Summary
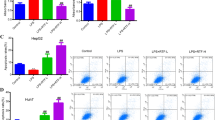
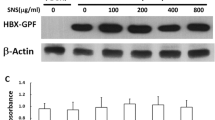
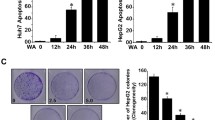
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common malignancies worldwide. Treatment options, especially in advanced tumor stages, are still limited. Inhibition of signaling cascades involved in the pathogenesis of HCC - such as NF-ĸB - offer a promising therapeutic approach. Aim of this study was to examine anti-neoplastic effects of (+)-episesamin which has been isolated from an anti-fibrotic extract of Lindera obtusiloba on human HCC cells with particular interest in activation of NF-κB. The human HCC cell lines HepG2, Huh-7 and SK-Hep1 were treated with (+)-episesamin. Beside measurement of proliferation, invasion and apoptosis, effects of (+)-episesamin on NF-κB-activity, VEGF secretion and enzymatic MMP-9 activity were determined. Anti-inflammatory effects were assessed by IL-6 ELISA using HCC cells and RAW264.7 macrophages. 10 μM (+)-episesamin reduced the proliferation of HCC cells by ~50%, suppressed invasion and induced apoptosis. DNA-binding ELISA experiments revealed that (+)-episesamin treated HCC cells showed a suppressed basal and TNFα-induced activation of NF-κB and a subsequent suppression of TNFα- and LPS-induced IL-6 production. Further, (+)-episesamin exhibited inhibitory effects on the enzymatic activity of recombinant MMP-9 and the secretion of MMP-9 and VEGF by HCC cells into their supernatants. Our findings show that anti-neoplastic effects of (+)-episesamin are mediated via suppressed activation of NF-κB which entails a decreased release of pro-inflammatory IL-6. In addition, (+)-episesamin inhibits MMP-9, which is strongly expressed in invasive HCC, and the production of proangiogenic VEGF. We conclude that (+)-episesamin has the potential to be further explored as a complementary treatment for HCC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
El-Serag HB, Rudolph KL (2007) Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 132(7):2557–2576
Villanueva A, Newell P, Chiang DY, Friedman SL, Llovet JM (2007) Genomics and signaling pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis 27(1):55–76
Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S, Kim JS, Luo R, Feng J, Ye S, Yang TS, Xu J, Sun Y, Liang H, Liu J, Wang J, Tak WY, Pan H, Burock K, Zou J, Voliotis D, Guan Z (2009) Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 10(1):25–34
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A, Schwartz M, Porta C, Zeuzem S, Bolondi L, Greten TF, Galle PR, Seitz JF, Borbath I, Haussinger D, Giannaris T, Shan M, Moscovici M, Voliotis D, Bruix J (2008) Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 359(4):378–390
Coussens LM, Werb Z (2002) Inflammation and cancer. Nature 420(6917):860–867
Kessenbrock K, Plaks V, Werb Z (2010) Matrix metalloproteinases: regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell 141(1):52–67
Arii S, Mise M, Harada T, Furutani M, Ishigami S, Niwano M, Mizumoto M, Fukumoto M, Imamura M (1996) Overexpression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 gene in hepatocellular carcinoma with invasive potential. Hepatology 24(2):316–322
Sato H, Kita M, Seiki M (1993) v-Src activates the expression of 92-kDa type IV collagenase gene through the AP-1 site and the GT box homologous to retinoblastoma control elements. A mechanism regulating gene expression independent of that by inflammatory cytokines. J Biol Chem 268(31):23460–23468
Lin WW, Karin M (2007) A cytokine-mediated link between innate immunity, inflammation, and cancer. J Clin Invest 117(5):1175–1183
Freise C, Erben U, Neuman U, Kim K, Zeitz M, Somasundaram R, Ruehl M (2010) An active extract of Lindera obtusiloba inhibits adipogenesis via sustained Wnt signaling and exerts anti-inflammatory effects in the 3 T3-L1 preadipocytes. J Nutr Biochem 21(12):1170–1177
Ruehl M, Erben U, Kim K, Freise C, Dagdelen T, Eisele S, Trowitzsch-Kienast W, Zeitz M, Jia J, Stickel F, Somasundaram R (2009) Extracts of Lindera obtusiloba induce antifibrotic effects in hepatic stellate cells via suppression of a TGF-beta-mediated profibrotic gene expression pattern. J Nutr Biochem 20(8):597–606
Freise C, Ruehl M, Erben U, Neumann U, Seehofer D, Kim KY, Trowitzsch-Kienast W, Stroh T, Zeitz M, Somasundaram R (2011) A hepatoprotective Lindera obtusiloba extract suppresses growth and attenuates insulin like growth factor-1 receptor signaling and NF-kappaB activity in human liver cancer cell lines. BMC Complement Altern Med 11:39
Trowitzsch-Kienast W, Ruehl M, Kim KY, Emmerling F, Erben U, Somasundaram R, Freise C (2011) Absolute configuration of antifibrotic (+)-episesamin isolated from Lindera obtusiloba BLUME. Z Naturforsch C 66c, #–# (in press)
Umeda-Sawada R, Ogawa M, Igarashi O (1998) The metabolism and n-6/n-3 ratio of essential fatty acids in rats: effect of dietary arachidonic acid and a mixture of sesame lignans (sesamin and episesamin). Lipids 33(6):567–572
Ogawa H, Sasagawa S, Murakami T, Yoshizumi H (1995) Sesame lignans modulate cholesterol metabolism in the stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rat. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol Suppl 22(1):S310–312
Fuchs BC, Fujii T, Dorfman JD, Goodwin JM, Zhu AX, Lanuti M, Tanabe KK (2008) Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and integrin-linked kinase mediate sensitivity to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition in human hepatoma cells. Cancer Res 68(7):2391–2399
Freise C, Erben U, Muche M, Farndale R, Zeitz M, Somasundaram R, Ruehl M (2009) The alpha 2 chain of collagen type VI sequesters latent proforms of matrix-metalloproteinases and modulates their activation and activity. Matrix Biol 28(8):480–489, Epub 2009 Aug 2019
Hah N, Lee ST (2003) An absolute role of the PKC-dependent NF-kappaB activation for induction of MMP-9 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 305(2):428–433
Xu W, Liu LZ, Loizidou M, Ahmed M, Charles IG (2002) The role of nitric oxide in cancer. Cell Res 12(5–6):311–320
Okun I, Balakin KV, Tkachenko SE, Ivachtchenko AV (2008) Caspase activity modulators as anticancer agents. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 8(3):322–341
Kaur G, Hollingshead M, Holbeck S, Schauer-Vukasinovic V, Camalier RF, Domling A, Agarwal S (2006) Biological evaluation of tubulysin A: a potential anticancer and antiangiogenic natural product. Biochem J 396(2):235–242
Dalwadi H, Krysan K, Heuze-Vourc'h N, Dohadwala M, Elashoff D, Sharma S, Cacalano N, Lichtenstein A, Dubinett S (2005) Cyclooxygenase-2-dependent activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 by interleukin-6 in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11(21):7674–7682
Calvisi DF, Pinna F, Ladu S, Pellegrino R, Muroni MR, Simile MM, Frau M, Tomasi ML, De Miglio MR, Seddaiu MA, Daino L, Sanna V, Feo F, Pascale RM (2008) Aberrant iNOS signaling is under genetic control in rodent liver cancer and potentially prognostic for the human disease. Carcinogenesis 29(8):1639–1647
Salminen A, Kaarniranta K (2009) Insulin/IGF-1 paradox of aging: regulation via AKT/IKK/NF-kappaB signaling. Cell Signal 22(4):573–577
Sun B, Karin M (2008) NF-kappaB signaling, liver disease and hepatoprotective agents. Oncogene 27(48):6228–6244
Liu TZ, Hu CC, Chen YH, Stern A, Cheng JT (2000) Differentiation status modulates transcription factor NF-kappaB activity in unstimulated human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Lett 151(1):49–56
Wu JM, Sheng H, Saxena R, Skill NJ, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Yu M, Nakshatri H, Maluccio MA (2009) NF-kappaB inhibition in human hepatocellular carcinoma and its potential as adjunct to sorafenib based therapy. Cancer Lett 278(2):145–155
Gialeli C, Theocharis AD, Karamanos NK (2011) Roles of matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression and their pharmacological targeting. Febs J 278(1):16–27
Shimada C, Ninomiya Y, Suzuki E, Umezawa K (2010) Efficient cellular uptake of the novel NF-kappaB inhibitor (−)-DHMEQ and irreversible inhibition of NF-kappaB in neoplastic cells. Oncol 18(11–12):529–535.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Collaborative Research Centers (SFB366 C5/C10) and (SFB633 Z1) from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft and the Berliner Sparkassenstiftung Medizin.
Declaration of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Freise, C., Trowitzsch-Kienast, W., Ruehl, M. et al. (+)-Episesamin exerts anti-neoplastic effects in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines via suppression of nuclear factor-kappa B and inhibition of MMP-9. Invest New Drugs 30, 2087–2095 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-011-9762-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-011-9762-x