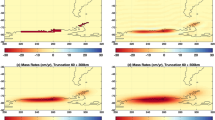
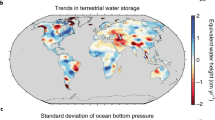
Abstract
The main objective of the US-German twin-satellite mission GRACE (Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment), launched in March 2002, is a precise survey of the Earth’s time-variable gravity field at unprecedented temporal and spatial scales. Temporal changes in the gravity field are related to continuous mass redistributions near the Earth’s surface which are caused by various geophysical and climatologically driven processes. Vice versa, transferring the GRACE-based gravity variations into time series of the spatial variability of surface mass anomalies, the mission allows for the first time for a quantification of the ongoing mass transport. Such data is of unique importance for a comprehensive modeling, understanding and interplay of these processes. In this contribution we give an overview of the basic features of the GRACE satellite mission, the gravity recovery process and the derived gravity products at GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam (GFZ), as well as the interpretation of the GRACE gravity data with the focus on the detection of hydrological signals. This includes a description of the evolution and present status of the quality of GFZ’s GRACE-based global gravity models on the actual fourth model generation (called GFZ-RL04), and an overview of recent findings using GRACE data in hydrological applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bettapur S (2007) CSR Level-2 processing standards document for level-2 product release 0004, GRACE 327–742, Rev. 3.1
Davis JL, Elsegui P, Mitrovica JX, Tamisiea ME (2004) Climate-driven deformation of the solid Earth from GRACE and GPS. Geophys Res Lett 31:L24605
Fenoglio-Marc L, Kusche J, Becker M (2006) Mass variation in the Mediterranean Sea from GRACE and its validation by altimetry, steric and hydrologic fields. Geophys Res Lett 33:L19606
Flechtner F (2007) GFZ Level-2 processing standards document for level-2 product release 0004, GRACE 327-743, Rev. 1.0
Frappart F, Ramillien G, Biancamaria S, Mognard NM, Cazenave A (2006) Evolution of high-latitude snow mass derived from the GRACE gravimetry mission (2002–2004). Geophys Res Lett 33:L02501
Han S-C, Jekeli C, Shum CK (2004) Time-variable aliasing effects of ocean tides, atmosphere, and continental water mass on monthly mean GRACE gravity field. J Geophys Res (Solid Earth) 109:B04403
Han S-C, Shum CK, Jekeli C, Kuo C-Y, Wilson C, Seo K-W (2005) Non-isotropic filtering of GRACE temporal gravity for geophysical signal enhancement. Geophys J Int 163:18–25
Heiskanen W, Moritz H (1967) Physical Geodesy. W.H. Freeman and Co., San Francisco, CA/USA
Hinderer J, Andersen O, Lemoine F, Crossley D, Boy JP (2006) Seasonal changes in the European gravity field from GRACE: a comparison with superconducting gravimeters and hydrology model predictions. J Geodynam 41:59–68
Horwath M, Dietrich R (2006) Errors of regional mass variations inferred from GRACE monthly solutions. Geophys Res Lett 33:L07502
Ilk K-H et al (2005) Mass transport and mass distribution in the Earth system – contribution of the new generation of satellite gravity and altimetry to geosciences, GOCE Projektbüro, TU München and GFZ Potsdam, Downloadable PDF file at www.massentransporte.de using the link “Documents”
Jekeli C (1981) Alternative methods to smooth the Earth’s gravity field. Tech. Rep., Department of Geodetic Science, Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio
King M, Moore P, Clarke P, Lavalle D (2006) Choice of optimal averaging radii for temporal GRACE gravity solutions, a comparison with GPS and satellite altimetry. Geophys J Int 166:1–11
Klees R, Zapreeva EA, Winsemius HC, Savenije HHG (2007) The bias in GRACE estimates of continental water storage variations, Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 11:1227–1241
Kusche J (2007) Approximate decorrelation and non-isotropic smoothing of time-variable GRACE-type gravity field models. J Geod 81:733–749
Lemoine J-M, Bruinsma S, Loyer S, Biancale R, Marty J-C, Perosanz F, Balmino G (2007) Temporal gravity field models inferred from GRACE data. Adv Space Res 39:1620–1629
Llubes M, Lemoine J-M, Rmy F (2007) Antarctica seasonal mass variations detected by GRACE. Earth Planet Sci Lett 260:127–136
Luthcke SB, Rowlands DD, Lemoine FG, Klosko SM, Chinn D, McCarthy JJ (2006) Monthly spherical harmonic gravity field solutions determined from GRACE inter-satellite range-rate data alone. Geophys Res Lett 33:L02402
Mayer-Gürr T, Eicker A, Ilk KH (2006) Gravity field recovery from GRACE-SST Data of Short Arcs. In: Flury J, Rummel R, Reigber C, Rothacher M, Boedecker G, Schreiber U (eds) Observation of the earth system from Space, Springer, Berlin, ISBN 3-540-29520-8, pp. 131–148
Neumeyer J, Barthelmes F, Dierks O, Flechtner F, Harnisch M, Harnisch G, Hinderer J, Imanishi Y, Kroner C, Meurers B, Petrovic S, Reigber C, Schmidt R, Schwintzer P, Sun H-P, Virtanen H (2006) Combination of temporal gravity variations resulting from superconducting gravimeter (SG) recordings, GRACE satellite observations and global hydrology models. J Geod 79:573–585
Ngo-Duc T, Laval K, Ramillien G, Polcher J, Cazenave A (2007) Validation of the land water storage simulated by Organising Carbon and Hydrology in Dynamic Ecosystems (ORCHIDEE) with Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) data. Water Resour Res 43:W04427
Niu G-Y, Seo K-W, Yang Z-L, Wilson C, Su H, Chen J, Rodell M (2007) Retrieving snow mass from GRACE terrestrial water storage change with a land surface model. Geophys Res Lett 34:L15704
Ramillien G, Cazenave A, Brunau O (2004) Global time variations of hydrological signals from GRACE satellite gravimetry. Geophys J Int 158:813–826
Ramillien G, Lombard A, Cazenave A, Ivins ER, Llubes M, Remy F, Biancale R (2006) Interannual variations of the mass balance of the Antarctica and Greenland ice sheets from GRACE. Global Planet Change 53:198–208
Ray RD, Luthcke SB (2006) Tide model errors and GRACE gravimetry: towards a more realistic assessment. Geophys J Int 167(3):1055–1059
Reigber Ch et al (2005) An Earth gravity field model complete to degree and order 150 from GRACE: EIGEN-GRACE02S. J Geodynam 39:1–10
Rodell M, Famiglietti JS (1999) Detectability of variations in continental water storage from satellite observations of the time dependent gravity field. Water Resour Res 35:2705–2723
Rodell M, Famiglietti JS (2001) An analysis of terrestrial water storage variations in Illinois with implications for the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE). Water Resour Res 37:1327–1340
Rodell M, Famiglietti JS, Chen J, Seneviratne SI, Viterbo P, Holl S, Wilson CR (2004) Basin scale estimates of evapotranspiration using GRACE and other observations. Geophys Res Lett 31:L20504
Rodell M, Chen J, Kato H, Famiglietti JS, Nigro J, Wilson CR (2007) Estimating groundwater storage changes in the Mississippi River basin (USA) using GRACE. Hydrogeol J 15:159–166
Sasgen I, Martinec Z, Fleming K (2007) Wiener optimal combination and evaluation of the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) gravity fields over Antarctica. J Geophys Res (Solid Earth) 112:B04401
Schmidt R, Schwintzer P, Flechtner F, Reigber Ch, Güntner A, Döll P, Ramillien G, Cazenave A, Petrovic S, Jochmann H, Wünsch J (2006) GRACE observations of changes in continental water storage. Glob Planet Change 50:112–126
Schmidt R, Flechtner F, König R, Meyer U, Neumayer K-H, Reigber Chr, Rothacher M, Petrovic S, Zhu SY, Güntner A (2007) GRACE Time-Variable Gravity Accuracy Assessment. In: Tregoning P, Rizos Chr (eds) Dynamic planet, IAG symposium vol. 130. Springer, Berlin, ISBN 3-540-49349-5, pp 237–243
Schrama EJO, Wouters B, Lavalle DA (2007) Signal and noise in Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) observed surface mass variations. J Geophys Res (Solid Earth) 112:B08407
Seo K-W, Wilson CR (2005) Simulated estimation of hydrological loads from GRACE. J Geod 78:442–456
Swenson S, Wahr J (2002) Methods for inferring regional surface-mass anomalies from Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) measurements of time-variable gravity. J Geophys Res (Solid Earth) 107(B9):2193
Swenson S, Wahr J (2006) Post-processing removal of correlated errors in GRACE data. Geophys Res Lett 33:L16401
Swenson S, Wahr J (2007) Multi-sensor analysis of water storage variations of the Caspian Sea. Geophys Res Lett 34:L16401
Swenson S, Wahr J, Milly PCD (2003) Estimated accuracies of regional water storage variations inferred from the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE). Water Resour Res 39(8):1223
Swenson S, Yeh PJ-F, Wahr J, Famiglietti J (2006) A comparison of terrestrial water storage variations from GRACE with in situ measurements from Illinois. Geophys Res Lett 33:L16401
Syed TH, Famiglietti JS, Chen J, Rodell M, Seneviratne SI, Viterbo P, Wilson CR (2005) Total basin discharge for the Amazon and Mississippi River basins from GRACE and a land-atmosphere water balance. Geophys Res Lett 32:L24404
Tapley BD, Reigber Ch (2001) The GRACE Mission: status and future plans. EOS Trans. AGU, 82(47), Fall Meeting, Suppl. G14C-02
Tapley BD, Bettadpur S, Ries JC, Thompson PF, Watkins MM (2004) GRACE measurements of mass variability in the earth system. Science 305:503–505
Thompson PF, Bettadpur SV, Tapley BD (2004) Impact of short period, non-tidal, temporal mass variability on GRACE gravity estimates. Geophys Res Lett 31:L06619
van Dam T, Wahr J, Lavalle D (2007) A comparison of annual vertical crustal displacements from GPS and Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) over Europe. J Geophys Res (Solid Earth) 112:B03404
Wahr J, Molenaar M, Bryan F (1998) Time variability of the Earth's gravity field: hydrological and oceanic effects and their possible detection using GRACE. J Geophys Res 103:30205–30230
Wahr J, Swenson S, Zlotnicki V, Velicogna I (2004) Time-variable gravity from GRACE: first results. Geophys Res Lett 31:L11501
Wahr J, Swenson S, Velicogna I (2006) Accuracy of GRACE mass estimates. Geophys Res Lett 33:L06401
Watkins M, Yuan D (2007) JPL level-2 processing standards document for level-2 product release 0004, GRACE 327-744, Rev. 4.1
Winsemius HC, Savenije HHG, van de Giesen NC, van den Hurk BJJM, Zapreeva EA, Klees R (2006) Assessment of Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) temporal signature over the upper Zambezi. Water Resour Res 42:W12201
Wolf M (1969) Direct measurement of the Earth’s Gravitational Potential Using a Satellite Pair. J Geophy Res 75:22
Yamamoto K, Fukuda Y, Nakaegawa T, Nishijima J (2007) Landwater variation in four major river basins of the Indochina peninsula as revealed by GRACE. Earth Planets Space 59:193–200
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank two anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments, which helped to improve the manuscript. The German Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) and the German Research Foundation (DFG) supports these investigations within the geoscientific R+D programme GEOTECHNOLOGIEN “Erfassung des Systems Erde aus dem Weltraum” under grants 03F0436A, 03F0423A and 03F0424A and within the Special Priority Programme (SPP) 1257 “Mass Transport and Mass Distribution within the Earth System” under grants FL 592/1-1, FL 592/2-1, FL 592/3-1, KU 1207/6-1 and KU 1207/7-1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, R., Flechtner, F., Meyer, U. et al. Hydrological Signals Observed by the GRACE Satellites. Surv Geophys 29, 319–334 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-008-9033-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-008-9033-3