Summary
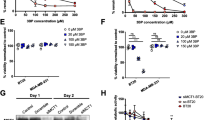
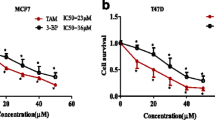
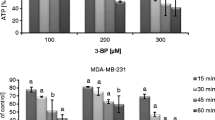
Purpose: To evaluate the anti-glycolytic effects of 3-BrPA on rats bearing RMT mammary tumors, by determining FDG uptake after intravenous administration of the therapeutic dose. Materials and Methods: Sixteen rats bearing RMT tumors were treated either with 15 mM 3-BrPA in 2.5 ml of PBS or with 2.5 ml of PBS. After treatment, all rats received FDG and were sacrificed 1 h later. Results: 3-BrPA treatment significantly decreased FDG uptake in tumors by 77% (p = 0.002). FDG uptake did not significantly decrease in normal tissues after treatment. Conclusion: Our study showed that 3-BrPA exhibits a strong anti-glycolytic effect on RMT cells implanted in rats.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E et al (2008) Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin 58:71–96
Dumitrescu RG, Cotarla I (2005) Understanding breast cancer risk—where do we stand in 2005? J Cell Mol Med 9:208–221
Louwman MW, Vriezen M, van Beek MW et al (2007) Uncommon breast tumors in perspective: incidence, treatment and survival in The Netherlands. Int J Cancer 121:127–135
Elias D, Pietroantonio DD (2006) Surgery for liver metastases from breast cancer. HPB Oxf 8:97–99
Perez EA (1999) Current management of metastatic breast cancer. Semin Oncol 26:1–10
Anderson DM, Rolnick SJ, Jackson J, Amundson J, Asche SE, Loes LM (2007) Impact of chemotherapy in women with metastatic breast cancer diagnosed 1990–2003. Clin Breast Cancer 7:801–803
Rabbani SA, Mazar AP (2007) Evaluating distant metastases in breast cancer: from biology to outcomes. Cancer Metastasis Rev 26:663–674
Trotti A, Colevas AD, Setser A et al (2003) CTCAE v3.0: development of a comprehensive grading system for the adverse effects of cancer treatment. Semin Radiat Oncol 13:176–181
Geschwind JF, Georgiades CS, Ko YH, Pedersen PL (2004) Recently elucidated energy catabolism pathways provide opportunities for novel treatments in hepatocellular carcinoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 4:449–457
Isidoro A, Casado E, Redondo A et al (2005) Breast carcinomas fulfill the Warburg hypothesis and provide metabolic markers of cancer prognosis. Carcinogenesis 26:2095–2104
Shin SW, Han H, Choo SW et al (2006) Hepatic intra-arterial injection of 3-bromopyruvate in rabbit VX2 tumor. Acta Radiol 47:1036–1041
Vali M, Liapi E, Kowalski J et al (2007) Intraarterial therapy with a new potent inhibitor of tumor metabolism (3-bromopyruvate): identification of therapeutic dose and method of injection in an animal model of liver cancer. J Vasc Interv Radiol 18:95–101
Ko YH, Pedersen PL, Geschwind JF (2001) Glucose catabolism in the rabbit VX2 tumor model for liver cancer: characterization and targeting hexokinase. Cancer Lett 173:83–91
Xu RH, Pelicano H, Zhou Y et al (2005) Inhibition of glycolysis in cancer cells: a novel strategy to overcome drug resistance associated with mitochondrial respiratory defect and hypoxia. Cancer Res 65:613–621
Kim W, Yoon JH, Jeong JM et al (2007) Apoptosis-inducing antitumor efficacy of hexokinase II inhibitor in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther 6:2554–2562
Tatsumi M, Cohade C, Mourtzikos KA, Fishman EK, Wahl RL (2006) Initial experience with FDG-PET/CT in the evaluation of breast cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 33:254–262
Delbeke D (1999) Oncological applications of FDG PET imaging. J Nucl Med 40:1706–1715
Ethier SP, Cundiff KC (1987) Importance of extended growth potential and growth factor independence on in vivo neoplastic potential of primary rat mammary carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 47:5316–5322
Wahl RL, Henry CA, Ethier SP (1992) Serum glucose: effects on tumor and normal tissue accumulation of 2-[F-18]-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose in rodents with mammary carcinoma. Radiology 183:643–647
Margolis DJ, Hoffman JM, Herfkens RJ, Jeffrey RB, Quon A, Gambhir SS (2007) Molecular imaging techniques in body imaging. Radiology 245:333–356
Avril N, Menzel M, Dose J et al (2001) Glucose metabolism of breast cancer assessed by 18F-FDG PET: histologic and immunohistochemical tissue analysis. J Nucl Med 42:9–16
Endo K, Oriuchi N, Higuchi T et al (2006) PET and PET/CT using 18F-FDG in the diagnosis and management of cancer patients. Int J Clin Oncol 11:286–296
Pantaleo MA, Nannini M, Maleddu A et al (2008) Conventional and novel PET tracers for imaging in oncology in the era of molecular therapy. Cancer Treat Rev 34:103–121
Minn H, Kangas L, Knuutila V, Paul R, Sipila H (1991) Determination of 2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose uptake and ATP level for evaluating drug effects in neoplastic cells. Res Exp Med (Berl) 191:27–35
Yamada K, Brink I, Bisse E, Epting T, Engelhardt R (2005) Factors influencing [F-18] 2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose (F-18 FDG) uptake in melanoma cells: the role of proliferation rate, viability, glucose transporter expression and hexokinase activity. J Dermatol 32:316–334
Geschwind JF, Ko YH, Torbenson MS, Magee C, Pedersen PL (2002) Novel therapy for liver cancer: direct intraarterial injection of a potent inhibitor of ATP production. Cancer Res 62:3909–3913
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Buijs and Vossen contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buijs, M., Vossen, J.A., Geschwind, JF.H. et al. Specificity of the anti-glycolytic activity of 3-bromopyruvate confirmed by FDG uptake in a rat model of breast cancer. Invest New Drugs 27, 120–123 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-008-9145-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-008-9145-0