Abstract
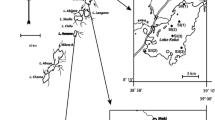
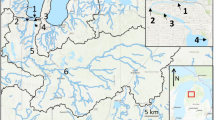
Semipermeable membrane devices (SPMDs) were deployed at eight sites within the Buffalo Slough, near Portland, Oregon, to (1) measure the spatial and seasonal distribution of dissolved polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) and organochlorine (OC) compounds in the slough, (2) assess the usefulness of SPMDs as a tool for investigating and monitoring hydrophobic compounds throughout the Columbia Slough system, and (3) evaluate the utility of SPMDs as a tool for measuring the long-term effects of watershed improvement activities. Data from the SPMDs revealed clear spatial and seasonal differences in water quality within the slough and indicate that for hydrophobic compounds, this time-integrated passive-sampling technique is a useful tool for long-term watershed monitoring. In addition, the data suggest that a spiking rate of 2–5 μg/SPMD of permeability/performance reference compounds, including at least one compound that is not susceptible to photodegradation, may be optimum for the conditions encountered here.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Denoux, G., Gardinali, P. and Wade, T. L.: 1998, ‘Quantitative determination of polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry — selected ion monitoring (SIM) mode’, in: Sampling and Analytical Methods of the National Status and Trends Program, Mussel Watch Project: 1993–1996 Update. NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS ORCA 130, 1998, 129–139.
Huckins, J. N., Manuweera, G. K., Petty, J. D., Mackay, D. and Lebo, J. A.: 1993, ‘Lipid-containing semipermeable membrane devices for monitoring organic contaminants in water’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 27(12), 2489–2496.
Huckins, J. N., Petty, J. D., Orazio, C. E., Lebo, J. A., Clark, R. C., Gibson, V. L., Gale, W. R. and Echols, K. R.: 1999, ‘Determination of uptake kinetics (sampling rates) by lipid-containing semipermeable membrane devices (SPMDs) for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in water’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 33(21), 3918–3923.
Huckins, J. N., Petty, J. D., Prest, H. F., Clark, R. C., Alvarez, D. A., Orazio, C. E., Lebo, J. A., Cranor, W. L. and Johnson, B. T.: 2000, ‘A guide for the use of semipermeable membrane devices (SPMDs) as samplers of waterborne hydrophobic organic contaminants’. Publication No. 4690, American Petroleum Institute, Columbia, Missouri.
Huckins, J. N., Petty, J. D., Lebo, J. A., Almeida, F. V., Booij, K., Alvarez, D. A., Cranor, W. L., Clark, R. C. and Mogensen, B. B.: 2002, ‘Development of the permeability/performance reference compound approach for in situ calibration of semipermeable membrane devices’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 36(1), 85–91.
Kersens, B. J.: 2005, ‘Determination of groundwater flux into the Buffalo Slough Using Thermal and Hydraulic Gradients: A One Dimensional Analysis in VS2DHI’, Master of Science thesis, Portland State University, Portland, OR.
McCarthy, K. A. and Gale, R. W.: 1999, ‘Investigation of the Distribution of Organochlorine and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Compounds in the Lower Columbia River Using Semipermeable Membrane Devices’, U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 99–4051.
McCarthy, K. A. and Gale, R. W.: 2001, ‘Evaluation of persistent hydrophobic organic compounds in the Columbia River Basin using semipermeable-membrane devices’, Hydrol. Process. 15, 1271–1283.
Orazio, C. E., Haynes, S., Lebo, J. A., Peterman, P. H., Meadows, J. C., Huckins, J. N. and Petty, J. D.: 2002, ‘Potential for photodegradation of contaminants during SPMD sampling’, poster presentation at Society for Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry World Congress, Salt Lake City, UT, November 2002.
Oregon Department of Environmental Quality: 1999, ‘Columbia Slough total maximum daily loads (TMDLs) for: Chlorophyll a, dissolved oxygen, pH, phosphorus, bacteria, DDE/DDT, PCBs, Pb, Dieldrin and 2.3.7.8 TCDD’, Oregon Department of Environmental Quality, Northwest Region, January 1999, 181 pp.
Parametrix, Inc.: 1995, ‘Screening level risk assessment, Columbia Slough Sediment Remedial Investigation/Feasibility Study’, prepared for the City of Portland Bureau of Environmental Services, February 1995.
Sericano, J. L., Gardinali, P. and Wade, T. L.: 1998. ‘Quantitative determination of chlorinated hydrocarbons’, in: Sampling and Analytical Methods of the National Status and Trends Program, Mussel Watch Project: 1993–1996 Update. NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS ORCA 130, 1998, 160–167.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McCarthy, K. Assessment of the Usefulness of Semipermeable Membrane Devices for Long-Term Watershed Monitoring in an Urban Slough System. Environ Monit Assess 118, 293–318 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-1502-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-1502-x