Summary
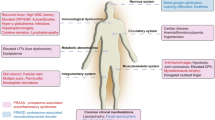
Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndromes (MDSs) form a group of autosomal recessive disorders characterized by profoundly decreased mitochondrial DNA copy numbers in affected tissues. Three main clinical presentations are known: myopathic, encephalomyopathic and hepatocerebral. The first is associated with mutations in thymidine kinase 2 (TK2) and p53-induced ribonucleotide reductase B subunit (RRM2B); the second with mutations in succinate synthase A (SUCLA2) and B (SUCLG1); the third with mutations in Twinkle (PEO1), pol-γA (POLG1), deoxyguanosine kinase (DGUOK) and MPV17 (MPV17). In this work, we review the MDS-associated phenotypes and present our own experience of 32 MDS patients, with the aim of defining the mutation frequency of the known genes, the clinical spectrum of the diseases, and the genotype–phenotype correlations. Five of our patients carried previously unreported mutations in one of the eight MDS genes.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CK:
-
creatine kinase
- COX:
-
cytochrome-c oxidase
- MDS:
-
mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome
- mtDNA:
-
mitochondrial DNA
- NAA:
-
N-acetylaspartate
- OXPHOS:
-
oxidative phosphorylation
- RC:
-
respiratory chain
- RRF:
-
ragged-red fibres
- SANDO:
-
sensory ataxic neuropathy with dysarthria and ophthalmoplegia
- SCAE:
-
spinocerebellar ataxia-epilepsy syndrome
- SCS:
-
succinyl-CoA synthase
- SDH:
-
succinate dehydrogenase
- SMA:
-
spinal muscular atrophy
References
Akman HO, Dorado B, López LC, et al (2008) Thymidine kinase 2 (H126N) knockin mice show the essential role of balanced deoxynucleotide pools for mitochondrial DNA maintenance. Hum Mol Genet 17: 2433–2440. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddn143.
Alberio S, Mineri R, Tiranti V, et al (2007) Depletion of mtDNA: syndromes and genes. Mitochondrion 7: 6–12. doi:10.1016/j.mito.2006.11.010.
Ashley N, Adams S, Slama A, et al (2007) Defects in maintenance of mitochondrial DNA are associated with intramitochondrial nucleotide imbalances. Hum Mol Genet 16: 1400–1411. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddm090.
Baruffini E, Lodi T, Dallabona C, Puglisi A, Zeviani M, Ferrero I (2006) Genetic and chemical rescue of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae phenotype induced by mitochondrial DNA polymerase mutations associated with progressive external ophthalmoplegia in humans. Hum Mol Genet 15: 2846–2855. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddl219.
Bornstein B, Area E, Flanigan KM, et al (2008) Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome due to mutations in the RRM2B gene. Neuromuscul Disord 18: 453–459. doi:10.1016/j.nmd.2008.04.006.
Bourdon A, Minai L, Serre V, et al (2007) Mutation of RRM2B, encoding p53-controlled ribonucleotide reductase (p53R2), causes severe mitochondrial DNA depletion. Nat Genet 39: 776–780. doi:10.1038/ng2040.
Bugiani M, Invernizzi F, Alberio S, et al (2004) Clinical and molecular findings in children with complex I deficiency. Biochim Biophys Acta 1659: 136–147. doi:10.1016/j.bbabio.2004.09.006.
Carrozzo R, Dionisi-Vici C, Steuerwald U et al (2007) SUCLA2 mutations are associated with mild methylmalonic aciduria, Leigh-like encephalomyopathy, dystonia and deafness. Brain 130: 862–874. doi:10.1093/brain/awl389.
Chan SS, Longley MJ, Nviaux RK, et al (2005) Mono-allelic POLG expression resulting from nonsense-mediated decay and alternative splicing in a patient with Alpers syndrome. DNA Repair (Amst) 4: 1381–1389. doi:10.1016/j.dnarep.2005.08.010.
Dimmock DP, Zhang Q, Dionisi-Vici C, et al (2008) Clinical and molecular features of mitochondrial DNA depletion due to mutations in deoxyguanosine kinase. Hum Mutat 29: 330–331. doi:10.1002/humu.9519.
Elpeleg O, Miller C, Hershkovitz E, et al (2005) Deficiency of the ADP-forming succinyl-CoA synthase activity is associated with encephalomyopathy and mitochondrial DNA depletion. Am J Hum Genet 76: 1081–1086. doi:10.1086/430843.
Engelsen BA, Tzoulis C, Karlsen B, et al (2008) POLG1 mutations cause a syndromic epilepsy with occipital lobe predilection. Brain 131: 818–828. doi:10.1093/brain/awn007.
Ferrari G, Lamatea E, Donati A, et al (2005) Infantile hepatocerebral syndromes associated with mutations in the mitochondrial DNA polymerase-gamma A. Brain 128: 723–731. doi:10.1093/brain/awh410.
Freisinger P, Fütterer N, Lankes E, et al (2006) Hepatocerebral mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome caused by deoxyguanosine kinase (DGUOK) mutations. Arch Neurol 63: 1129–1134. doi:10.1001/archneur.63.8.1129.
Galbiati S, Bordoni A, Papadimitriou D, et al (2006) New mutations in TK2 gene associated with mitochondrial DNA depletion. Pediatr Neurol 34: 177–185. doi:10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2005.07.013.
Hakonen AH, Isohanni P, Paetau A, et al (2007) Recessive Twinkle mutations in early onset encephalopathy with mtDNA depletion. Brain 130: 3032–3040. doi:10.1093/brain/awm242.
He L, Chinnery PF, Durham SE, et al (2002) Detection and quantification of mitochondrial DNA deletions in individual cells by real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 30: e68. doi:10.1093/nar/gnf067.
Ho SN, Hunt HD, Horton RM, Pullen JK, Pease LR (1989) Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene 77: 51–59. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(89)90358-2.
Kimura T, Takeda S, Sagiya Y, et al (2003) Impaired function of p53r2 in Rrm2b-null mice causes severe renal failure through attenuation of dNTP pools. Nat Genet 34: 440–445. doi:10.1038/ng1212.
Mancuso M, Salviati L, Sacconi S, et al (2002) Mitochondrial DNA depletion: mutations in thymidine kinase gene with myopathy and SMA. Neurology 59: 1197–1202.
Mandel H, Szargel R, Labay V, et al (2001) The deoxyguanosine kinase gene is mutated in individuals with depleted hepatocerebral mitochondrial DNA. Nat Genet. 29: 337–341. doi:10.1038/ng746.
Mariotti C, Uziel G, Carrara F, et al (1995) Early-onset encephalomyopathy associated with tissue-specific mitochondrial DNAdepletion: a morphological, biochemical and molecular-genetic study. J Neurol 242: 547–556. doi:10.1007/BF00868806.
Meyer zum Gottesberge AM, Felix H (2005) Abnormal basement membrane in the inner ear and the kidney of the Mpv17−/− mouse strain: ultrastructural and immunohistochemical investigations. Histochem Cell Biol 124: 507–516. doi:10.1007/s00418-005-0027-7.
Milone M, Brunetti-Pierri N, Tang LY, et al (2008) Sensory ataxic neuropathy with ophthalmoparesis caused by POLG mutations. Neuromuscul Disord. 18: 626–632. doi:10.1016/j.nmd.2008.05.009.
Moraes CT, Shanske S, Tritschler HJ, et al (1991) mtDNA depletion with variable tissue exèression: a novel genetic abnormality in mitochondrial diseases. Am J Hum Genet 48: 492–501.
Naïmi M, Bannwarth S, Procaccio V, et al (2006) Molecular analysis of ANT1, TWINKLE and POLG in patients with multiple deletions or depletion of mitochondrial DNA by a dHPLC-based assay. Eur J Hum Genet 14: 917–922. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201627.
Naviaux RK, Nguyen KV (2004) POLG mutations associated with Alpers’ syndrome and mitochondrial DNA depletion. Ann Neurol 55: 706–712. doi:10.1002/ana.20079.
Nordlund P, & Reichard P (2006) Ribonucleotide reductases. Annu Rev Biochem 75: 681–706. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.75.103004.142443.
Oskoui M, Davidzon G, Pascual J, et al (2006) Clinical spectrum of mitochondrial DNA depletion due to mutations in the thymidine kinase 2 gene. Arch Neurol 63: 1122–1126. doi:10.1001/archneur.63.8.1122.
Ostergaard E, Hansen FJ, Sorensen N, Duno M, et al (2007a) Mitochondrial encephalomyopathy with elevated methylmalonic acid is caused by SUCLA2 mutations. Brain 130: 853–861. doi:10.1093/brain/awl383.
Ostergaard E, Christensen E, Kristensen E, et al (2007b) Deficiency of the subunit of succinate–coenzyme A ligase causes fatal infantile lactic acidosis with mitochondrial DNA depletion. Am J Hum Genet 81: 383–387. doi:10.1086/519222.
Poggi GM, Lamatea E, Ciani F, et al (2000) Fatal neonatal outcomein a case of muscular mitochondrial DNA depletion. JInherit Metab Dis 23: 755–757. doi:10.1023/A:1005663804214.
Saada A, Shaag A, Mandel H, et al (2001) Mutant mitochondrial thymidine kinase in mitochondrial DNA depletion myopathy. Nat Genet 29: 342–344. doi:10.1038/ng751.
Salviati L, Sacconi S, Mancuso M, et al (2002) Mitochondrial DNA depletion and dGK gene mutations. Ann Neurol 52: 311–319. doi:10.1002/ana.10284.
Sarzi E, Goffart S, Serre V, Chretien D, et al (2007) Twinkle helicase (PEO1) gene mutation causes mitochondrial DNA depletion. Ann Neurol 62: 579–587. doi:10.1002/ana.21207.
Slonimski PP, Tzagoloff A (1976) Localization in yeast mitochondrial DNA of mutations expressed in a deficiency of cytochrome oxidase and/or coenzyme QH2-cytochrome creductase. Eur J Biochem 61: 27–41. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb09994.x.
Spinazzola A, Viscomi C, Fernandez-Vizarra E, et al (2006) MPV17 encodes an inner mitochondrial membrane protein and is mutated in infantile hepatic mitochondrial DNA depletion. Nat Genet 38: 570–571. doi:10.1038/ng1765.
Spinazzola A, Massa V, Hirano M, Zeviani M (2008a) Lack of founder effect for an identical mtDNA depletion syndrome (MDS)-associated MPV17 mutation shared by Navajos and Italians. Neuromuscul Disord 18: 315–318. doi:10.1016/j.nmd.2007.12.007.
Spinazzola A, Santer R, Akman OH, et al (2008b) Hepatocerebral form of mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome: novel MPV17 mutations. Arch Neurol 65: 1108–1113. doi:10.1001/archneur.65.8.1108.
Tanaka H, et al (2000) A ribonucleotide reductase gene involved in a p53-dependent cell-cycle checkpoint for DNA damage. Nature 404(6773): 42–49. doi:10.1038/35003506.
Tanji K, Bonilla E (2001) Optical imaging techniques (histochemical, immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization staining methods) to visualize mitochondria. Methods Cell Biol 65: 311–332. doi:10.1016/S0091-679X(01)65019-2.
Tritschler HJ, Andreetta F, Moraes CT, et al (1992) Mitochondrial myopathy of childhood associated with depletion of mitochondrial DNA. Neurology 42: 209–217.
Trott A, Morano KA (2004) SYM1 is the stress-induced Saccharomyces cerevisiae ortholog of the mammalian kidney disease gene Mpv17 and is required for ethanol metabolism and tolerance during heat shock. Eukaryotic Cell 3: 620–631. doi:10.1128/EC.3.3.620-631.2004.
Tzoulis C, Engelsen BA, Telstad W, et al (2006) The spectrum of clinical disease caused by the A467T and W748S POLG mutations: a study of 26 cases. Brain 129: 1685–1692. doi:10.1093/brain/awl097.
Van Goethem G, Dermaut B, Lofgren A, Martin JJ, Van Broeckhoven C (2001) Mutation of POLG is associated with progressive external ophthalmoplegia characterized by mtDNA deletions. Nat Genet 28: 211–212. doi:10.1038/90034.
Van Goethem G, Martin JJ, Dermaut B, et al (2003) Recessive POLG mutations presenting with sensory and ataxic neuropathy in compound heterozygote patients with progressive external ophthalmoplegia. Neuromuscul Disord 13: 133–142. doi:10.1016/S0960-8966(02)00216-X.
Vilà MR, Segovia-Silvestre T, Gámez J, et al (2003) Reversion of mtDNA depletion in a patient with TK2 deficiency. Neurology 60: 1203–1205.
Viscomi C, Spinazzola A, Maggioni M, et al (2008) Early-onset liver mtDNA depletion and late-onset proteinuric nephropathy in Mpv17 knockout mice. Hum Mol Genet [Epub ahead of print Sep 29.]. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddn309.
Vu TH, Tanji K, Holve SA, et al (2001) Navajo neurohepatopathy: a mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome? Hepatology 34: 116–120. doi:10.1053/jhep.2001.25921.
Wang L, Limongelli A, Vila MR, et al (2005) Molecular insight into mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome in two patients with novel mutations in the deoxyguanosine kinase and thymidine kinase 2 genes. Mol Genet Metab 84: 75–82. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2004.09.005.
Winterthun s, Ferrari G, He L, et al (2005) Autosomal recessive mitochondrial ataxic syndrome due to mitochondrial polymerase gamma mutations. Neurology 64: 1204–1208.
Wong LJ, Naviaux RK, Brunetti-Pierri N, et al (2008) Molecular and clinical genetics of mitochondrial diseases due to POLG mutations. Hum Mutat 29: E150–E172. doi:10.1002/humu.20824.
Zhou X, Solaroli N, Bjerke M, et al (2008) Progressive loss of mitochondrial DNA in thymidine kinase 2-deficient mice. Hum Mol Genet 17: 2329–2335.
Acknowledgments
We thank the patients and their families for the collaboration, understanding and support given to our work. This work was supported by the Pierfranco and Luisa Mariani Foundation, Fondazione Telethon-Italy grant no. GGP07019, Italian Ministry of University and Research (FIRB 2003 – project RBLA038RMA), the Italian Ministry of Health RF2006 ex 56/05/21, Marie Curie intra-European fellowship (FP6-2005-Mobility-5) no. 040140-MAD, MITOCIRCLE and EUMITOCOMBAT (LSHM-CT-2004–503116) network grants from the European Union framework program 6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicating editor: Gary Brown
Competing interests: None declared
References to electronic databases: MDS myopathic form: OMIM #609560. MDS encephalomyopathic form: OMIM #612073. MDS, encephalomyopathic form, with renal tubulopathy: OMIM #612075. MDS hepatocerebral form: OMIM #251880.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spinazzola, A., Invernizzi, F., Carrara, F. et al. Clinical and molecular features of mitochondrial DNA depletion syndromes. J Inherit Metab Dis 32, 143–158 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-008-1038-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-008-1038-z