Abstract
Background
Sustained virological response (SVR) rates in patients with hepatitis C are heterogeneous and are influenced by a wide range of host and viral factors.
Aim
To evaluate the efficacy of combination therapy with pegylated interferon alfa (PEG-IFN-α) and ribavirin (RBV), and document the SVR rates taking into consideration various predictive factors in patients with chronic hepatitis C (CHC) genotype 3.
Methods
Ninety-seven treatment-naive patients with CHC genotype 3 (mean age 41.46 ± 11.51 years, M:F ratio 79:18), who received a combination of PEG-IFN (α-2a or α-2b) and RBV were retrospectively analyzed (2006–2008) for the early virological response (EVR) at 12 weeks, end of treatment response (ETR), and SVR at 6 months.
Results
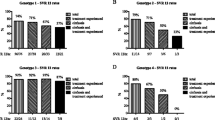
Eighty-four (86.6%) patients achieved EVR and 81 (83.5%) achieved ETR, while SVR was achieved in 65 (67.0%) patients. Of the 84 patients who achieved EVR, 77 (91.7%) achieved ETR and 61 (72.6%) achieved SVR at 6 months. Age and body mass index (BMI) were found to be important predictors (*P < 0.05) of SVR. CHC patients with a history of alcohol intake showed decreased SVR (52%) (*P = 0.035) as compared to nonalcoholics (80%). Cirrhotic versus noncirrhotic patients showed no difference in SVR (54.5% vs. 70.7%) (P = 0.157). Serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) (P = 0.169) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA levels (P = 0.42) also did not have an influence on the SVR.
Conclusion
Combination therapy with PEG-IFN-α and RBV demonstrated good tolerability in CHC genotype 3 infection. Age, BMI, and alcohol consumption play an important role in determining treatment outcome.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ghany MG, Strader DB, Thomas DL, et al.; American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatitis C: an update. Hepatology. 2009;49:1335–1374.
Pal SK, Chalamalasetty BS, Choudhuri G. Hepatitis C: a major health problem of India. Curr Sci. 2002;83:1058–1059.
Schiff ER, Ozden N. Hepatitis C and alcohol. Alcohol Res Health. 2003;27:232–239.
McMahon JM, Tortu S. A potential hidden source of hepatitis C infection among noninjecting drug users. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2003;35:455–460.
Foster GR. Pegylated interferon with ribavirin therapy for chronic infection with the hepatitis C virus. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2003;4:685–691.
David J, Rajasekar A, Daniel HD, et al. Infection with hepatitis C virus genotype 3—experience of a tertiary health care centre in south India. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2010;28:155–157.
Vutien P, Nguyen NH, Trinh HN, et al. Similar treatment response to peginterferon and ribavirin in Asian and Caucasian patients with chronic hepatitis C. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105:1110–1115.
National Institutes of Health. National Institutes of Health consensus development conference statement: management of hepatitis C: 2002—June 10–12, 2002. Hepatology. 2002;36:S3–S20.
Zeuzem S. Heterogeneous virologic response rates to interferon-based therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C: who responds less well? Ann Intern Med. 2004;140:370–381.
Hadziyannis SJ, Sette H Jr, Morgan TR, et al.; PEGASYS International Study Group. Peginterferon-alpha2a and ribavirin combination therapy in chronic hepatitis C: a randomized study of treatment duration and ribavirin dose. Ann Intern Med. 2004;140:346–355.
Fried MW, Shiffman ML, Reddy KR, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:975–982.
Martinot-Peignoux M, Marcellin P, Pouteau M, et al. Pretreatment serum hepatitis C virus RNA levels and hepatitis C virus genotype are the main and independent prognostic factors of sustained response to interferon alfa therapy in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 1995;4:1050–1056.
McHutchison JG, Gordon SC, Schiff ER, et al. Interferon alfa-2b alone or in combination with ribavirin as initial treatment for chronic hepatitis C. Hepatitis Interventional Therapy Group. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:1485–1492.
Poynard T, Marcellin P, Lee SS, et al. Randomised trial of interferon alpha2b plus ribavirin for 48 weeks or for 24 weeks versus interferon alpha2b plus placebo for 48 weeks for treatment of chronic infection with hepatitis C virus. International Hepatitis Interventional Therapy Group (IHIT). Lancet. 1998;352:1426–1432.
Zeuzem S, Feinman SV, Rasenack J, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a in patients with chronic hepatitis C. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:1666–1672.
Manns MP, McHutchison JG, Gordon SC, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin compared with interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2001;358:958–965.
Bressler BL, Guindi M, Tomlinson G, et al. High body mass index is an independent risk factor for nonresponse to antiviral treatment in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2003;38:639–644.
Jeffers LJ, Cassidy W, Howell CD, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a (40 kd) and ribavirin for black American patients with chronic HCV genotype 1. Hepatology. 2004;39:1702–1708.
Muir AJ, Bornstein JD, Killenberg PG; Atlantic Coast Hepatitis Treatment Group. Peginterferon alfa-2b and ribavirin for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C in blacks and non-Hispanic whites. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2265–2271.
Andriulli A, Mangia A, Iacobellis A, et al. Meta-analysis: the outcome of anti-viral therapy in HCV genotype 2 and genotype 3 infected patients with chronic hepatitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008;28:397–404.
Dahlan Y, Ather HM, Al-ahmadi M, et al. Sustained virological response in a predominantly hepatitis C virus genotype 4 infected population. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15:4429–4433.
Mecenate F, Pellicelli AM, Barbaro G, et al. Short versus standard treatment with pegylated interferon alfa-2A plus ribavirin in patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 2 or 3: the cleo trial. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010;10:21.
Garg G, Kar P. Management of HCV infection: current issues and future options. Trop Gastroenterol. 2009;30:11–18.
Slavenburg S, Weggelaar I, van Oijen MG, et al. Optimal length of antiviral therapy in patients with hepatitis C virus genotypes 2 and 3: a meta-analysis. Antivir Ther. 2009;14:1139–1148.
Kogure T, Ueno Y, Fukushima K, et al. Pegylated interferon plus ribavirin for genotype Ib chronic hepatitis C in Japan. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:7225–7230.
Morisco F, Stroffolini T, Medda E, et al. Retrospective, observational, multicentre study on an Italian population affected by chronic hepatitis C who failed to clear HCV-RNA after the combined therapy (PEG-IFN and ribavirin): NADIR study. J Viral Hepat. 2010;17:427–434.
Freshwater DA, O’Donnell K, Mutimer DJ. Inferior response of Asian vs. non-Asian hepatitis C genotype 3 infection to combination antiviral therapy. J Viral Hepat. 2008;15:115–119.
Sood A, Midha V, Sood N, et al. Pegylated interferon alfa 2b and oral ribavirin in patients with HCV-related cirrhosis. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2006;25:283–285.
Davis GL, Wong JB, McHutchison JG, et al. Early virologic response to treatment with peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2003;38:645–652.
Zuberi BF, Zuberi FF, Memon SA, et al. Sustained virological response based on rapid virological response in genotype-3 chronic hepatitis C treated with standard interferon in the Pakistani population. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:2218–2221.
Lagging M, Langeland N, Pedersen C, et al. Randomized comparison of 12 or 24 weeks of peginterferon alpha-2a and ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 2/3 infection. Hepatology. 2008;47:1837–1845.
Foster GR, Fried MW, Hadziyannis SJ, et al. Prediction of sustained virological response in chronic hepatitis C patients treated with peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) and ribavirin. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2007;42:247–255.
Pattullo V, Ravindran NC, Mazzulli T, et al. Pegylated interferon plus optimized weight-based ribavirin dosing negate the influence of weight and body mass index on early viral kinetics and sustained virological response in chronic hepatitis C. J Viral Hepat. 2010;17:834–838.
Walsh MJ, Jonsson JR, Richardson MM, et al. Non-response to antiviral therapy is associated with obesity and increased hepatic expression of suppressor of cytokine signalling 3 (SOCS-3) in patients with chronic hepatitis C, viral genotype 1. Gut. 2006;55:529–535.
Floreani A, Baldo V, Rizzotto ER, et al. Pegylated interferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin for naive patients with HCV-related cirrhosis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2008;42:734–737.
Shiffman ML, Di Bisceglie AM, Lindsay KL, et al.; Hepatitis C Antiviral Long-Term Treatment Against Cirrhosis Trial Group. Peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin in patients with chronic hepatitis C who have failed prior treatment. Gastroenterology. 2004;126:1015–1023.
Oshita M, Hayashi N, Kasahara A, et al. Increased serum hepatitis C virus RNA levels among alcoholic patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 1994;20:1115–1120.
Siu L, Foont J, Wands JR. Hepatitis C virus and alcohol. Semin Liver Dis. 2009;29:188–199.
Loguercio C, Di Pierro M, Di Marino MP, et al. Drinking habits of subjects with hepatitis C virus-related chronic liver disease: prevalence and effect on clinical, virological and pathological aspects. Alcohol Alcohol. 2000;35:296–301.
McCartney EM, Beard MR. Impact of alcohol on hepatitis C virus replication and interferon signaling. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:1337–1343.
Liu CH, Liu CJ, Lin CL, et al. Pegylated interferon-alpha-2a plus ribavirin for treatment-naive Asian patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection: a multicenter, randomized controlled trial. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47:1260–1269.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tohra, S.K., Taneja, S., Ghosh, S. et al. Prediction of Sustained Virological Response to Combination Therapy with Pegylated Interferon Alfa and Ribavirin in Patients with Genotype 3 Chronic Hepatitis C. Dig Dis Sci 56, 2449–2455 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-011-1770-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-011-1770-3