogen reduction measures without a simultaneous decrease of phosphorus concentration.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berger, C., 1989. In situ primary production, biomass and light regime in the Wolderwijd, the most stable Oscillatoria agardhii lake in The Netherlands. Hydrobiologia 185: 233–244.
Bulgakov, N. G. & A. P. Levich, 1999. The nitrogen:phosphorus ratio as a factor regulating phytoplankton community structure. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 146: 3–22.
Downing, J. A., S. B. Watson & E. McCauley, 2001. Predicting Cyanobacteria dominance in lakes. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 58: 1905–1908.
Falkowski, P. G. & C. S. Davis, 2004. Natural proportions. Redfield ratios, the uniformity of elemental ratios in the oceans and the life they contain underpins our understanding of marine biogeochemistry. Nature 431: 131.
Genkai-Kato, M. & S. R. Carpenter, 2005. Eutrophication due to phosphorus recycling in relation to lake morphometry, temperature, and macrophytes. Ecology 86: 210–219.
Grasshoff, K., M. Ehrhardt & K. Kremling (eds), 1983. Methods of Seawater Analysis. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, 419 pp.
Hall, S. R., V. H. Smith, D. A. Lytle, & M. A. Leibold, 2005. Constraints on primary producer N:P stoichiometry along N:P supply ratio gradients. Ecology 86: 1894–1904.
Harris, G. P., 1986. Phytoplankton Ecology. Chapman and Hall, USA, 137–165.
Havens, K. E., R. T. James, T. L. East & V. H. Smith, 2003. N:P ratios, light limitation, and cyanobacterial dominance in a subtropical lake impacted by non-point source nutrient pollution. Environmental Pollution 122: 379–390.
Howarth, R. W., J. J. Cole & R. Marino, 1988. Nitrogen fixation in freshwater, estuarine and marine ecosystems. 2. Biogeochemical controls. Limnology and Oceanography 33: 688–701.
Huisman, J. & F. Hulot, 2005. Population dynamics of harmful cyanobacteria. Factors affecting species composition. In Huisman, J., H. C. P. Matthijs & P. M. Visser (eds), Harmful Cyanobacteria. Springer-Verlag, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 143–176.
Huisman, J., H. C. P. Matthijs & P. M. Visser (eds), 2005. Harmful Cyanobacteria. Springer-Verlag, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 241 pp.
Lathrop, R. C., S. R. Carpenter, C. A. Stow, P. A. Soranno & J. C. Panuska, 1998. Phosphorus loading reductions needed to control blue-green algal blooms in Lake Mendota. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 55: 1169–1178.
Laugaste, R., T. Nõges, P. Nõges, V. V. Jastremskij, A. Milius & I. Ott, 2001. Algae. In Pihu, E. & J. Haberman (eds), Lake Peipsi. Flora and Fauna. Sulemees Publishers, Tallinn, 31–49.
Michard, M., L. Aleya & J. Verneaux, 1996. Mass occurrence of the Cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa in the hypereutrophic Villerest Reservoir (Roanne, France): Usefulness of the biyearly examination of N/P (nitrogen phosphorus) and P/C (protein/carbohydrate) couplings. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 135: 337–359.
von zur Mühlen, M. & G. Schneider, 1920. Der See Wirzjerw in Livland. Archiv für die Naturkunde des Ostbaltikums 14: 1–156.
Nõges, T., V. Kisand, P. Nõges, A. Põllumäe, L. Tuvikene & P. Zingel, 1998. Plankton seasonal dynamics and its controlling factors in shallow polymictic eutrophic Lake Võrtsjärv, Estonia. International Review of Hydrobiology 83: 279–296.
Nõges, T., P. Nõges & R. Laugaste, 2003. Water level as the mediator between climate change and phytoplankton composition in a large shallow temperate lake. Hydrobiologia 506: 257–263.
Nõges, T., I. Tõnno, R. Laugaste, E. Loigu & B. Skakalski, 2004. The impact of changes in nutrient loading on cyanobacterial dominance in Lake Peipsi (Estonia/Russia). Archiv für Hydrobiologie 160: 261–279.
Nõges, T., A. Järvet, A. Kisand, E. Loigu, B. Skakalski & P. Nõges, 2007. Reaction of large and shallow lakes Peipsi and Võrtsjärv to the changes of nutrient loading. Hydrobiologia 584: 253–264.
Paerl, H. W., R. S. Fulton, P.H. Moisander & J. Dyble, 2001. Harmful freshwater algal blooms, with an emphasis on cyanobacteria. The Scientific World Journal 1: 76–113.
Redfield, A. S., 1958. The biological control of chemical factors in the environment. American Scientist 46: 205–211.
Reynolds, C. S., 1984. The Ecology of Freshwater Phytoplankton. Cambridge University Press, UK.
Scheffer, M., 1998. Ecology of Shallow Lakes. Chapman and Hall, London, UK.
Scheffer, M., S. Rinaldi, A. Gragnani, L. R. Mur & E. H. van Nes, 1997. On the dominance of filamentous cyanobacteria in shallow, turbid lakes. Ecology 78: 272–282.
Schindler, D. W., 1977. Evolution of phosphorus limitation in lakes. Science 195: 260–262.
Seip, K. L., 1994. Phosphorus and nitrogen limitation of algal biomass across trophic gradients. Aquatic Sciences 56: 16–28.
Smith, V. H., 1983. Low nitrogen to phosphorus ratios favour dominance by blue-green algae in lake phytoplankton. Science 221: 669–771.
Smith, V. H., 1985. Predictive models for the biomass of blue-green algae in lakes. Water Resources Bulletin 21: 433–439.
Smith, V. H., E. Willén & B. Karlsson, 1987. Predicting the summer peak biomass of four species of blue-green algae (Cyanophyta/cyanobacteria) in Swedish lakes. Water Resources Bulletin 23: 397–402.
Smith, V. H., V. J. Bierman, B. L. Jones & K. E. Havens, 1995. Historical trends in the Lake Okeechobee ecosystem IV. Nitrogen:phosphorus ratios, cyanobacterial dominance, and nitrogen fixation potential. Archiv für Hydrobiologie, Monographische Beiträge 107: 71–88.
Sterner, R. W. & J. J. Elser, 2002. Ecological Stoichiometry: The Biology of Elements from Molecules to the Biosphere. Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey, USA.
Tõnno, I. & T. Nõges, 2003. Nitrogen fixation in a large shallow lake: rates and initiation conditions. Hydrobiologia 490: 23–30.
Utermöhl, H., 1958. Zur Vervollkomnung der quantitativen Phytoplanktonmethodik. Mitteilungen der Internationalen Vereinigung für Limnologie 9: 1–38.
van Duin, E. H. S., R. H. Aalderink & L. Lijklema, 1995. Light adaptation of Oscillatoria agardhii at different time scales. Water Science and Technology 32: 35–48.
Willén, E., 1992. Long-term changes in the phytoplankton of large lakes in response to changes in nutrient loading. Nordic Journal of Botany 12: 575–587.
Acknowledgements
Funding for this research was provided by target funding project 03962480s03 by the Estonian Ministry of Education and by Estonian Science Foundation grant 5738. We used data obtained from frames of the State Monitoring Program of the Estonian Ministry of Environment. The authors are grateful to the guest editor Heikki Simola and to two anonymous reviewers for valuable advice and comments for improving the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest editors: T. Nõges, R. Eckmann, K. Kangur, P. Nõges, A. Reinart, G. Roll, H. Simola & M. Viljanen
European Large Lakes—Ecosystem changes and their ecological and socioeconomic impacts
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nõges, T., Laugaste, R., Nõges, P. et al. Critical N:P ratio for cyanobacteria and N2-fixing species in the large shallow temperate lakes Peipsi and Võrtsjärv, North-East Europe. Hydrobiologia 599, 77–86 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-007-9195-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-007-9195-x