Abstract
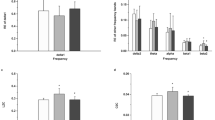
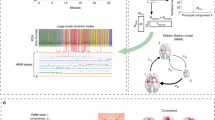
Narcolepsy is a chronic disorder of the sleep-wake cycle with pathological shifts between sleep stages. These abrupt shifts are induced by a sleep-regulating flip-flop mechanism which is destabilized in narcolepsy without obvious alterations in EEG oscillations. Here, we focus on the question whether the pathology of narcolepsy is reflected in EEG microstate patterns. 30 channel awake and NREM sleep EEGs of 12 narcoleptic patients and 32 healthy subjects were analyzed. Fitting back the dominant amplitude topography maps into the EEG led to a temporal sequence of maps. Mean microstate duration, ratio total time (RTT), global explained variance (GEV) and transition probability of each map were compared between both groups. Nine patients reached N1, 5 N2 and only 4 N3. All healthy subjects reached at least N2, 19 also N3. Four dominant maps could be found during wakefulness and all NREM- sleep stages in healthy subjects. During N3, narcolepsy patients showed an additional fifth map. The mean microstate duration was significantly shorter in narcoleptic patients than controls, most prominent in deep sleep. Single maps’ GEV and RTT were also altered in narcolepsy. Being aware of the limitation of our low sample size, narcolepsy patients showed wake-like features during sleep as reflected in shorter microstate durations. These microstructural EEG alterations might reflect the intrusion of brain states characteristic of wakefulness into sleep and an instability of the sleep-regulating flip-flop mechanism resulting not only in pathological switches between REM- and NREM-sleep but also within NREM sleep itself, which may lead to a microstructural fragmentation of the EEG.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamantidis AR, Zhang F, Aravanis AM, Deisseroth K, Lecea L (2007) Neural substrates of awakening probed with optogenetic control of hypocretin neurons. Nature 450:420–424
Alloway CE, Ogilvie RD, Shapiro CM (1997) The alpha attenuation test: assessing excessive daytime sleepiness in narcolepsy-cataplexy. Sleep 20:258–266
American Academy of Sleep Medicine (2005) The international classification of sleep disorders. Diagnostic and coding manual, 2nd edn. American Academy of Sleep Medicine, Darien
American Academy of Sleep Medicine (2007) The AASM manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events: rules terminology and technical specifications. American Academy of Sleep Medicine, Darien
Brenneis C, Brandauer E, Frauscher B, Schocke M, Trieb T, Poewe W, Högl B (2005) Voxel-based morphometry in narcolepsy. Sleep Med 6:531–536
Britz J, van de Ville D, Michel CM (2010) BOLD correlates of EEG topography reveal rapid resting-state network dynamics. Neuroimage 52:1162–1170
Brodbeck V, Kuhn A, von Wegner F, Morzelewski A, Tagliazucchi E, Borisov S, Michel CM, Laufs H (2012) EEG microstates of wakefulness and NREM sleep. Neuroimage 62:2129–2139
Brunet D, Murray MM, Michel CM (2011) Spatiotemporal analysis of multichannel EEG: CARTOOL. Comput Intell Neurosci 2011:813870
Burgess CR, Scammell TE (2012) Narcolepsy: neural mechanisms of sleepiness and cataplexy. J Neurosci 32:12305–12311
Daly DD, Yoss RE (1957) Electroencephalogram in narcolepsy. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 9:109–120
Dang-Vu TT, Schabus M, Desseilles M, Albouy G, Boly M, Darsaud A, Gais S, Rauchs G, Sterpenich V, Vandewalle G, Carrier J, Moonen G, Balteau E, Degueldre C, Luxen A, Phillips C, Maquet P (2008) Spontaneous neural activity during human slow wave sleep. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:15160–15165
Dantz B, Edgar DM, Dement WC (1994) Circadian rhythms in narcolepsy: studies on a 90 min day. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 90:24–35
de Lecea L, Kilduff TS, Peyron C, Gao X, Foye PE, Danielson PE, Fukuhara C, Battenberg EL, Gautvik VT, Bartlett FS, Frankel WN, van den Pol AN, Bloom FE, Gautvik KM, Sutcliffe JG (1998) The hypocretins: hypothalamus-specific peptides with neuroexcitatory activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:322–327
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Neurologie (2012). S1-Leitlinie Narkolepsie
Dierks T, Jelic V, Julin P, Maurer K, Wahlund LO, Almkvist O, Strik WK, Winblad B (1997) EEG-microstates in mild memory impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: possible association with disturbed information processing. J Neural Transm 104:483–495
Eggermann E, Serafin M, Bayer L, Machard D, Saint-Mleux B, Jones BE, Mühlethaler M (2001) Orexins/hypocretins excite basal forebrain cholinergic neurones. Neuroscience 108:177–181
Foral P, Knezevich J, Dewan N, Malesker M (2011) Medication-induced sleep disturbances. Consult Pharm 26:414–425
Freyer F, Becker R, Anami K, Curio G, Villringer A, Ritter P (2009) Ultrahigh-frequency EEG during fMRI: pushing the limits of imaging-artifact correction. Neuroimage 48:94–108
Giraud AL, Kleinschmidt A, Poeppel D, Lund TE, Frackowiak RS, Laufs H (2007) Endogenous cortical rhythms determine cerebral specialization for speech perception and production. Neuron 56:1127–1134
Hudson JI, Pope HG, Sullivan LE, Waternaux CM, Keck PE, Broughton RJ (1992) Good sleep, bad sleep: a meta-analysis of polysomnographic measures in insomnia, depression, and narcolepsy. Biol Psychiatry 32:958–975
Jahnke K, von Wegner F, Morzelewski A, Borisov S, Maischein M, Steinmetz H, Laufs H (2012) To wake or not to wake? The two-sided nature of the human K-complex. Neuroimage 59:1631–1638
Joo EY, Jeon S, Lee M, Kim ST, Yoon U, Koo DL, Lee J-M, Hong SB (2011) Analysis of cortical thickness in narcolepsy patients with cataplexy. Sleep 34:1357–1364
Kanbayashi T, Inoue Y, Chiba S, Aizawa R, Saito Y, Tsukamoto H, Fujii Y, Nishino S, Shimizu T (2002) CSF hypocretin-1 (orexin-A) concentrations in narcolepsy with and without cataplexy and idiopathic hypersomnia. J Sleep Res 11:91–93
Kaufmann C, Schuld A, Pollmächer T, Auer DP (2002) Reduced cortical gray matter in narcolepsy: preliminary findings with voxel-based morphometry. Neurology 58:1852–1855
Khatami R, Landolt H-P, Achermann P, Rétey JV, Werth E, Mathis J, Bassetti CL (2007) Insufficient non-REM sleep intensity in narcolepsy-cataplexy. Sleep 30:980–989
Kikuchi M, Koenig T, Munesue T, Hanaoka A, Strik W, Dierks T, Koshino Y, Minabe Y (2011) EEG microstate analysis in drug-naive patients with panic disorder. PLoS ONE 6:e22912
Kim JW, Shin H-B, Robinson PA (2009) Quantitative study of the sleep onset period via detrended fluctuation analysis: normal versus narcoleptic subjects. Clin Neurophysiol 120:1245–1251
Kindler J, Hubl D, Strik WK, Dierks T, Koenig T (2011) Resting-state EEG in schizophrenia: auditory verbal hallucinations are related to shortening of specific microstates. Clin Neurophysiol 122:1179–1182
Koenig T, Lehmann D, Merlo MC, Kochi K, Hell D, Koukkou M (1999) A deviant EEG brain microstate in acute, neuroleptic-naive schizophrenics at rest. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 249:205–211
Koenig T, Prichep L, Lehmann D, Sosa PV, Braeker E, Kleinlogel H, Isenhart R, John ER (2002) Millisecond by millisecond, year by year: normative EEG microstates and developmental stages. Neuroimage 16:41–48
Kryger MH, Roth T, Dement WC (2011) Principles and practice of sleep medicine, 5th edn. Elsevier, Philadelphia
Lamphere J, Young D, Roehrs T, Wittig RM, Zorick F, Roth T (1989) Fragmented sleep, daytime somnolence and age in narcolepsy. Clin Electroencephalogr 20:49–54
Laufs H, Daunizeau J, Carmichael DW, Kleinschmidt A (2008) Recent advances in recording electrophysiological data simultaneously with magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroimage 40:515–528
Laufs H (2012) A personalized history of EEG-fMRI integration. Neuroimage 62:1056–1067
Lee S-H, Dan Y (2012) Neuromodulation of brain states. Neuron 76:209–222
Lehmann D, Ozaki H, Pal I (1987) EEG alpha map series: brain micro-states by space-oriented adaptive segmentation. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 67:271–288
Lehmann D, Wackermann J, Michel CM, Koenig T (1993) Space-oriented EEG segmentation reveals changes in brain electric field maps under the influence of a nootropic drug. Psychiatry Res 50:275–282
Lehmann D, Faber PL, Galderisi S, Herrmann WM, Kinoshita T, Koukkou M, Mucci A, Pascual-Marqui RD, Saito N, Wackermann J, Winterer G, Koenig T (2005) EEG microstate duration and syntax in acute, medication-naive, first-episode schizophrenia: a multi-center study. Psychiatry Res 138:141–156
Lehmann D, Pascual-Marqui RD, Michel CM (2009) EEG Microstates, Vol. 4, No. 3, 7632. http://www.scholarpedia.org/article/EEG_microstates. Accessed 24 Nov 2013
Massimini M, Huber R, Ferrarelli F, Hill S, Tononi G (2004) The sleep slow oscillation as a traveling wave. J Neurosci 24:6862–6870
Methippara MM, Alam MN, Szymusiak R, McGinty D (2000) Effects of lateral preoptic area application of orexin-A on sleep-wakefulness. NeuroReport 11:3423–3426
Mignot E, Lammers GJ, Ripley B, Okun M, Nevsimalova S, Overeem S, Vankova J, Black J, Harsh J, Bassetti C, Schrader H, Nishino S (2002) The role of cerebrospinal fluid hypocretin measurement in the diagnosis of narcolepsy and other hypersomnias. Arch Neurol 59:1553–1562
Montplaisir J, Billiard M, Takahashi S, Bell IR, Guilleminault C, Dement WC (1978) Twenty-four-hour recording in REM-narcoleptics with special reference to nocturnal sleep disruption. Biol Psychiatry 13:73–89
Murray MM, Brunet D, Michel CM (2008) Topographic ERP analyses: a step-by-step tutorial review. Brain Topogr 20(4):249–264
Musso F, Brinkmeyer J, Mobascher A, Warbrick T, Winterer G (2010) Spontaneous brain activity and EEG microstates. A novel EEG/fMRI analysis approach to explore resting-state networks. Neuroimage 52:1149–1161
Nobili L, Besset A, Ferrillo F, Rosadini G, Schiavi G, Billiard M (1995) Dynamics of slow wave activity in narcoleptic patients under bed rest conditions. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 95:414–425
Ohayon MM, Carskadon MA, Guilleminault C, Vitiello MV (2004) Meta-analysis of quantitative sleep parameters from childhood to old age in healthy individuals: developing normative sleep values across the human lifespan. Sleep 27:1255–1273
Pascual-Marqui RD, Michel CM, Lehmann D (1995) Segmentation of brain electrical activity into microstates: model estimation and validation. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 42:658–665
Sakurai T, Amemiya A, Ishii M, Matsuzaki I, Chemelli RM, Tanaka H, Williams SC, Richarson JA, Kozlowski GP, Wilson S, Arch JR, Buckingham RE, Haynes AC, Carr SA, Annan RS, McNulty DE, Liu WS, Terrett JA, Elshourbagy NA, Bergsma DJ, Yanagisawa M (1998) Orexins and orexin receptors: a family of hypothalamic neuropeptides and G protein-coupled receptors that regulate feeding behavior. Cell 92:1 (page following 696)
Saletu M, Anderer P, Saletu-Zyhlarz GM, Mandl M, Arnold O, Zeitlhofer J, Saletu B (2004) EEG-tomographic studies with LORETA on vigilance differences between narcolepsy patients and controls and subsequent double-blind, placebo-controlled studies with modafinil. J Neurol 251:1354–1363
Saletu MT, Anderer P, Saletu-Zyhlarz GM, Mandl M, Arnold O, Nosiska D, Zeitlhofer J, Saletu B (2005) EEG-mapping differences between narcolepsy patients and controls and subsequent double-blind, placebo-controlled studies with modafinil. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 255:20–32
Saper CB, Fuller PM, Pedersen NP, Lu J, Scammell TE (2010) Sleep state switching. Neuron 68:1023–1042
Saper CB (2013) The neurobiology of sleep. Continuum (Minneap Minn) 19:19–31
Schlegel F, Lehmann D, Faber PL, Milz P, Gianotti LRR (2012) EEG microstates during resting represent personality differences. Brain Topogr 25:20–26
Skrandies W (1989) Data reduction of multichannel fields: global field power and principal component analysis. Brain Topogr 2:73–80
Smit AS, Droogleever Fortuyn HA, Eling PATM, Coenen AML (2005) Diurnal spectral EEG fluctuations in narcoleptic patients during rest and reaction time tasks. J Sleep Res 14:455–461
Strelets V, Faber PL, Golikova J, Novototsky-Vlasov V, Koenig T, Gianotti LRR, Gruzelier JH, Lehmann D (2003) Chronic schizophrenics with positive symptomatology have shortened EEG microstate durations. Clin Neurophysiol 114:2043–2051
Strik WK, Dierks T, Becker T, Lehmann D (1995) Larger topographical variance and decreased duration of brain electric microstates in depression. J Neural Transm Gen Sect 99:213–222
Strik WK, Chiaramonti R, Muscas GC, Paganini M, Mueller TJ, Fallgatter AJ, Versari A, Zappoli R (1997) Decreased EEG microstate duration and anteriorisation of the brain electrical fields in mild and moderate dementia of the Alzheimer type. Psychiatry Res 75:183–191
Tagliazucchi E, von Wegner F, Morzelewski A, Brodbeck V, Laufs H (2012) Dynamic BOLD functional connectivity in humans and its electrophysiological correlates. Front Hum Neurosci 6:339
Tagliazucchi E, Laufs H (2014) Decoding wakefulness levels from typical fMRI resting state data reveals reliable drifts between wakefulness and sleep. Neuron 82:695–708
Tagliazucchi E, Von Wegner F, Morzelewski A, Brodbeck V, Borisov S, Jahnke K, Laufs H (2013) Large-scale brain functional modularity is reflected in slow electroencephalographic rhythms across the human non-rapid eye movement sleep cycle. Neuroimage 70:327–339
Wackermann J, Lehmann D, Michel CM, Strik WK (1993) Adaptive segmentation of spontaneous EEG map series into spatially defined microstates. Int J Psychophysiol 14:269–283
Yoss RE, Daly DD (1957) Criteria for the diagnosis of the narcoleptic syndrome. Proc Staff Meet Mayo Clin 32:320–328
Yuan H, Zotev V, Phillips R, Drevets WC, Bodurka J (2012) Spatiotemporal dynamics of the brain at rest-exploring EEG microstates as electrophysiological signatures of BOLD resting state networks. Neuroimage 60:2062–2072
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (Grant 01 EV 0703) and the LOEWE Neuronale Koordination Forschungsschwerpunkt Frankfurt (NeFF). We thank Brooks Ferebee (Institute of Mathematics, Goethe University Frankfurt) for statistical support and are indebted to all our study participants. We especially thank Professor Geert Mayer for referring patients to our study.
Ethical Standards
Written informed consent was obtained by all subjects/patients and the study was approved by the local ethics committee.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuhn, A., Brodbeck, V., Tagliazucchi, E. et al. Narcoleptic Patients Show Fragmented EEG-Microstructure During Early NREM Sleep. Brain Topogr 28, 619–635 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-014-0387-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-014-0387-1