Summary
1. The pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy is a complex phenomenon, the mechanisms of which are not fully understood. Our previous studies have shown that the intracellular calcium signaling is impaired in primary and secondary nociceptive neurons in rats with streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetes. Here, we investigated the effect of prolonged treatment with the L-type calcium channel blocker nimodipine on diabetes-induced changes in neuronal calcium signaling and pain sensitivity.
2. Diabetes was induced in young rats (21 p.d.) by a streptozotocin injection. After 3 weeks of diabetes development, the rats were treated with nimodipine for another 3 weeks. The effect of nimodipine treatment on calcium homeostasis in nociceptive dorsal root ganglion neurons (DRG) and substantia gelatinosa (SG) neurons of the spinal cord slices was examined with fluorescent imaging technique.
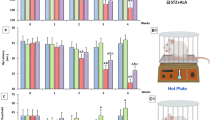
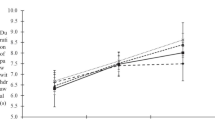
3. Nimodipine treatment was not able to normalize elevated resting intracellular calcium ([Ca2+] i ) levels in small DRG neurons. However, it was able to restore impaired Ca2+ release from the ER, induced by either activation of ryanodine receptors or by receptor-independent mechanism in both DRG and SG neurons.
4. The beneficiary effects of nimodipine treatment on [Ca2+] i signaling were paralleled with the reversal of diabetes-induced thermal hypoalgesia and normalization of the acute phase of the response to formalin injection. Nimodipine treatment was also able to shorten the duration of the tonic phase of formalin response to the control values.
5. To separate vasodilating effect of nimodipine Biessels et al., (Brain Res. 1035:86–93) from its effect on neuronal Ca2+ channels, a group of STZ-diabetic rats was treated with vasodilator – enalapril. Enalapril treatment also have some beneficial effect on normalizing Ca2+ release from the ER, however, it was far less explicit than the normalizing effect of nimodipine. Effect of enalapril treatment on nociceptive behavioral responses was also much less pronounced. It partially reversed diabetes-induced thermal hypoalgesia, but did not change the characteristics of the response to formalin injection.
6. The results of this study suggest that chronic nimodipine treatment may be effective in restoring diabetes-impaired neuronal calcium homeostasis as well as reduction of diabetes-induced thermal hypoalgesia and noxious stimuli responses. The nimodipine effect is mediated through a direct neuronal action combined with some vascular mechanism.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Agrawal, R., Marx, A., and Haller, H. (2006). Efficacy and safety of lercanidipine versus hydrochlorothiazide as add-on to enalapril in diabetic populations with uncontrolled hypertension. J. Hypertens. 24:185–192.
Biessels, G., and Gispen, W. H. (1996). The calcium hypothesis of brain aging and neurodegenerative disorders: significance in diabetic neuropathy. Life Sci. 59:379–387.
Biessels, G. J., ter Laak, M. P., Hamers, F. P., and Gispen, W. H. (2002). Neuronal Ca(2+) disregulation in diabetes mellitus. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 447:201–209.
Biessels, G. J., ter Laak, M. P., Kamal, A., and Gispen, W. H. (2005). Effects of the Ca2+ antagonist nimodipine on functional deficits in the peripheral and central nervous system of streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Brain Res. 1035:86–93.
Bliss, T. V., and Collingridge, G. L. (1993). A synaptic model of memory: Long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 361:31–39.
Bowersox, S. S., Gadbois, T., Singh, T., Pettus, M., Wang, Y. X., and Luther, R. R. (1996). Selective N-type neuronal voltage-sensitive calcium channel blocker, SNX-111, produces spinal antinociception in rat models of acute, persistent and neuropathic pain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 279:1243–1249.
Brewster, W. J., Fernyhough, P., Diemel, L. T., Mohiuddin, L., and Tomlinson, D. R. (1995). Changes in nerve growth factor and preprotachykinin messenger RNA levels in the iris and trigeminal ganglion in diabetic rats: Effects of treatment with insulin or nerve growth factor. Mol. Brain Res. 29:131–139.
Calcutt, N. A., Freshwater, J. D., and Mizisin, A. P. (2004). Prevention of sensory disorders in diabetic Sprague-Dawley rats by aldose reductase inhibition or treatment with ciliary neurotrophic factor. Diabetologia 47:718–724.
Cameron, N. E., and Cotter, M. A. (1994). The relationship of vascular changes to metabolic factors in diabetes mellitus and their role in the development of peripheral nerve complications. Diabetes Metab. Rev. 10:189–224.
Coderre, T. J., Vaccarino, A. L., and Melzack, R. (1990). Central nervous system plasticity in the tonic pain response to subcutaneous formalin injection. Brain Res. 535:155–158.
Coppey, L. J., Davidson, E. P., Rinehart, T. W., Gellett, J. S., Oltman, C. L., Lund, D. D., and Yorek, M. A. (2006). ACE inhibitor or angiotensin II receptor antagonist attenuates diabetic neuropathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes 55:341–348.
Finkel, T., and Holbrook, N. J. (2000). Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature 408:239–247.
Gispen, W. H., and Hamers, F. P. (1994). Calcium and neuronal dysfunction in peripheral nervous system. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 747:419–430.
Greene, D. A., Chakrabarti, S., Lattimer, S. A., and Sima, A. A. (1987). Role of sorbitol accumulation and myo-inositol depletion in paranodal swelling of large myelinated nerve fibers in the insulin-deficient spontaneously diabetic bio-breeding rat. Reversal by insulin replacement, an aldose reductase inhibitor, and myo-inositol. J. Clin. Invest. 79:1479–1485.
Greene, D. A., Lattimer, S., Ulbrecht, J., and Carroll, P. (1985). Glucose-induced alterations in nerve metabolism: Current perspective on the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy and future directions for research and therapy. Diabetes Care 8:290–299.
Grynkiewicz, G., Poenie, M., and Tsien, R. Y. (1985). A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J. Biol. Chem. 260:3440–3450.
Hall, K. E., Liu, J., Sima, A. A., and Wiley, J. W. (2001). Impaired inhibitory G-protein function contributes to increased calcium currents in rats with diabetic neuropathy. J. Europhysiol. 86:760–770.
Hall, K. E., Sima, A. A., and Wiley, J. W. (1995). Voltage-dependent calcium currents are enhanced in dorsal root ganglion neurones from the Bio Bred/Worchester diabetic rat. J. Physiol. 486:313–322.
Huang, T. J., Sayers, N. M., Fernyhough, P., and Verkhratsky, A. (2002). Diabetes-induced alterations in calcium homeostasis in sensory neurones of streptozotocin-diabetic rats are restricted to lumbar ganglia and are prevented by neurotrophin-3. Diabetologia 45:560–570.
Isaev, D., Gerber, G., Park, S. K., Chung, J. M., and Randic, M. (2000). Facilitation of NMDA-induced currents and Ca2+ transients in the rat substantia gelatinosa neurons after ligation of L5-L6 spinal nerves. Neuroreport 11:4055–4061.
Janicki, P. K., Horn, J. L., Singh, G., Franks, W. T., and Franks, J. J. (1994). Diminished brain synaptic plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase activity in rats with streptozocin-induced diabetes: Association with reduced anesthetic requirements. Life Sci. 55:L359–L364.
Kamei, J., Taki, K., Ohsawa, M., and Hitosugi, H. (2000). Modulation of the formalin-induced nociceptive response by diabetes: Possible involvement of intracellular calcium. Brain Res. 862:257–261.
Kappelle, A. C., Biessels, G., Bravenboer, B., van Buren, T., Traber, J., de Wildt, D. J., and Gispen, W. H. (1994). Beneficial effect of the Ca2+ antagonist, nimodipine, on existing diabetic neuropathy in the BB/Wor rat. Br. J. Pharmacol. 111:887–893.
Kappelle, A. C., Bravenboer, B., van Buren, T., Traber, J., Erkelens, D. W., and Gispen, W. H. (1993). Amelioration by the Ca2+ antagonist, nimodipine of an existing neuropathy in the streptozotocin-induced, diabetic rat. Br. J. Pharmacol. 108:780–785.
Kostyuk, E., Pronchuk, N., and Shmigol, A. (1995). Calcium signal prolongation in sensory neurones of mice with experimental diabetes. Neuroreport 6:1010–1012.
Kostyuk, E., Voitenko, N., Kruglikov, I., Shmigol, A., Shishkin, V., Efimov, A., and Kostyuk, P. (2001). Diabetes-induced changes in calcium homeostasis and the effects of calcium channel blockers in rat and mice nociceptive neurons. Diabetologia 44:1302–1309.
Kristian, T., Ouyang, Y., and Siesjo, B. K. (1996). Calcium-induced neuronal cell death in vivo and in vitro: Are the pathophysiologic mechanisms different? Adv. Neurol. 71:107–113.
Kristian, T., and Siesjo, B. K. (1996). Calcium-related damage in ischemia. Life Sci. 59:357–367.
Kruglikov, I., Gryshchenko, O., Shutov, L., Kostyuk, E., Kostyuk, P., and Voitenko, N. (2004). Diabetes-induced abnormalities in ER calcium mobilization in primary and secondary nociceptive neurons. Pflugers Arch. 448:395–401.
Landsberg, L., and Molitch, M. (2004). Diabetes and hypertension: Pathogenesis, prevention and treatment. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 26:621–628.
Levy, J., Gavin, J. R., III, and Sowers, J. R. (1994). Diabetes mellitus: A disease of abnormal cellular calcium metabolism? Am. J. Med. 96:260–273.
Liu, C., and Hermann, T. E. (1978). Characterization of ionomycin as a calcium ionophore. J. Biol. Chem. 253:5892–5894.
Mancia, G., Omboni, S., Agabiti-Rosei, E., Casati, R., Fogari, R., Leonetti, G., Montemurro, G., Nami, R., Pessina, A. C., Pirrelli, A., and Zanchetti, A. (2000). Antihypertensive efficacy of manidipine and enalapril in hypertensive diabetic patients. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 35:926–931.
Mancia, G., Omboni, S., and Zanchetti, A. (1998). Clinical advantages of lipophilic dihydropyridines. Blood Press Suppl. 2:23–26.
Manschot, S. M., Biessels, G. J., Cameron, N. E., Cotter, M. A., Kamal, A., Kappelle, L. J., and Gispen, W. H. (2003a). Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition partially prevents deficits in water maze performance, hippocampal synaptic plasticity and cerebral blood flow in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Brain Res. 966:274–282.
Manschot, S. M., Gispen, W. H., Kappelle, L. J., and Biessels, G. J. (2003b). Nerve conduction velocity and evoked potential latencies in streptozotocin-diabetic rats: Effects of treatment with an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 19:469–477.
Millan, M. J. (1999). The induction of pain: An integrative review. Prog. Neurobiol. 57:1–164.
Nag, S., and Kilty, D. W. (1997). Cerebrovascular changes in chronic hypertension. Protective effects of enalapril in rats. Stroke 28:1028–1034.
Neugebauer, V., Vanegas, H., Nebe, J., Rumenapp, P., and Schaible, H. G. (1996). Effects of N- and L-type calcium channel antagonists on the responses of nociceptive spinal cord neurons to mechanical stimulation of the normal and the inflamed knee joint. J. Neurophysiol. 76:3740–3749.
Ouardouz, M., Nikolaeva, M. A., Coderre, E., Zamponi, G. W., McRory, J. E., Trapp, B. D., Yin, X., Wang, W., Woulfe, J., and Stys, P. K. (2003). Depolarization-induced Ca2+ release in ischemic spinal cord white matter involves L-type Ca2+ channel activation of ryanodine receptors. Neuron 40:53–63.
Richard, S. (2005). Vascular effects of calcium channel antagonists: New evidence. Drugs 65(Suppl 2):1–10.
Robertson, S., Cameron, N. E., and Cotter, M. A. (1992). The effect of the calcium antagonist nifedipine on peripheral nerve function in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Diabetologia 35:1113–1117.
Roca-Cusachs, A., and Triposkiadis, F. (2005). Antihypertensive effect of manidipine. Drugs 65(Suppl 2):11–19.
Shibata, M., Ohkubo, T., Takahashi, H., and Inoki, R. (1989). Modified formalin test: Characteristic biphasic pain response. Pain 38:347–352.
Smith, J. B., Zheng, T., and Lyu, R. M. (1989). Ionomycin releases calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum and activates Na+/Ca2+ exchange in vascular smooth muscle cells. Cell Calcium 10:125–134.
Stanfa, L. C., and Dickenson, A. H. (1999). The role of non-N-methyl-d-aspartate ionotropic glutamate receptors in the spinal transmission of nociception in normal animals and animals with carrageenan inflammation. Neuroscience 93:1391–1398.
Tuomilehto, J., Rastenyte, D., Birkenhдger, W. H., Thijs, L., Antikainen, R., Bulpitt, C. J., Fletcher, A. E., Forette, F., Goldhaber, A., Palatini, P., Sarti, C., and Fagard, R. (1999). Effects of calcium-channel blockade in older patients with diabetes and systolic hypertension. Systolic Hypertension in Europe Trial Investigators. N. Engl. J. Med. 340:677–684.
Voitenko, N., Gerber, G., Youn, D., and Randic, M. (2004). Peripheral inflamation-induced increase of AMPA-mediated currents and Ca2+ transients in the presence of cyclothiazide in the rat substantia gelatinosa neurons. Cell Calcium 35:461–469.
Voitenko, N. V., Kostyuk, E. P., Kruglikov, I. A., and Kostyuk, P. G. (1999). Changes in calcium signalling in dorsal horn neurons in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Neuroscience 94:887–890.
Voitenko, N. V., Kruglikov, I. A., Kostyuk, E. P., and Kostyuk, P. G. (2000). Effect of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on the activity of calcium channels in rat dorsal horn neurons. Neuroscience 95:519–524.
Wenzel, R. R. (2005). Renal protection in hypertensive patients: Selection of antihypertensive therapy. Drugs 65(Suppl 2):29–39.
Zhou, S., Bonasera, L., and Carlton, S. M. (1996). Peripheral administration of NMDA, AMPA or KA results in pain behaviors in rats. Neuroreport 7:895–900.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This work was supported by Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation grant #1-2004-30 to NV.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shutov, L., Kruglikov, I., Gryshchenko, O. et al. The Effect of Nimodipine on Calcium Homeostasis and Pain Sensitivity in Diabetic Rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 26, 1539–1555 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-006-9107-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-006-9107-z